There are some electronic components that have occupied the certain market niches for many decades. They succeeded due to the successful combination of cost, technical parameters, mass-size indicators. These devices include the 1N4001-1N4007 series of silicon diodes. They are beyond competition in their field.
Contents
Description of diodes series 1N400X
The most popular series of silicon single-amp rectifier diodes among designers, manufacturers and amateurs is 1N400X series, where X=1...7 (means series device number).
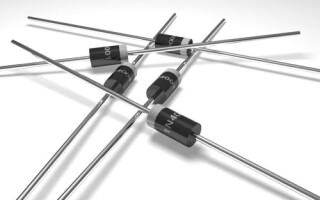
Diodes are available in a DO-41 package, specifically designed for dual lead semiconductor devices designed for relatively high currents and voltages. It consists of a cylinder of non-flammable polymer and two wire leads. The cathode is marked with a white (silver) circular band. Another name of the package is DO-204-AL. The SOD-66 marking is also used. The dimensions are set for this package:
- diameter of plastic cylinder - 2,04...2,71 mm;
- cylinder length - 4.07...5.2 mm;
- lead diameter - 0,72...0,86 mm;
- length of the lead before molding - 25,4 mm.
It is possible to bend the leads not closer than 1.27 mm from the body.
All devices of the series have the same dimensions, so you can distinguish them inside the lineup only by the inscription on the case. Unfortunately, diodes of unknown manufacturers do not always have this marking. 1N400X series devices are used very widely. Producing a huge series allows us to keep the wholesale price of diodes not more than a few cents apiece, and it also serves as a reason for the frenzied popularity of the product.
Key Technical Characteristics of Diodes
The 1N400X series diodes share the following parameters in addition to a maximum operating current of 1 A:
- The highest current in a pulse (duration of 8.3 ms) is 30 A;
- The highest voltage drop in the open state - 1 V (usually 0,6...0,8 V);
- operating temperature range - minus 55...+125 °C;
- the longest soldering time, /at temperature, - 10 s/260 ° C (although no one has yet managed to disable this diode - and even change its parameters - when soldering);
- thermal resistance (typical value) - 50 °С/W;
- the highest weight - 0.35 grams;
- the greatest reverse current (at the greatest reverse voltage) - 5 μA.
The other parameters are different for each last digit in the device designation:
| Diode type | 1N4001 | 1N4002 | 1N4003 | 1N4004 | 1N4005 | 1N4006 | 1N4007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum reverse voltage (constant), V | 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| Peak reverse voltage (pulsed), V | 50 | 100 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| RMS permissible value of reverse voltage, V | 35 | 70 | 140 | 280 | 420 | 560 | 700 |
Diodes of this series are designed to be mounted in any position.
Compared to pulse diodes, the 1N4001 to 1N4007 series diodes have a rather high capacitance of about 20 pF without applying voltage. This reduces the frequency range of the rectifier elements, but amateurs use them as varicaps.
These low-frequency diodes are not designed to work as switching elements. The manufacturer does not regulate their on or off time.
Application of 1N400X Series Rectifier Diodes
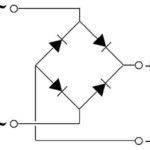
The application field of diodes is determined by their technical parameters. Without having high frequency characteristics, 1N400X devices are mostly used in rectifier devices. But this area is extremely wide, almost any mains-powered device has this node. The small size and cheapness of the diodes allow them to be included in parallel where there is not enough maximum operating current and in series where there is not enough voltage - in some cases it is more profitable than using diodes with higher characteristics.
Rectifier diodes are also used in parallel with inductors to "cut off" the negative pulse when switching. For example, if driving electromagnetic relay with a transistor switch, a reverse voltage surge would occur during switching and the transistor could fail. To avoid this, a semiconductor diode is connected in parallel with the relay winding. semiconductor diode with the cathode to the plus side. The diode has no effect on normal operation, but "eats up" the negative surge.
Also, devices of this series can be used to eliminate the connection of the power of the wrong polarity. You have to keep in mind that the open voltage drop on a diode can be as high as 1 V. This can be critical at supply voltages of 5V or lower. In this case it is necessary to use germanium devices.
Domestic and foreign analogues
There is no complete domestic analogue of diodes (body, series, line characteristics). Therefore, the replacement must be approached creatively based on the availability of space for installation.
The optimal variant is. KD258 in a glass case ("drop"). Parameters are much the same, and there will be no contradiction in mounting dimensions. You should also pay attention to the most popular domestic 1A diode KD212 (with a reverse voltage of 200 V). Replacement is somewhat difficult due to the mismatch of dimensions. Dimensions allow you to put KD212 instead of 1N4001 - 1N4007, but the height of the Russian diode is 6 mm against 2.7 foreign, so you must look at the availability of free space vertically. Also, the fact that the distance between the leads of KD212 is only 5 mm, and the leads of 1N400X can be bent at a distance of not less than 8 mm (body length plus 2x1,27 mm) makes direct replacement difficult. And this also makes direct replacement difficult.
If you know for sure that the actual direct operating current is much less than 1 A, you can try to replace the foreign device with KD105 or KD106. Their highest forward current is 0.3 A (reverse voltage, respectively, 800 and 100 V). These diodes resemble the 1N400X in shape, although they are larger in size. The KD105 also has ribbon leads, which creates additional problems for installation in existing holes. But you can try soldering directly to the tracks on the back side of the board.
If the KD105(106) does not have enough operating current, you can replace it with the KD208. Here you will also have to solve the problem of the increased size of the case as well as the ribbon leads. You can look for other analogs that match the parameters - there is nothing super outstanding and unique in the characteristics of the 1N400X series.
Of the foreign diodes, the HER101...HER108, a one-amp diode in the same package, is an excellent substitute. It costs more, because its characteristics are higher - reverse voltage up to 1000 V. This device has a high response time. But this replacement does not use these parameters.
You should also pay attention to imported products:
- HERP0056RT;
- BYW27-1000;
- BY156;
- BYW43;
- 1N2070.
In many cases, these devices can replace 1N400X, but you have to look at the parameters in each case.
The need to find an analog is a rare case. The 1N400X diode is available at any electronic components store, you can get it from any defective donor device. In this case, you should check the semiconductor device for proper operation before installing it.
Related articles: