Understanding how the units of measurement "lumens" and "lux" are properly related, and where they apply, is necessary to successfully address the following domestic situations:
- Determining and checking the illumination in a living space for compliance with the standard;
- positioning of luminaires to create the same illumination anywhere in the room;
- preventing overconsumption of energy by lighting fixtures;
- prevention of eye diseases due to lack of light and negative body conditions caused by biorhythm disturbances.
Contents
What is lumen and lux
Any light source can be characterized by the intensity of the light it emits. In the international metric system it is measured in candela (cd). A derivative of the candela is the value that characterizes the luminous flux itself - lumen, abbreviated - lm.
Important: Modern lamps and products with LEDs indicate the value of the luminous flux they emit in lumens or the value of light output in lumens per watt (lm/W).
The luminous efficacy in concrete numbers describes the efficiency of the conversion of electrical energy into light and characterizes the economy of the lamp. To get only lumens, multiply the value in lm/W by the wattage of the product in watts. For example, the luminous efficacy of a 100 W incandescent lamp is 15 lm/W. So theoretically it emits light of 1500 lm. In reality, there are always losses in luminous efficacy. This is primarily due to the material of the lamp itself.
Considering the movement of light waves in space inevitably leads to the concept of illumination, because light does not shine into itself, it is always directed outward from the source and makes other objects visible to the human eye. Obviously, it falls on the surface of a certain area, so it becomes illuminated.
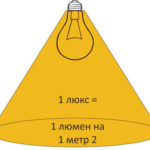
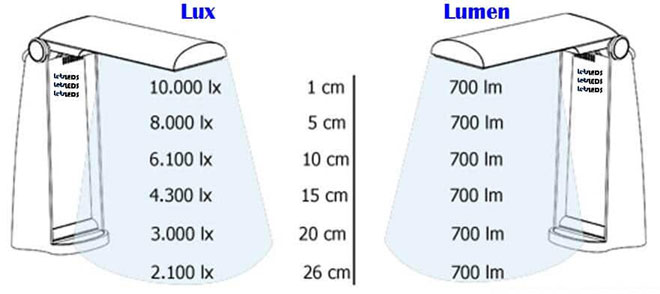
Lux is a unit of measurement of illumination. If luminous flux of 1 lumen falls perpendicularly and uniformly on a surface of unit area (1 m²), its illuminance will be 1 lux.
Absolute value of illuminance in lux will be always multiple of luminous flux in lumen for each specific light source, because relationship between these quantities is inversely proportional. The larger the illuminated area, the worse the characteristics of illuminance. So, for example, an incandescent bulb of 1500 lm, placed in an opaque cube with 1 m ² face area, strictly in the center, i.e. equidistant from all its sides, will illuminate only 6 m ² (4 sides of 1 m ², 1 lower + 1 upper). So the illumination inside such a cube would be:
1500 lm /6 m² = 250 lux.
Now let the same light bulb in a chandelier illuminate a square - for ease of calculation - room with a wall length of 4 m. It will be the same cube with an area of 16 square meters on each face, and the total area will be 96 square meters. In this case, for a clean calculation, the light bulb should be suspended in the center of the room at a mark of 2 m from the floor and ceiling. Then the illuminance at each point in the room would be:
1500 lm/96 m² = 15.625 lux.
In practice nobody does this, the maximum suspension length of the chandelier is only 0.5 m. Focusing on visual sensations, a person will feel that the light directly under the lamp is more than in the corners of the room, and best illuminated by a small area on the ceiling at the mounting point of the lamp, provided that its design is open at the top.

In the home, in addition to the luminous intensity, the following factors affect the illuminance of the surface:
- distance to the light source;
- the location of the light source;
- its shape;
- angle of incidence of light (rotation and inclination of bases);
- curvature of the surface itself;
- changes in spatial characteristics;
- reflective properties of the surface (for example, a black velvet surface and mirrors should be illuminated differently).
So in practice theoretical calculations are useless, and a luxmeter is used to measure illuminance.
How to convert lux into lumens
However, if you know the required value of illumination in lux and area of the illuminated surface, you can calculate the required value of luminous flux in lumens. It should be understood that the calculation will be performed with many assumptions, as it is not possible to approximate the conditions of its implementation to the physically ideal. When calculating, it should be assumed that:
- the light source is located in the center;
- illumination is uniform over the whole area, which is practically impossible;
- on the entire surface area the light falls at the same angle;
- the surface is illuminated from inside a mental sphere assumed around the source.
Important! The practical formulation of this problem sounds much simpler: there is a norm of illumination in lux for a particular room, for example, for an office - 300 lux. How many luminaires should be placed to meet it? To do this, you first calculate the required value in lumens. Unavoidable unevenness in illumination can be corrected by additional illumination.
In order to get the value in lumens, you need to multiply the norm in lux by the value of the area needing illumination.
Example: Let's say that an office with the norm of 300 lux has 10 meters long walls and 4 meters high ceilings. You need to calculate the minimum number of lumens required to comply with the standard.
The floor and ceiling area will be: 10 x 10 = 100 m².
The area of each wall: 4 x 10 = 40 m².
Theoretically, assuming uniform illumination and location of the source equidistant from all points on the surface, the problem is solved as follows:
300 lx x (4 x 40 + 100 + 100) m² = 300 x 360 = 108,000 lumens.
If you "translate" this astronomical value into ordinary 100-watt incandescent bulbs, you only need... 72 pieces.
The practical approach would be different. There is no need to light the ceiling at all - the employees' workplaces are downstairs. Moreover, the design of many ceiling fixtures makes it impossible to spread light upwards. So you need to remove the ceiling area from the calculations:
300 lux x 260 m² = 78,000 lm.
Modern LED ceiling luminaires can deliver 5,000 lumens. Accordingly, you will need 16 pieces (78,000/5000) rounded to a whole number.
This number can be reduced. According to SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 the measurement of illumination is carried out over the working surface, as well as in the control points away from the walls and the light apertures on 1 m. It is sufficient to place lighting fixtures over the working places of employees. Mathematically reducing the geometric characteristics of the floor for 1 m on each side, we get:
300 lx x (160 + 64)m² = 300 x 224 = 67200 lm.
Which in ceiling lights would be: 14 pieces, rounded to a whole number.
Lumen values for different lighting fixtures
Modern requirements for lighting fixtures packaging are obliged to bring their technical specifications to the consumer in full. Therefore, finding the value in lumens under the abbreviation "lm" or "lm" will be easy. For example:
- A 100 W incandescent bulb is 1300-1500 lm;
- 60W incandescent light bulb "General Electric" - 660 lm;
- NetHaus" energy-saving lamp, halogen 13W - 250 lm;
- Gauss Elementary LED lamp 12 W "as for 100 W" - 1130 lm;
- Gauss Elementary 6W LED lamp "as for 60W" - 420 lm;
- LED lamp Elektrostandard LTB0201D 60 cm 18V - 1200 lm;
- Maytoni Nastro 15W LED table lamp - 900 lumens;
- TL-ECO office lamp on LEDs 48.5 W - 4530 lm (total luminous flux after all losses).
As you can see from the ratio of luminous flux to the power of the device, LED lighting fixtures are the most economical and efficient on light output.
Warning. Since January 1, 2020, all compact, tubular and industrial fluorescent lamps containing mercury and other hazardous metals have been banned in the Russian Federation, they are not included in the list.
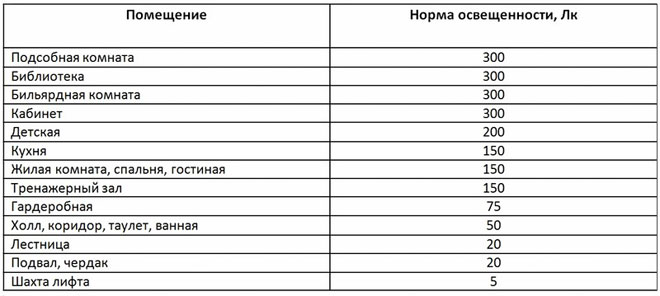
Illumination standards
Sanitary Regulations SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 regulates the average illumination of buildings, structures and institutions of different purposes, as well as lighting of railway stations, roads, crosswalks, parks and stadiums.
Standards for artificial lighting in residential premises are as follows:
- office - 300 lux;
- children's room - 200 lux;
- living rooms and kitchen - 150 lux;
- dressing-room - 75 lux;
- Bathroom and bathroom - 50 lux; the corridor - 50 lux;
- corridor - 50 lux; - corridor - 50 lux; - storage room - 30 lux;
- pantry - 30 lux.
However, in most cases, the illumination of rooms and living areas is selected based on personal preferences of the occupants, and compliance with the norms is carried out only in relation to industrial and working areas.
As a conclusion it is worth remembering the following:
- The numerical value of luminous flux is indicated on the packaging of the lighting product in lumens.
- To get the value of illumination in lux, it must be divided by the value of the area to be illuminated, expressed in square meters.
- There are sanitary standards for the illumination of any type of room.
- The most economical and efficient on light output are LED (light-emitting diode) lamps.