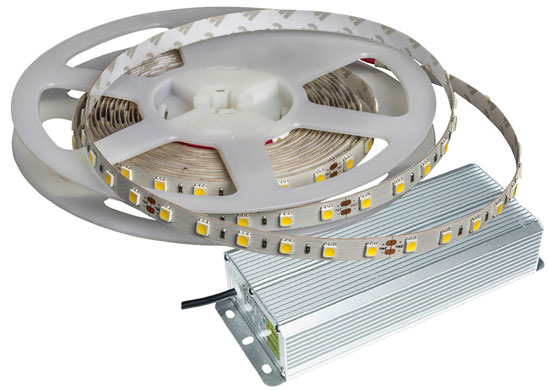
When installing decorative lighting or basic lighting from LED tapes there is inevitably a problem that is quite difficult to solve for the average person without electrical skills - how to connect the LED strips to each other and to the power supply. We will try to answer this question in this article.
Content
Ways to connect LED strips to a network of 220 V
The most common types of LED tapeswhich are mass-produced for the market in Russia and other countries, are designed to be connected to direct current with a voltage of 12 volts.
Can you connect the LED strip to 220 without a power supply
There are ways of connecting, which allow you to connect such strips to 220 V directly: using diode bridge, capacitors and serial connection of the strips to each other. But this method is inconvenient, difficult to install and impractical in terms of practical application. The cost of components for such a connection is comparable to the cost of buying a power supply, so it is widely used exactly the method of connection with the help of special step-down transformers from 220 V AC to 12 or 24 volts DC.
Diagram of connection to a 12 volt power supply unit
For ease and convenience of connection, as well as stable and clean lighting, 12-24 volt power supply units are used. Such devices are pulse and can step down the voltage to the required voltage and rectify the current by forming pulses of high frequency (10 kHz).
The power supply unit is chosen according to the wattage of the LED strip (which is determined according to the type, density and length of the LED strip), making sure to leave enough power reserve for safe and reliable operation.
Recommendation! Choose power supply with 20-30% more power reserve than the total power of the LED strip it will power.
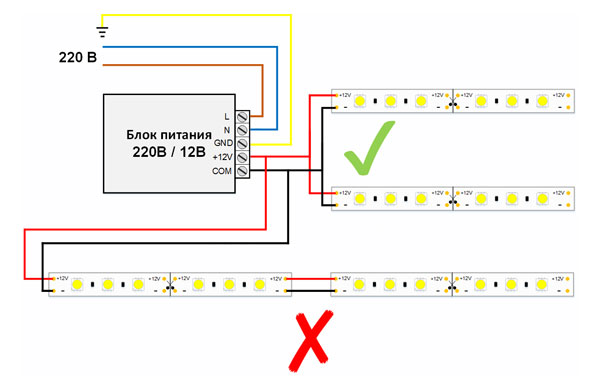
Power supply for LED lighting has input terminals for connecting to a 220 V mains supply and output terminals for powering the lighting device. Connecting the LED strip to the transformer is carried out by using wires with a certain cross section to the terminals "plus" and "minus. It is important to understand that the polarity is important, so the poles of the strip and the poles of the power supply unit when connected must be the same (plus to the plus, minus to the minus) otherwise the system will not work. In the conventional color coding., the red wire means "plus" and the black wire means "minus".
When installing lighting with an LED strip, the easiest thing to do is to connect a single-color strip. Such a device is connected directly to the "plus" and "minus" of the power supply, and the power supply is connected to the network (If necessary, switches or controls are inserted into the circuit). The only difficulty that may arise in this installation - soldering wires to the contacts of the LED strip.
The markings on the power supply

Standard power supply for LED tapes have a special marking on its body, which indicates the voltage and power of the device. This information is necessary for Selecting the right power supply to the parameters of the LED strip. To connect the lights, you only need to know the pin designations to which the conductors will be connected. In general the power supply unit will have L (contact for the connection of the phase conductor) and N (neutral conductor) and on the other side there will be "+V" and "-V" signs (+12V and -12V DC.).
Some power supplies have a cable with a plug already connected and do not require a separate wire to bring power to the terminals L and N terminals and are simply plugged into a socket.
Connecting a colored RGB strip
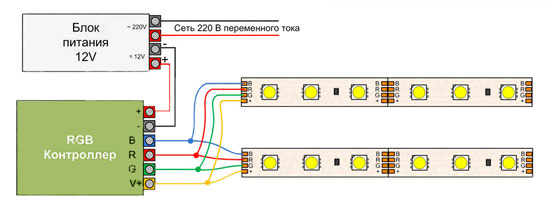
The connecting link between the step-down transformer and RGB LED strip is a special controller, with which you can connect such a device and control the shades of lighting or set the modes of operation. Without it, it will be impossible to connect such a strip and use all its functions.
Connecting the RGB strip is generally as follows: to the contacts of the controller with the designations R, G, B and V+ are connected to the corresponding contacts of the LED strip. Then to the terminals "plus" and "minus" of the controller connect the conductors that are connected to the "plus" and "minus" of the transformer and then the transformer is plugged into a socket or connected to the network in the standard way.
Note! In this circuit, there is no need to add a switch or additional control device to the circuit, as standard controllers include this feature.
Each controller has a limit to the power that can be connected to it. Therefore, a special amplifier can be used when several ribbons are connected in parallel. In general, this connection does not greatly complicate the circuit, because the amplifiers are connected to the additional tapes, which are powered from a common high-power adapter or an additional power supply unit.
Wiring diagram of high-power ribbons
LED strips, as well as any lighting fixtures have different emissivity, which directly affects the power of the strip. For high-power devices there are no differences with conventional devices when connecting, except for more powerful power supplies and controllers (in the case of RGB variant).
When connecting high-power LED devices, it is important to consider their heating. Such strips should be mounted on special aluminum profiles for fast and reliable heat dissipation. This will protect the strip from overheating and significantly increase the longevity of such lighting.
Ways to connect multiple LED strips
Typically, manufacturers produce LED tapes in coils of length of 5 meters. This is the standard unified length, which is convenient for most manufacturers. For various tasks there is a need to connect multiple LED strips for simultaneous operation in different parts of the premises or with a large length of the illuminated area. There are certain nuances and difficulties in this connection.
Parallel wiring diagram
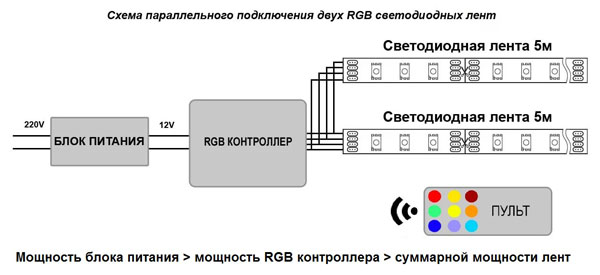
As with most lighting fixtures, the most common and convenient option is parallel connection LED strips. This method is suitable when you need the simultaneous operation of tapes without reducing their light output.
The connection looks like this:
- To the contacts of the strips solder (or connect the) conductors;
- Then connect the "pluses" of all the tapes;
- Connect the "minuses" of all the tapes;
- The common plus and common minus are connected to the corresponding poles of the transformer with the calculated power.
Ways of connecting the two tapes to each other
If it is necessary to install the tapes on the same plane one after another, they are also connected in parallel. But to simplify the scheme and save wires, this connection can be made using connectors or short wires.
Connecting the LED-tape with plastic connectors

To simplify the connection and in the absence of soldering skills (or soldering iron) you can use special plastic connectors for LED-tape to connect multiple single-color or multi-color tapes with each other. They are available for sale in most electrical stores or stores lighting fixtures. The principle of connection using such components is simple: the contacts of LED strips are connected to the contacts of the connector and fixed.
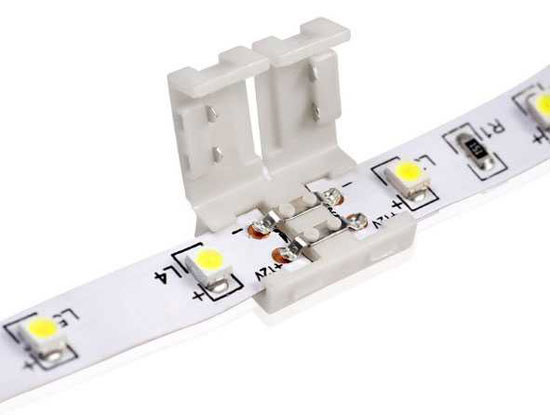
Connectors come in both straight and designed for corners and different variants of bending.
Solder connection
The most reliable option for connecting LED strips is soldering. At the same time, this method is the most time consuming and requires certain skills and tools.
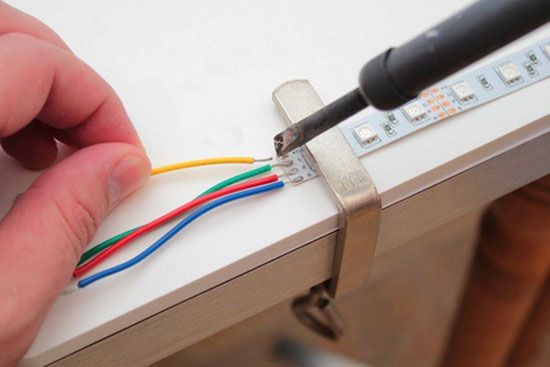
You can make such a connection in two ways:
- Connect the tapes by soldering directly.
This method involves soldering two pieces of tape without using conductors. The tapes are overlapped and soldered at the point of contact. This method is used when the tape is installed in a prominent place so that it is not visible wires and tape joints are not visible.
- Connect with wires
This is the preferred method, as it is reliable. Conductors are soldered to the pins of one segment, which are soldered to the other tape according to polarity. And the conductors can have any length if necessary.
Advantages and disadvantages of the different connections
- Soldering connection
| Advantages | disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
- Connection with connectors
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Mistakes when connecting the LED strip
No one is immune from mistakes, so when connecting the LED strips, they are allowed to both home masters and professionals. The most common mistakes when connecting LED strips are:
- Overlapping contacts when soldering;
- Overheating of the contacts with a soldering iron, thereby violating the integrity of the tape and contacts at the soldering point;
- Incorrect calculation of power supply power, the connection of several strips of power exceeding the parameters of the transformer;
- Installation of high-power ribbons without a heat sink;
- Improper ribbon selection (For example, using outdoor ribbons or transformers not protected against moisture);
- Connecting several RGB strips to one controller without amplifiers;







