Current in an electrical circuit flows through the conductors from the voltage source to the load, that is, to the lamps, appliances. In most cases, copper wires are used as the conductor. A circuit may contain several elements with different resistances. In a device circuit, the conductors can be connected in parallel or in series, and there can also be mixed types.
Item circuit with a resistance is called a resistor, the voltage of this element is the potential difference between the ends of the resistor. Parallel and series electrical connection of conductors is characterized by the same principle of operation, according to which the current flows from the plus to the minus, respectively the potential decreases. In wiring diagrams, the wiring resistance is taken as 0 because it is negligible.
Parallel connection implies that the circuit elements are connected to the source in parallel and switched on at the same time. A series connection means that the resistance conductors are connected in close succession to each other.
The calculation uses the idealization method, which makes it much easier to understand. In fact, in electrical circuits, the potential gradually decreases as it moves through the wiring and elements that are part of a parallel or series connection.
Contents
Connecting conductors in series
A connection in series means that the conductors are connected in a certain order one after the other. And the current in all of them is equal. These elements create a total voltage in the area. Charges do not accumulate in the nodes of the electrical circuit, because otherwise there would be a change in voltage and current. With a constant voltage, the current is determined by the resistance value of the circuit, so in a series circuit the resistance changes if one load changes.
The disadvantage of this circuit is that if one element fails, the others also lose the ability to function because the circuit is broken. An example would be a garland which does not work if one bulb burns out. This is a key difference from a parallel connection, in which the elements can function individually.
The series circuit assumes that because the conductors are connected in a single level, their resistance at any point in the network is equal. The total resistance is equal to the sum of the decreasing voltages of the individual network elements.
In this type of connection, the beginning of one conductor is connected to the end of another. The key feature of the connection is that all conductors are on the same wire without branching, and one electric current flows through each of them. However, the total voltage is equal to the sum of the voltages on each. It is also possible to consider the connection from another point of view - all conductors are replaced by one equivalent resistor, and the current on it is the same as the total current that passes through all resistors. The equivalent total voltage is the sum of the voltage values across each resistor. This is how the potential difference across the resistor manifests itself.
The use of series connection is useful when you want to specifically switch a certain device on and off. For example, an electric bell can only ring when there is a connection to a voltage source and a button. The first rule states that if there is no current on at least one element of the circuit, there will be no current on the others. Accordingly, if there is current in one conductor, there is also current in the others. Another example would be a battery-powered flashlight, which only shines if there is a battery, a functioning bulb, and a pressed button.
In some cases, a series circuit is not practical. In an apartment where the lighting system consists of many lamps, sconces, chandeliers, it is not worth organizing a scheme of this type, since there is no need to turn on and off the lighting in all the rooms simultaneously. To this end, it is better to use a parallel connection to be able to turn on the lights in individual rooms.
Parallel connection of conductors
In a parallel circuit, the conductors are a set of of resistorsone end of which is assembled in one node and the other ends in a second node. It is assumed that the voltage in the parallel type of connection is the same in all sections of the circuit. Parallel sections of an electrical circuit are called branches and run between two connecting nodes, they carry the same voltage. Such a voltage is equal to the value on each conductor. The sum of the values inverse to the resistance of the branches is also inverse to the resistance of the individual circuit section of the parallel circuit.
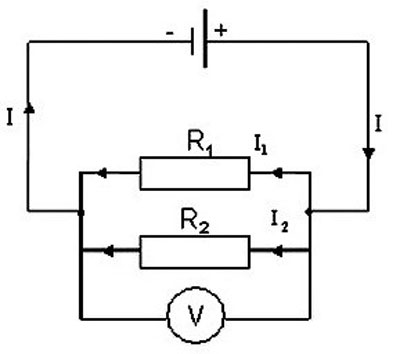
With parallel and series connections, the system for calculating the resistances of individual conductors is different. In the case of a parallel circuit, the current flows along the branches, which increases the conductivity of the circuit and reduces the total resistance. If several resistors with similar values are connected in parallel, the total resistance of such an electrical circuit will be less than one resistor the number of times equal to the number of resistors in the circuit.
There is one resistor in each branch, and the electric current is divided and diverged to each resistor when reaching the point of branching, its final value is equal to the sum of the currents on all resistors. All resistors are replaced by one equivalent resistor. Applying Ohm's law, the value of resistance becomes clear - with a parallel circuit, the values inverse of the resistors are added up.
In this circuit, the current value is inversely proportional to the resistance value. The currents in the resistors are uncorrelated, so if one resistor is turned off, the others will not be affected in any way. For this reason, this circuit is used in many devices.
Considering the application of the parallel circuit in everyday life, it is advisable to note the lighting system of the apartment. All lamps and chandeliers should be connected in parallel, in which case the turning on and off of one of them does not affect the work of the rest of the lamps in any way. Thus, by adding switch of each bulb into a branch circuit, you can turn the corresponding lamp on and off as needed. All other lamps operate independently.
All electrical appliances are connected in parallel to the 220V power grid, then they are connected to the switchboard. That is, all appliances are connected independently of the connection of other devices.
Laws of series and parallel connection of conductors
For a detailed practical understanding of both types of connections, here are the formulas explaining the laws of these types of connections. Calculation of power in parallel and in series is different.
In a series connection, there is the same amperage in all conductors:
I = I1 = I2.
According to Ohm's law, these types of conductor connections are explained differently in different cases. Thus, in the case of a series circuit, the voltages are equal to each other:
U1 = IR1, U2 = IR2.
In addition, the total voltage is equal to the sum of the voltages of the individual conductors:
U = U1 + U2 = I(R1 + R2) = IR.
The total resistance of an electric circuit is calculated as the sum of the active resistances of all conductors, regardless of their number.
In the case of a parallel circuit, the total circuit voltage is the same as the voltages of the individual elements:
U1 = U2 = U.
And the cumulative strength of the electric current is calculated as the sum of the currents that exist across all conductors in parallel:
I = I1 + I2.
To maximize the efficiency of electrical networks, it is necessary to understand the essence of both types of connections and apply them judiciously, using the laws and calculating the rationality of practical implementation.
Mixed connection of conductors
Series and parallel resistance connection can be combined in the same electrical circuit if necessary. For example, it is allowed to connect parallel resistors in series to another resistor or their group, this type is considered as combined or mixed.
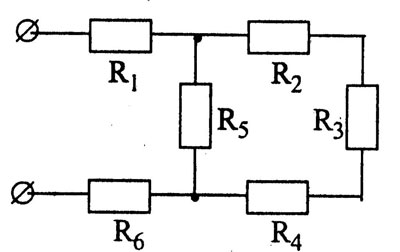
In this case, the total resistance is calculated by obtaining the sum of the values for the parallel connection in the system and for the series connection. First the equivalent resistances of the resistors in the series circuit must be calculated, and then the elements of the parallel circuit. The series connection is considered a priority, and circuits of this combined type are often used in household appliances and devices.
So, considering the types of connections of conductors in electrical circuits and based on the laws of their functioning, you can fully understand the essence of the organization of circuits of most household appliances. With parallel and series connections, the calculation of resistance and current values is different. Knowing the principles of calculation and formulas, you can competently use each type of circuit organization to connect the elements in the best way and with maximum efficiency.
Related articles: