Fluorescent lamps are electric gas discharge lamps, which are characterized by a long lifetime. Products provide artificial lighting in apartment complexes, office and shopping centers, industrial facilities. Developed versions of devices with different shades of radiation, type of base, the shape of the tube, functionality, etc.

Contents
Structure and function of the lamps
According to the history of the fluorescent lamp, the first gas discharge type lighting device was designed in 1856 by G. Heisler. The design of the devices improved. Daylight lamps were commercially available in the late 1830s.
The design is a gas-discharge light source, designed with a tube of glass, which is sealed on both sides. On the inside, a layer of a special substance (phosphor) is applied to the surface of the lamp. The device emits scattered light when connected to a power source. The inside of the bulb is filled with argon.
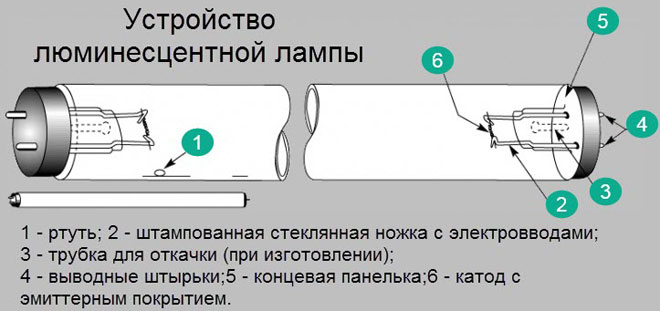
The luminescent device includes:
- cathodes protected by an emitter layer;
- lead pins;
- an end panel;
- noble gas escape tubes;
- mercury;
- glass stamped foot, complete with electric leads, etc.
The principle of operation is based on occurrence of electric discharge between electrodes after connection to electric network. After the interaction of the discharge with noble gases and mercury vapors, ultraviolet radiation is produced, which affects the phosphor, which converts the energy into light radiation. Mercury-containing devices use phosphors with different chemical components to correct tints.
The arc discharge in the bulb is created by an oxide self-shrinking cathode, which is affected by electricity. To turn on DRL and LD lamps, cathodes are heated by passing a current discharge. Cold cathode devices are started by ionic action in a high voltage glow discharge.
Luminescent devices require an additional unit (ballast) to function, which provides the choke and starter. The ballast regulates the strength of the discharge and comes in 2 types (electromagnetic and electronic).
The electromagnetic ballast is mechanical. The device belongs to the budget options, in operation the device may emit noise.

Electronic units are more expensive in cost, work quietly, quickly turn on the system, compact.
Classification of fluorescent lamps
According to the indicator of the spectral radiation of fluorescent-type devices are divided into 3 categories:
- standard;
- with enhanced color rendering;
- with special functional purposes.
Standard devices are equipped with single-layer phosphors that allow emission of different tones of white. The devices are optimal for lighting residential, administrative and industrial units.
Fluorescent lamps with advanced light transmission are equipped with a phosphor with 3-5 layers. The structure allows high-quality reflection of shades due to increased light output (12% more than standard lamps). Models are suitable for store windows, exhibition halls, etc.
Specialty fluorescent lamps are upgraded with different compositions in the tube to maintain a given frequency of the spectrum. The devices are used in hospitals, concert halls, etc.
The devices are divided into high-pressure and low-pressure models.
High-pressure designs are optimal for installation in street lamps and appliances with high power.
Low-pressure lamps are used in apartments, administrative complexes, industrial premises.
In terms of appearance, LL are represented by linear and compact versions.

Linear bulb design is elongated, used for industrial premises, shopping centers, offices, medical institutions, sports organizations, factory floors, etc. Linear model is represented by different variants of tube diameters and base configurations. Devices are designated by codes. A device with a diameter of 1.59 cm on the packaging is marked with the sign T5, with a size of 2.54 cm - T8, etc.
Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are a spiral-shaped glass tube and are intended for installation in apartments, offices, etc. CFLs are divided into 2 types, the main difference being the types of bases (standard and with a pin-shaped base).
Traditional threaded base is marked with "E" and a code with the size of the diameter.
The pin-shaped base is marked with the symbol "G"; the numerical data indicates the distance between the pins. This fork lamp is optimal for installation in table lamps, pendant sconces in small rooms.
Fluorescent lamps vary in wattage (weak and strong). The wattage of a fluorescent lamp can exceed 80 units. Devices with low power are represented by products up to 15 watts.
According to the indicator of light distribution, devices can be directional (reflector, slit type) or non-directional.
According to the type of discharge devices are divided into arc, glow or glow discharge devices.
There are different applications of lighting devices (outdoor, indoor, explosion-proof, cantilever).
Outdoor devices are suitable for decorating buildings from the outside, for lighting arbors, courtyard decoration, etc. When selecting, it is necessary to take into account the temperature conditions of the region.
Indoor are suitable for office and residential buildings. The devices are equipped with protection against moisture and dust. Body parts are connected in a sealed way. The design of the lamps can be straight, suspended, designed to be attached to the ceiling surface.
Explosion-proof devices are designed for areas with a risk of explosion (warehouses, dye shops, etc.).
Devices of cantilever type are mounted by means of special fasteners and have an individual case.
Marking
The marking of fluorescent lamps is indicated on the box and contains information about the company, power, design of the base, period of operation, shade of luminescence, etc.
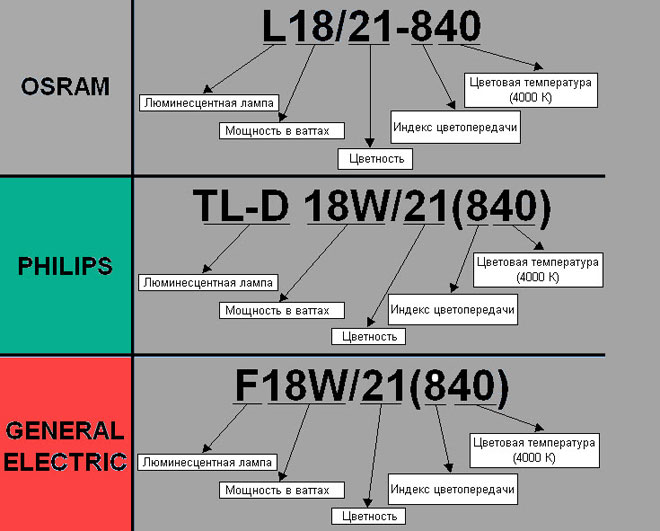
According to the deciphering of the index, the first letter of the fluorescent bulb marking is L. Subsequent letters indicate the shade of radiation of the device (daylight, white, cool tone white, ultraviolet, etc.). The code value will include the symbols D, B, UV, etc.
Design features on the markings are denoted by the corresponding letters:
- u-shaped fluorescent lamps (U);
- ring shaped products (K);
- reflector type devices (P);
- quick start lamps (B).
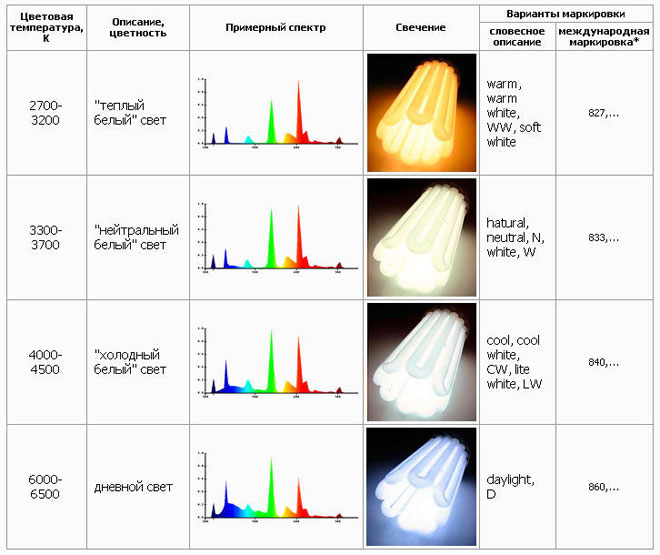
In fluorescent-type devices, luminescence values are also shown on the marking, the unit of measure being Kelvin (K). The temperature value of 2700 K in shade corresponds to the radiation of an incandescent lamp.The marking of 6500 K denotes a cold white tone.
The power of the devices is marked with a number and unit of measurement - watts. Standard indicators are represented by devices from 18 to 80 watts.
The label also presents the designation of lamps according to such characteristics as length, diameter and shape of the bulb.
The diameter of the bulb on the lamp is fixed by the letter "T" with a code designation. The device designated by code T8 has a diameter of 26 mm, T12 has a diameter of 38 mm, etc.
The marking of devices by type of socket contains the letters E, G and a numerical code. The designation for the miniature form of the threaded base is E14. The average threaded base has a code E27. The plug-in type base for decorative designs and chandeliers is marked with the symbol G9. The u-shaped fixtures are marked with the symbol G23, double u-shaped fixtures are marked with G24, etc.
Technical data
Technical information on fluorescent fixtures includes data on the operating power, type of base, service life, etc.
Fluorescent fixtures range in life from 8,000 to 12,000 hours. The characteristics depend on the type of lamp. T8 and T12 devices last 9 to 13 thousand hours, T5 lamps last 20 thousand hours.
Light efficiency of devices is 80 Lm/W. Heat release during combustion is low, wind resistance is medium, the burning position is horizontal. Parameters of permissible ambient temperature for the lamps are +5 ... +55 ° C. Optimal operating characteristics are +5 ... +25°C. Devices with amalgam coating are used at +60°C.
Depending on the model, the color temperature of the devices varies from 2000 to 6500 K. The efficiency of the luminaire is 45-75%.
Chromaticity and emission composition of lamps
The color rendering characteristics show the quality of the display compared to the natural type of lighting. High definition color transmission is present in halogen fixtures and is indicated by the code 100.
There are different shades of light emitted by devices that change the color characteristics of objects.
According to GOST 6825-91 regulations, fluorescent devices have the following types of shades of radiation:
- daylight (D);
- white (B);
- natural shade of white (E);
- white with a warm tone (TB);
- white with a cool tone (CB);
- ultraviolet (UV);
- cold natural luminescence (LCE), etc.
The addition of the C sign in the color indication indicates the use of a phosphor composition with improved color rendering.
Colors in lighting fixtures with a special purpose are indicated separately. Lamps with ultraviolet radiation are fixed by the code LUF, reflective blue light devices - LSR, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
Fluorescent devices have advantages, advantages and disadvantages. Lamps have a high light output. Fluorescent devices of 20 watts provide lighting in the room that incandescent devices and illumination lamps of 100 watts.
The products have a high efficiency factor. Energy-saving lamps are used up to 20 thousand hours if the operating requirements are met.
The light in fluorescent designs is not directional, but diffuse. In northern regions, it is recommended to use fluorescent daylight lamps in residential and public buildings.
The advantage of fluorescent devices in a variety of designs. Different shapes, color shades of devices allow to realize original design solutions in the architecture of public and residential complexes.
The disadvantages of fluorescent devices include the content of mercury in the design, depending on the size of the lamp, the volume of the substance ranges from 2.3 mg to 1 g. However, manufacturers develop designs that are not dangerous in use.
It is necessary to take into account the complexity in the installation of switching circuits and the limited power per unit (150 W). Operation of devices depends on climatic conditions, because when the temperature drops, the devices go out or do not light up. The luminous flux in the lamps decreases towards the end of operation of the device.
How to choose a lamp
When selecting a lamp, the temperature mode of the device, the electrical voltage in the network, the size of the lamps, the luminous flux, the shade of radiation are important. Parameters of the bases of fluorescent lamps should correspond to the types of lamps, floor lamps, etc.
The selection of lamps according to the type of room (hallways, living rooms, bedrooms, bathrooms, etc.) differs. For living spaces, models with a threaded base and electronic ballast are suitable, because they do not have harsh flicker and are silent.
For hallways, you need powerful lights with intense, yet diffuse lighting. For wall sconces are suitable compact type fixtures with a warm shade (930) and high quality color rendering. Above the cornice under the ceiling, you can mount strip lights with lamps of a cool shade (860) and a tubular design.
In the living room, fluorescent devices are used for sconces, which are mounted to highlight areas or decorative elements. The color is selected white, high quality (940). It is possible to install lighting devices along the perimeter of the ceiling.
In bedrooms, it is recommended to choose standard fluorescent devices with an index of 930-933 or compact devices with similar qualities.
Lighting in the kitchen area should be multi-level (general and local). As ceiling lights are recommended compact devices with power not less than 20 W, the shade of light should be warm, with an indicator not lower than 840. For the arrangement of the working area in the kitchen, linear fluorescent lamps that do not create glare on the surfaces are optimal.
Related articles: