History has kept for us the names of those Who invented the incandescent light bulb and worked on its original models. The path of creation of the most useful invention of the late 19th century is interesting and unusual. Today, artificial lighting in the home is a common thing. But many years have passed since the electric lamp has become familiar to us and was put into production.

Contents
Chronology of the Invention
The history of the incandescent light bulb begins in the 19th century. The useful invention was still about 50 years away from being presented to the world. However, the English scientist Humphrey Davy in his laboratory already conducted experiments with the incandescence of conductors by electric current. Still, he wasn't the one who invented the light bulbsuitable for lighting. Over the course of two decades, a number of leading European and American physicists tried to improve on Humphrey Davy's experience by heating metal and carbon conductors.
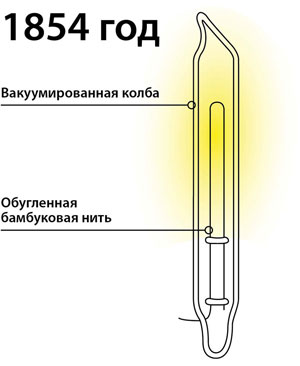
The German watchmaker Heinrich Goebel was the first who came up with the idea of lamp with incandescent elements, using the method of making barometers. The invention was presented in 1854 at an exhibition in New York. The design itself was made of cologne bottles and glass tubes in which Goebel used mercury to create vacuum. Inside he placed a charred bamboo thread, which in the flask ...with the air... air could burn for up to 200 hours.
From 1872 in St. Petersburg, work on the lamp Russian electrical engineers A. N. Lodygin and V. F. Didrichson. They placed a thin carbon rod between thick copper rods. A. N. Lodygin received the Lomonosov Prize for this invention. In 1875 V. F. Didrichson changes the carbon stick for a wooden one. A year later the naval officer and talented inventor Н. P. Bulygin improved the design invented by his compatriots. Externally, it was almost unchanged, but by covering the carbon rods with a layer of copper, the current strength was increased.
Many consider as the inventor of the of the first lamp, Thomas Edison. But before the device fell into the hands of the American inventorscientists in five European countries already had a patent for it. В what year Edison began his development of electric lighting, it is not known exactly.
In the 70s of the 19th century bulb Lodygin came to the United States. Thomas Edison did not bring anything new to the device of the Russian inventorHowever, he invented a superstructure design: a cartridge and screw base, switches and fuses, a power meter. With Edison's work begins the industrial history of invention..

The first conversions of energy into light
The advent of of the first incandescent light bulb was preceded by the greatest event of the 18th century - the discovery of electric current. He was the first to investigate electrical phenomena and to tackle the problem of obtaining current from different metals and chemicals, the Italian physicist Luigi Galvani.
In 1802, the Russian physicist-experimenter V.V. Petrov designed a powerful battery and with its help obtained an electric arc, which could produce light. However, a drawback of Petrov's discovery was that the charcoal used as an electrode burned out too quickly.
The first arc lamp capable of burning for a long time was designed by Englishman Humphrey Davy in 1806. He experimented with electricity and invented the electric light bulb with charcoal rods. However, it shone so brightly and unnaturally that no use was found for it.
The incandescent lamp: the prototypes
The invention of the incandescent light bulb is attributed to several scientists. Some of them worked at the same time, but in different countries. Scientists who worked at a later time made substantial improvements on the inventions of their predecessors. Thus, the creation of the incandescent light bulb - is the work of several people.
Direct development of designs with incandescent elements began in the 30s of the XIX century. Belgian scientist Jobar presented to the world the first design with a carbon core. His carbon lamp was not widely used only because it did not burn for more than 30 minutes. However, even this was progress at the time.

At the same time, the English physicist Warren de la Rue introduces his lamp with a platinum element in the form of a spiral. The platinum shone brightly, and the vacuum inside the glass bulb allowed it to be used in all weather conditions. Warren de la Rue's invention became a prototype for other designs, although it itself was not further developed because of its high cost.

Another English physicist, Frederic de Molain, slightly modified de la Rue's brainchild by installing platinum filaments instead of a coil. However, they quickly burned out. A little later, physicists King and John Starr improved on their English colleagues. Englishman King replaced the platinum filaments with carbon sticks, increasing their combustion time. And the American John Starr came up with a design with a carbon burner and a vacuum sphere.
The first results
First light source came from Heinrich Hebel's workshop. Heinrich Goebel's workshop .. He was not a professional inventorbut he discovered the world's first incandescent lamp. Goebel installed the lights in his watch store and fitted them in a stroller, where he invited all comers. However, due to a lack of money Goebel was unable to obtain a patent for his invention. Only at the end of his life was the German watchmaker recognized the inventor of lamp with incandescent elements.
In Russia, the first inventor of incandescent lamp elements was A. N. Lodygin. Together with his colleague V. F. Diedrichson, he laid the beginning of electric lighting of St. Petersburg. The first coal lighting constructions, created by Russian inventors, were installed in St. Petersburg Admiralty. A year later, artificial light appeared in some stores in the capital and on Alexander Bridge.

Struggle for patents
Since work on the creation of electric light sources was carried out in many countries, patents for similar inventions were obtained by several scientists at once. In the United States, however, this multiple discovery led to a struggle to obtain a patent for the incandescent lamp.
The first patent for an incandescent light bulb bulb ...were two venerable... inventors - The Englishman Joseph Swann and the American Thomas Edison. The Englishman patented a lamp with a carbon fiber, which began to be used in industrial production in the British Isles. Thomas Edison worked on improving Alexander Lodygin's filament lamp. He tried many metals as filaments and settled on carbon fiber, bringing the lamp's burn time to 40 hours.
Joseph Swann sued his American colleague for copyright infringement, so the lamp introduced by Edison was later called the Edison-Swann lamp. When bamboo fibers with a burn time of up to 600 hours were later imported from Japan, the scientists found themselves in court again as they began using this material in their inventions. The case ended with Edison and Swan founding a joint company to produce electric light bulbswhich quickly became a world leader.
Metal filaments
Instead of candles, incandescent carbon lamps appeared. And then the design was equipped with metallic filaments. At the end of the 19th century, the German physicist Walter Nernst produced a special alloy for the production of filaments. It included metals such as:
- yttrium;
- magnesium;
- thorium.
At the same time, A.N. Lodygin invented a fast-hardening filament made of tungsten. However, later the Russian inventor sold his discovery to a company founded by Thomas Edison. Tungsten filaments ushered in a new era of electric lighting.

Further Inventions
Before the twentieth century, there was not much interest in electric lighting among scientists. With the turn of the millennium, however, everything changed. The twentieth century was characterized by a wave of inventions of various electric lamps. In 1901, an American inventor Peter Hewitt introduced the mercury lamp to the world. And in 1911 the French chemist Georges Claudy created the neon lamp.
The first half of the 20th century saw designs such as xenon, fluorescent and sodium lamps. In the 1960s, the world saw LED lamps capable of illuminating large rooms. And in 1983 came the economical fluorescent lampsto reduce energy costs. However, the future is in fluorescent designs, which appeared recently. Not only can they save energy but they can also clean air.







