It is often a problem to determine which electrode is the cathode and which is the anode. To begin with, we need to understand the terms.
The concept of cathode and anode - a simple explanation
In complex substances, the electrons between atoms in compounds are not uniformly distributed. As a result of the interaction, the particles move from the atom of one substance to the atom of the other. The reaction is called a redox reaction. The loss of electrons is called oxidation, the element that gives up electrons is called the reducing agent.
The addition of electrons is called reduction; the element that takes the electrons in this process is the oxidizer. The transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent can flow through an external circuit, and then it can be used as a source of electrical energy. Devices in which the energy of a chemical reaction is converted into electrical energy are called galvanic cells.
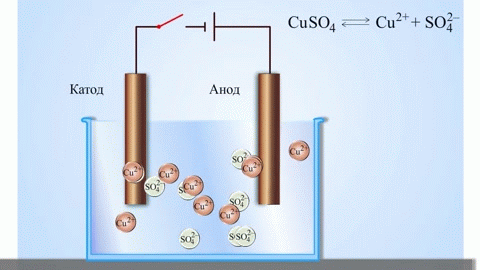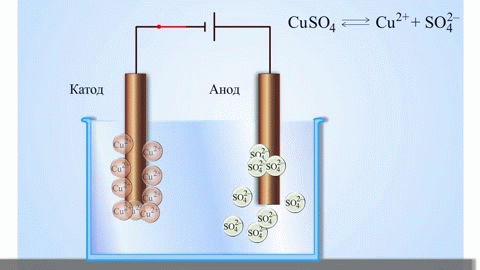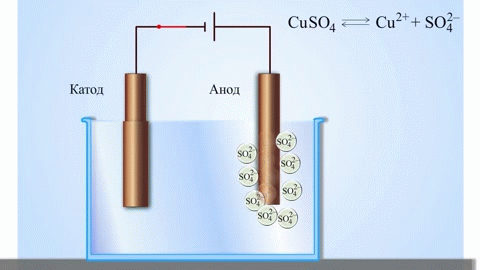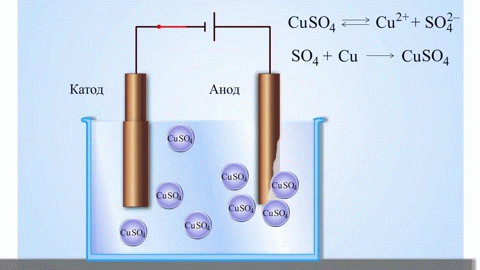
The simplest classic example of a galvanic cell is two plates made of different metals and immersed in an electrolyte solution. In such a system, oxidation occurs on one metal and reduction occurs on the other.
IMPORTANT! The electrode where the oxidation takes place is called the anode. The electrode where reduction takes place is called the cathode.
From school chemistry textbooks we know an example of a copper-zinc galvanic cell, which works due to the energy of the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate. In Jacoby-Daniel's device, a copper plate is placed in a solution of copper sulfate (copper electrode), and a zinc plate is immersed in a solution of zinc sulfate (zinc electrode). The zinc electrode gives off cations into the solution, creating an excess positive charge in it, while at the copper electrode the solution is depleted of cations, here the solution is negatively charged.
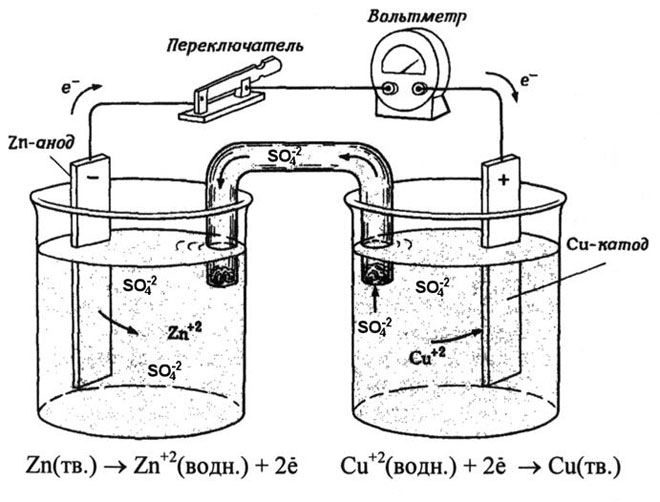
Closure of the external circuit causes electrons to flow from the zinc electrode to the copper electrode. The equilibrium relations at the phase boundaries are interrupted. The redox reaction takes place.
Energy of spontaneous chemical reaction turns into electric energy.
If the chemical reaction is provoked by external energy of electric current, there is a process called electrolysis. The processes involved in electrolysis are the reverse of those involved in the operation of a galvanic cell.
WARNING. The electrode where reduction takes place is also called the cathode, but in electrolysis it is negatively charged and the anode is positively charged.
Electrochemical Applications
Anodes and cathodes take part in many chemical reactions:
- Electrolysis;
- Electro-extraction;
- Electroplating;
- Electroplating.
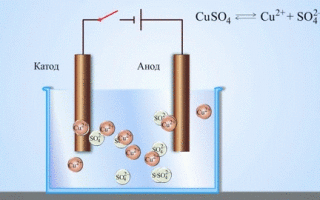
The electrolysis of molten compounds and aqueous solutions produces metals, purifies metals from impurities and extracts valuable components (electrolytic refining). Plates are cast from the metal to be refined. The plates are placed as anodes in the electrolyser. The metal is dissolved by an electric current. Its cations pass into the solution and are discharged at the cathode, forming a precipitate of pure metal. The impurities contained in the original crude metal plate either remain insoluble in the form of anodic sludge or pass into the electrolyte, from which they are removed. Copper, nickel, lead, gold, silver and tin are subjected to electrolytic refining.
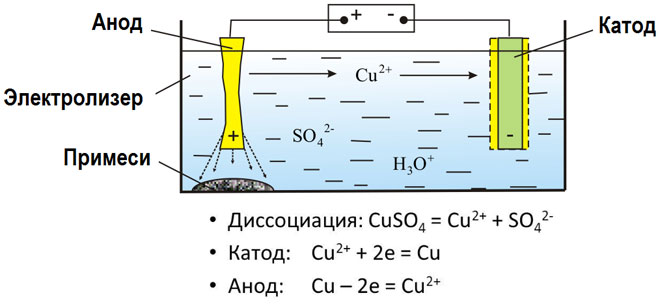
Electroextraction is the process of extracting metal from solution during electrolysis. The metal is treated with special reagents to make it pass into solution. In the course of the process a metal characterized by high purity is released at the cathode. This is how zinc, copper, and cadmium are produced.
To avoid corrosion, give strength, and decorate the product, the surface of one metal is covered with a layer of another. This process is called electroplating.

Electroplating is a process of making metal copies of three-dimensional objects by electro-deposition of metal.

Use in vacuum electronic devices
The principle of the cathode and anode in a vacuum apparatus can be demonstrated by an electron tube. It looks like a hermetically sealed vessel with metal parts inside. The device is used to rectify, generate and convert electrical signals. According to the number of electrodes are distinguished:
- diodes;
- triodes;
- tetrodes;
- pentodes, etc.
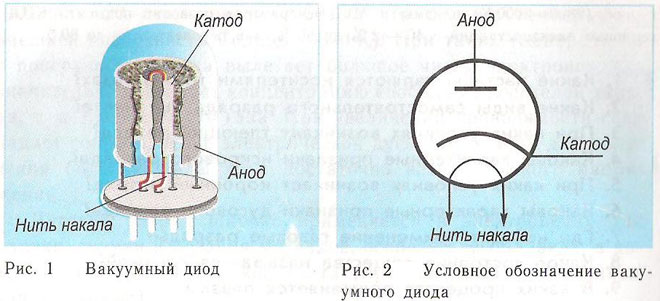
A diode is a vacuum device with two electrodes, a cathode and an anode. The cathode is connected to the negative pole of the power supply, the anode to the positive pole. The purpose of the cathode is to emit electrons under the influence of electric current heating to a certain temperature. Through the emitted electrons, a spatial charge is created between the cathode and the anode. The fastest electrons rush to the anode, overcoming the negative potential barrier of the space charge. The anode receives these particles. Anodic current in the external circuit is created. The electron flow is controlled by means of additional electrodes by applying an electric potential to them. Diodes are used to convert the alternating current into direct current.
Electronics applications
Today, semiconductor types of diodes are used.
The property of diodes to pass current in the forward direction and not to pass current in the reverse direction is widely used in electronics.
LED operation is based on the property of semiconductor crystals to glow when current passes through the p-n junction in the forward direction.
Galvanic sources of direct current - accumulators
Chemical sources of electrical current in which reversible reactions take place are called rechargeable batteries: they are recharged and used repeatedly.

When a lead battery works, a redox reaction occurs. Metal lead is oxidized, giving up its electrons, reducing lead dioxide, which receives the electrons. The metallic lead in the battery is the anode and is negatively charged. Lead dioxide is the cathode and is positively charged.
As the battery discharges, the substances of the cathode and anode and their electrolyte, sulfuric acid, are consumed. To charge the battery, it is connected to a current source (plus to plus, minus to minus). The direction of the current is now the opposite of what it was when the battery was discharged. The electrochemical processes at the electrodes are "reversed". Now the lead electrode becomes the cathode, the reduction process takes place on it, and the lead dioxide becomes the anode, with the oxidation procedure taking place. The substances necessary for the battery to work are again created in the battery.
Why is there confusion?
The problem arises because a particular sign of charge cannot be firmly attached to the anode or cathode. Often the cathode is the positively charged electrode and the anode is the negative electrode. Often, but not always. It all depends on the process taking place at the electrode.
WARNING. The part you put into the electrolyte can be both anode and cathode. It all depends on the purpose of the process: to put another layer of metal on it or to take it off.
How to determine the anode and cathode
In electrochemistry, the anode is the electrode where oxidation processes take place, and the cathode is the electrode where reduction takes place.
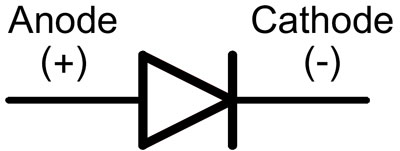
In a diode, the leads are called the anode and cathode. The current will flow through the diode if the "anode" lead is connected to the "plus" and the "cathode" lead is connected to the "minus".
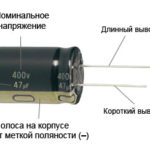
For a new LED with uncut pins, the anode and cathode are determined visually by length. The cathode is shorter.

If the contacts are cut, a battery attached to them will help. The light will appear when the polarities match.
The sign of the anode and cathode
In electrochemistry, it is more correct to talk not about the signs of the electrodes' charges, but about the processes going on at them. The reduction reaction takes place at the cathode and the oxidation reaction takes place at the anode.
In electrical engineering, for current to flow, the cathode is connected to the negative pole of the current source, the anode to the positive pole.
Related articles: