When designing electrical circuits it is often necessary to use voltage regulators of low or medium power (up to 1.5 A) or reference voltage sources. It is convenient if such a node is available in an integrated design, in the form of a single chip. A range of 9 DC voltage ratings from 5 to 24 V covers the stabilizer series 78XX. The niche of LM317 operation is voltages higher (up to 37 V) and below (up to 1.2 V) of this range, intermediate voltage values, regulated stabilizers.
Contents
What is the LM317 Microcircuit
This is a linear voltage regulator, the output value of which can be set within certain limits or regulated on-the-fly. Available in several three pin packages. The output voltage range of all variants is the same, but the maximum current can vary.
| Designation | Maximum current, A | Case |
|---|---|---|
| LM317T | 1,5 | TO-220 |
| LM317LZ | 0,1 | TO-92 |
| LM317P | 1,5 | ISOWAT-220 |
| LM317D2T | 1,5 | D2PAK |
| LM317K | 0,1 | TO-3 |
| LM317LD | 1,5 | SO-8 |
Basic specifications of the LM317 linear voltage regulator
The datasheets for the LM317 voltage regulator contain complete technical information, which can be read by examining the datasheet. The following are the parameters, non-compliance with which is most critical and if used incorrectly, the microcircuit can fail. First of all, it is the maximum operating current. It is given in the previous section for different versions. It should be added, that to get the maximum current of 1.5 A the microcircuit must be mounted on the heat sink.
The maximum voltage at the output of an LM317-based regulator can be up to 40V. If this is not enough, you have to choose a high voltage analogue of the regulator.
The minimum output voltage is 1.25 V. With this circuit design you can get less, but the overload protection will be triggered. This is not a good option - such protection should work from over current output, as it works in other integrated regulators. So in practice it is not possible to get a regulator that operates from zero when negative bias is applied to the Adjust pin.
The minimum input voltage value is not given in the datasheet, but can be determined from the following considerations:
- The minimum output voltage is 1.25 V;
- the minimum voltage drop for Uoutput=37V is three volts, it is logical to assume that for the minimum output it should not be less;
Based on these two assumptions, the input should be at least 3.5V to get the minimum output value. Also for stable operation the current through the divider should be at least 5 mA - so that the parasitic current of the ADJ pin does not introduce a significant voltage shift (in practice it can reach up to 0.5 mA).
This refers to the information from the classic datasheets of well-known manufacturers (Texas Instruments, etc.). In the datasheets of the new type from South-East Asian firms (Tiger Electronics, etc.) this parameter is specified, but implicitly, as a difference between input voltage and output voltage. It should be at least 3 volts for all voltages, which does not contradict the previous reasoning.
The maximum input voltage should not exceed the designed output voltage by more than 40V. This should also be taken into account when designing circuits.
Important! The stated parameters can be used as a reference if the chip is made by a well-known manufacturer. Products of unknown firms usually have lower characteristics
Pin assignment and operation
It was mentioned that the LM317 belongs to the class of linear stabilizers. This means that the output voltage is stabilized by the redistribution of energy between the load and the regulating element.
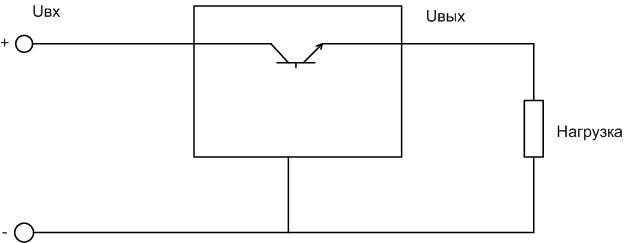
The transistor and the load form a input voltage divider. If the voltage set at the load decreases (due to changes in current, etc.), the transistor opens a bit. If it increases - it closes, the division ratio changes and the voltage on the load remains stable. The disadvantages of this circuit are known:
- it is necessary that the input voltage exceeds the output voltage;
- The regulating transistor dissipates a lot of power;
- Efficiency even theoretically can not exceed the ratio Uout/Uin.
But there are serious advantages (relative to pulse circuits):
- relatively simple and inexpensive microcircuit;
- requires a minimum of external pipelining;
- and the main advantage is that the output voltage is free of high-frequency parasitic components (power interference is minimal).
The standard circuit of the microcircuit:
- input voltage is applied to the Input pin;
- on the output pin - output voltage;
- on Ajust - the reference voltage, on which the output voltage depends.
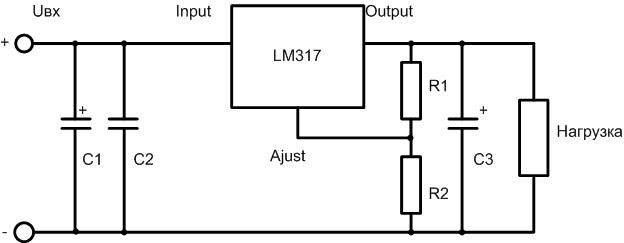
Resistors R1 and R2 set output voltage. It is calculated by the formula:
U out=1,25⋅ (1+R2/R1) +Iadj⋅R2.
Iadj is the parasitic current of the tuning output, according to the manufacturer it can be in the range of 5 μA. Practice shows that it can reach values an order or two higher.
Capacitor C1 can have a capacity of hundreds to several thousand microfarads. In most cases, it serves as the output capacitor of the rectifier. It must be connected to the microcircuit with wires not longer than 7 cm. If this condition for the rectifier capacitor cannot be met, an additional capacitor of about 100 µF must be connected in the immediate vicinity of the input terminal. The capacitor C3 should not have a capacitance of more than 100-200 µF for two reasons:
- To avoid the stabilizer going into auto-oscillation mode;
- to eliminate the current surge on the charge when the power supply is applied.
In the second case, the overload protection may be triggered.
It should not be forgotten that when current flows through the resistors, they heat up (this is also possible if the ambient temperature rises). Resistors R1 and R2 change, and there is no guarantee that they will change proportionally. Therefore the output voltage can change with warming or cooling. If this is critical, resistors with a normalized temperature coefficient of resistance can be used. They can be distinguished by the presence of six stripes on the housing. But such elements are more expensive and harder to buy. Another option would be to use a stolitron for a suitable voltage instead of R2.
What analogs exist
There are similar microcircuits developed by other firms in other countries. Complete analogs are:
- GL317;
- SG317;
- UPC317;
- ECG1900.
Stabilizers with higher electrical characteristics are also available. Higher currents can deliver:
- LM338 - 5 A;
- LM138 - 5 A
- LM350 - 3 A.
If a regulated voltage source with an upper limit of 60V is required, the LM317HV, LM117HV stabilizers must be used. The index HV stands for High Voltage.
A full analog of a domestic microcircuit is the KR142EN12, but it is only available in the TO-220 package. This should be considered when designing printed circuit boards.
Examples of LM317 regulator switching circuits
Typical circuit diagrams of the microcircuit are given in the datasheet. The standard application - fixed voltage regulator - is considered above.
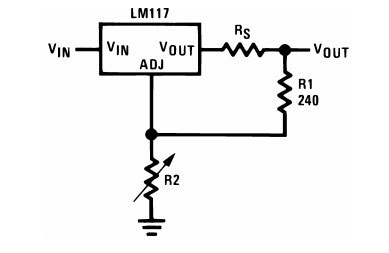
If a variable resistor is installed instead of R2, the output voltage of the regulator can be adjusted promptly. It should be considered that the potentiometer will be the weak point in the circuit. Even with good quality variable resistors the point of contact of the slider with the conductive layer will have some connection instability. In practice, this will result in additional instability in the output voltage.
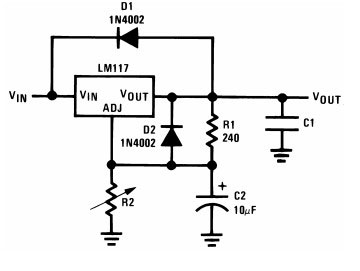
For protection the manufacturer recommends to include two diodes D1 and D2. The first diode should protect against a situation where the output voltage will be higher than the input voltage. In practice this situation is very rare and can only occur if there are other voltage sources on the output side. The manufacturer notes that this diode also protects against a short circuit at the input - the capacitor C1 in this case will create a discharge current of opposite polarity, which will lead the chip to failure. But inside the chip in parallel to this diode there is a chain of of stabilizing diodes and resistors, which will work exactly the same way. Therefore the need for this diode is questionable. And D2 in this situation will protect the input of the stabilizer from the current of the capacitor C2.
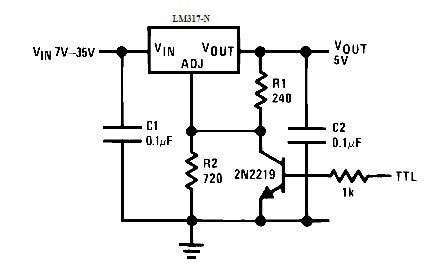
If you put in parallel R2 transistor, the operation of the stabilizer can be controlled. When voltage is applied to the base of the transistor, it opens and shunts R2. The output voltage is reduced to 1,25V. Here you have to make sure that the difference between the input voltage and the output voltage does not exceed 40V.
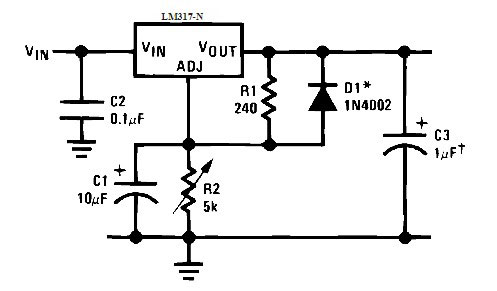
The detrimental effect of the potentiometer contact on the stability of the output voltage can be reduced by connecting a capacitor in parallel to the variable resistance. In this case the protection diode D1 does not interfere.
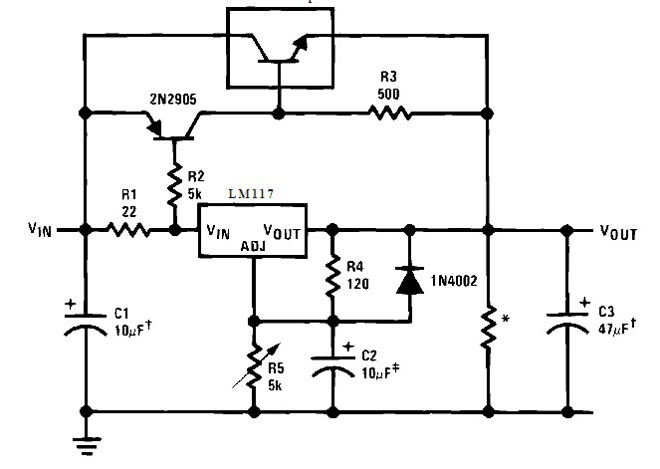
If the output current of the stabilizer is not enough, it can be boosted with an external transistor.
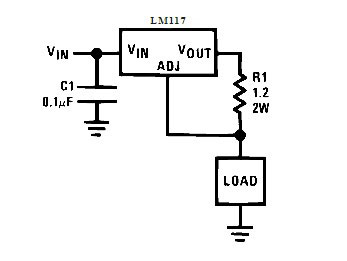
From a voltage regulator you can get a current regulator by including an LM317 in this circuit. The output current is calculated with the formula I=1,25⋅R1. A similar inclusion is often used as a driver for LEDs - the LED is turned on as a load.
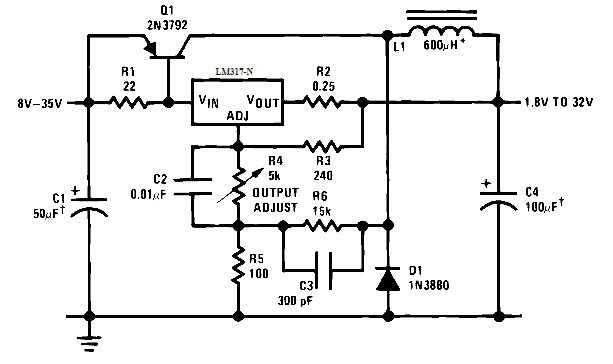
Finally, an unusual inclusion of a linear stabilizer - a circuit based on it is created switching power supply. The positive feedback for the oscillation is given by the C3R6 circuit.
The LM317 chip has a significant number of weaknesses. But the art of creating circuits and is to use the advantages of the stabilizer, bypass the disadvantages. All the disadvantages of the chip are identified, tips on how to neutralize them are given. Therefore, the LM317 is popular with the creators of professional and amateur radio equipment.
Related articles: