A circuit diagram is a detailed drawing showing all the electronic components and accessories that are interconnected by wires. Knowing how electrical circuits function is the key to a properly assembled electrical appliance. That is, the assembler must know how the electronic elements are marked on the schematic, what icons, alphabetic or numeric symbols correspond to them. In this material, we will understand the key designations and the basics of how to learn to read electrical schematics.
Any electrical circuit includes a number of parts, consisting of smaller elements. Let's take as an example an electric iron, which contains a heating element inside, a temperature sensor, light bulbs, fuses, and also has a wire with a plug. Other household appliances have an advanced configuration with circuit breakers, electric motors, transformers, and between them there are connectors for the full interaction of the components of the device and the purpose of each of them.
Therefore, the problem often arises of how to learn how to decipher electrical schemes, which contain graphic designations. The principles of reading wiring diagrams are important for those involved in electrical installation, repair of household appliances, and connection of electrical devices. Knowing the principles of reading wiring diagrams is necessary to understand the interaction of elements and the functioning of devices.
Types of wiring diagrams
All electrical circuits are presented in the form of an image or drawing, where along with the equipment, the links of the electrical circuit are indicated. Schemes differ in purpose, on the basis of which the classification of different electrical circuits is developed:
- Primary circuits and secondary circuits.
Primary circuits are created to supply the main electric voltage from the current source to the consumers. They generate, transform, and distribute electricity during transmission. Such circuits involve a primary circuit and circuits for various needs.
In the secondary circuits, the voltage does not exceed 1 kW and is used to provide automation, control and protection tasks. Secondary circuits are used to control consumption and metering of electricity;
- Single line, full line.
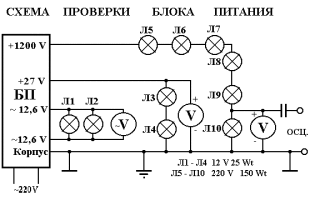
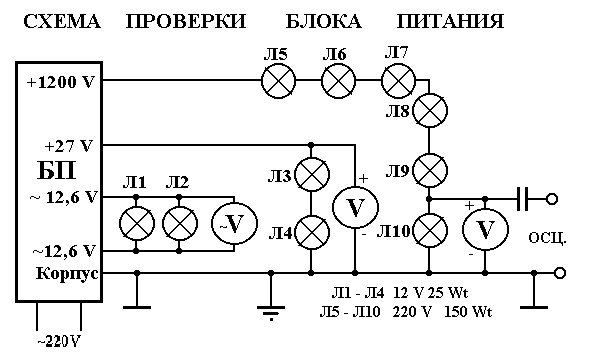
Full-line circuits are designed for use on three-phase circuits, and they show devices connected on all phases.
Single-line diagrams show only devices in the middle phase;
- circuit diagrams and wiring diagrams.
A schematic general wiring diagram shows only the key elements, it does not show the secondary parts. This makes the diagrams simple and easy to understand.
Wiring diagrams show more detail, because it is these diagrams that are used for the actual installation of all elements of the electrical network.
Detailed diagrams with indication of secondary circuits help to identify auxiliary circuits, sections with separate protection.
Schematic symbols
Electrical circuits consist of elements and components which ensure the flow of electric current. All elements are divided into several categories:
- devices that generate electricity - power sources;
- Converters of electric current into other types of energy - consumers;
- parts responsible for the transmission of electricity from the source to the devices. Also included in this category are transformers and stabilizers that ensure voltage stability in the network.
A specific graphic designation is provided for each element in the diagram. In addition to the key designations, power transmission lines are indicated on the diagrams. Sections of the electrical circuit in which the same current flows are called branches, and at the points where they are connected, dots are placed in the diagram to indicate the connection nodes.
An electrical circuit implies a closed path of electric current through several branches. The simplest circuit consists of a single circuit, but for more complex devices there are schemes with several circuits.
On the circuit diagram, each element and connection corresponds to an icon or designation. Single-line and multi-line diagrams are used to show the insulation leads, the number of lines in which is determined by the number of leads. Sometimes mixed drawings are used for ease of reading and understanding diagrams, for example, the stator insulation is described in expanded form and the rotor insulation in general form.
The designations of transformers in electrical diagrams are drawn in general or expanded form, single-line and multi-line methods. Directly on the detail of the image depends on the method of displaying devices, their outputs, connections and assemblies on the diagram. For example, in current transformers, the primary winding is represented by a thick line with dots. The secondary winding can be displayed with a circle in a standard diagram or with two half circles in the case of an unfolded diagram.
Other elements are shown in the diagrams by the following designations:
- The contacts are divided into make contacts, break contacts, and switches, which are indicated by different signs. If necessary, contacts can be indicated in a mirror image. The base of the moving part is indicated as an unshaded dot;
- Switches - their base corresponds to a dot, and for circuit breakers, the category of the trip unit is drawn. A switch for open installation is usually designated separately;
- fuses, DC resistors and capacitors. Fuse elements are shown as a rectangle with taps, DC resistors can be marked with or without taps. The movable contact is drawn with an arrow. Electrolytic capacitors are designated according to polarity;
- semiconductors. Simple diodes with a p-p junction are shown as a triangle and a crossed electrocircuit line. The triangle represents the anode and the line represents the cathode;
- An incandescent bulb and other lighting elements are usually labeled
Understanding these icons and symbols makes reading electrical diagrams easy. Therefore, before you start wiring or disassembling appliances, we recommend familiarizing yourself with the basic symbols.
How to read wiring diagrams correctly
A circuit diagram of an electrical circuit shows all the parts and links between which current flows through the conductors. These diagrams are the basis for the design of electrical devices, so reading and understanding electrical circuits is a must for any electrician.
A competent understanding of circuits for beginners allows you to understand the principles of their composition and the correct connection of all the elements in an electrical circuit to achieve the expected result. To correctly read even complex circuits, it is necessary to learn the main and secondary images, symbols of elements. Symbols indicate the general configuration, specificity and purpose of the part, which allows you to make a complete picture of the device when reading the circuit.
You can start with small devices such as capacitors, speakers, and resistors to become familiar with circuits. The schematics of semiconductor electronic parts in the form of transistors, triacs, microcircuits are more difficult to understand. For example, bipolar transistors have at least three pins (base, collector and emitter), which requires more symbols. Due to the large number of different signs and drawings, it is possible to identify the individual characteristics of the element and its specifics. Symbols encode information to clarify the structure of elements and their specific characteristics.
Often the symbols have auxiliary clarifications - near the icons there are Latin letters for details. Their meanings are also recommended to be familiarized with before starting to work with diagrams. Also next to the letters there are often numbers that show the numbering or technical parameters of the elements.
So, to learn how to read and understand wiring diagrams, you need to become familiar with symbols (drawings, letters and numbers). This will allow you to get information from the circuit concerning the structure, construction and purpose of each element. That is, to understand circuits, you need to learn the basics of radio engineering and electronics.
Related articles: