Digital TV has already covered almost the entire territory of the country. New TV sets receive a high-quality digital signal independently, while older TV sets receive it with a special set-top box. What is the difference between the old analog signal and the new digital signal? Many people do not understand this and require clarification.
Contents
Types of signals
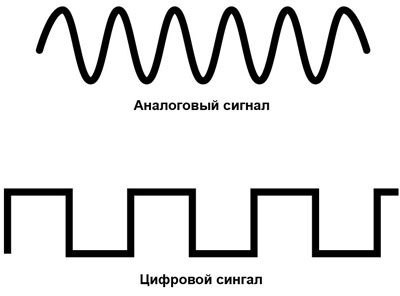
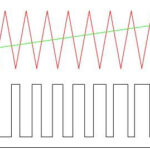
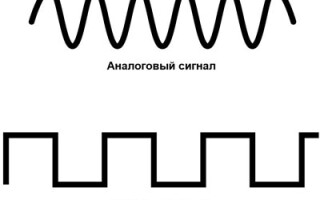
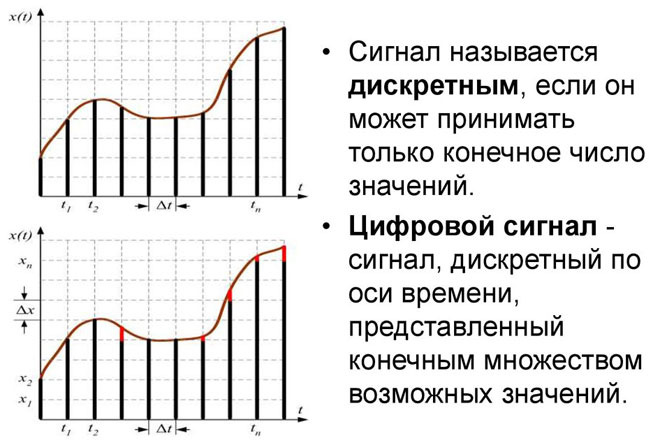
A signal is a change in a physical quantity in time and space. In essence, they are codes for data exchange in information and management environments. Graphically any signal can be represented as a function. From the line on the graph you can determine the type and characteristics of the signal. Analog will look like a continuous curve, digital as a broken rectangular line, jumping from zero to one. Everything we see with our eyes and hear with our ears comes in as an analog signal.
The analog signal
Sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch come to us as analog signals. The brain commands the organs and receives information from them in analog form. In nature, all information is transmitted only that way.
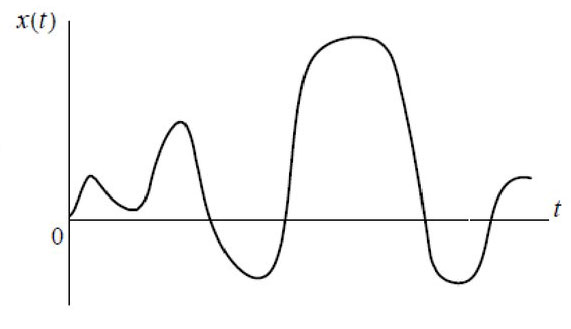
In electronics, the analog signal is based on the transmission of electricity. Certain voltages correspond to the frequency and amplitude of sound, the color and brightness of picture light, and so on. That is, color, sound, or information is analogous to electrical voltage.
For exampleLet's set the transmission of colors with a certain voltage blue 2 V, red 3 V, and green 4 V. By changing the voltage we will get a picture on the screen of the corresponding color.
It does not matter whether the signal is sent by wire or radio. The transmitter continuously sends and the receiver processes the analogue form of information. The receiver converts the voltage into the corresponding sound or color when it receives a continuous electrical signal over the wire or radio signal over the air. The image appears on the screen or the sound is broadcast through the speaker.
Discrete signal
The essence is in the name. Discrete from the Latin discretuswhich means discontinuous (divided). We can say that discrete repeats the amplitude of analog, but the smooth curve turns into a stepped curve. Changing either in time, remaining continuous in magnitude, or in level, not discontinuous in time.
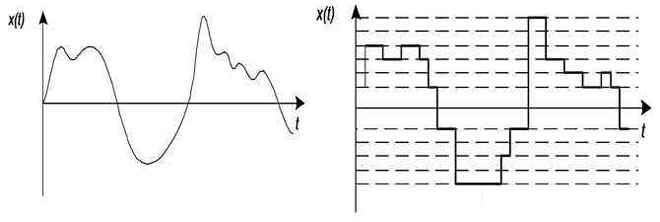
So, at a certain period of time (a millisecond or second, for example) the discrete signal will be of some set value. At the end of this time, it will change sharply up or down and remain so for another millisecond or second. And so it goes on continuously. So discrete is a converted analog. That is halfway to digital.
Digital signal.
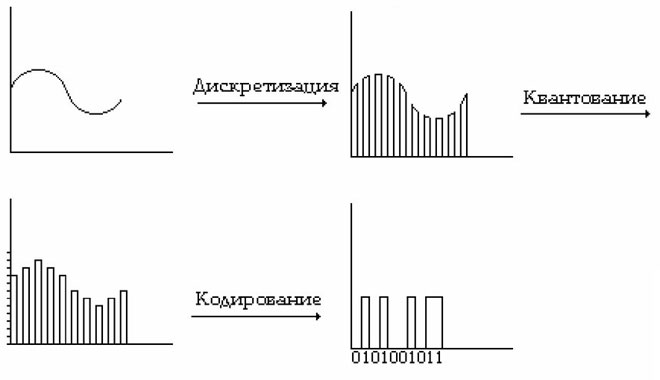
After the discrete, the next step in the conversion of the analog is the digital signal. The main feature is either it's there or it's not. All information is converted into time and magnitude limited signals. Digital data technology signals are encoded by zero and one in different variants. And the basis is a bit, which takes one of these values. A bit comes from the English binarydigit or binary digit.
But one bit has a limited ability to transfer information, so they were combined into blocks. The more bits in one block, the more information it carries. Digital technology uses bits joined into blocks of multiples of 8. An 8-bit block is called a byte. One byte is a small value, but can already store encrypted information about all the letters of the alphabet. However, adding just one bit doubles the number of combinations of zero and one. And if 8 bits make 256 encoding options possible, 16 is 65536. And a kilobyte or 1024 bytes is not a small amount at all.
WARNING! There is no mistake that 1 KB equals 1024 bytes. This is the accepted way in a binary computer environment. But in the world is widely used decimal number system, where kilo is 1000. Therefore, there are also decimal KB equal to 1000 bytes.
In a large number of combined bytes a lot of information is stored, the more combinations of 1 and 0 the more is encoded. So in 5 - 10 MB (5000 - 10000 KB) we have good quality music track data. Go further and in 1000 MB you already have a movie encoded.
But since all information around people is analog, it takes effort and some device to make it digital. For this purpose a DSP (digital signal processor) or DSP (digital signal processor) was created. Every digital device has one. The first ones appeared back in the seventies of the last century. Methods and algorithms change and improve, but the principle remains constant - the conversion of analog data into digital data.

The processing and transmission of a digital signal depends on the characteristics of the processor - the bit rate and the speed. The higher they are, the higher the quality of the signal. The speed is stated in millions of instructions per second (MIPS), and in good processors, it reaches several dozens of MIPS. The speed determines how many ones and zeros the device can "cram" into a second and qualitatively transmit a continuous analog signal curve. This determines the realism of the picture in a TV and the sound from the speakers.
The difference between a digital and a discrete signal
Everyone has probably heard of Morse code. It was invented by the artist Samuel Morse, other innovators improved it, and everyone used it. It is a way of transmitting text where dots and dashes encode letters. In simpler terms, the encoding is called morse code. It has long been used on the telegraph and for transmitting information over the radio. It can also be signaled with a spotlight or flashlight.
The morse code depends only on the sign itself. Not on its duration or volume (strength). No matter how you hit the key (flashlight blink), perceived only two options - a dot and a dash. You can only increase the speed of transmission. Neither the volume, nor the duration are taken into account. The main thing is for the signal to get there.
The same is true for a digital signal. It is important to encode the data with 0 and 1. The recipient only has to make out the combination of zeros and ones. It doesn't matter how loud or how long each signal is. The important thing is to get the zeros and ones. This is the essence of digital technology.
A discrete signal is obtained by encoding the volume (brightness) and duration of each dot and dash, or 0 and 1. In this case there are more encoding options, but also confusion. The volume and duration can be indistinguishable. This is the difference between digital and discrete signals. Digital is generated and perceived unambiguously, discrete with variations.
Comparison of Digital and Analog Signals
The signal of a television or cellular radio station can be transmitted in digital and analog form. For example, sound and image, are analog signals. A microphone and a camera pick up the surrounding reality and convert it into electromagnetic oscillations. The frequency of the oscillation output depends on the frequency of sound and light, and the amplitude of the transmission depends on the volume and brightness.
The image and sound converted into electromagnetic oscillations are propagated into space by the transmitting antenna. In the receiver, the reverse process occurs - electromagnetic oscillations into sound and video.
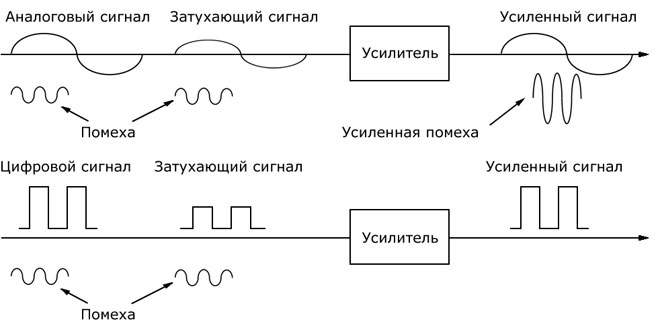
The propagation of electromagnetic vibrations in the air is hindered by clouds, thunderstorms, terrain, industrial electric currents, solar wind and other interference. Frequency and amplitude are often distorted and the signal from transmitter to receiver comes with variations.
The voice and image of the analog signal are reproduced with distortion caused by interference, and the background reproduces hissing, wheezing, and color distortion. The worse the reception is, the more pronounced these extraneous effects become. But if the signal is received, it is at least somewhat visible and audible.
With digital transmission, the image and sound are digitized before broadcasting and reach the receiver without distortion. The influence of extraneous factors is minimal. Sound and color are of good quality or none at all. The signal is guaranteed to reach a certain distance. But long distance transmission requires a number of repeaters. Therefore, to transmit a cellular signal, antennas are placed as close together as possible.
A clear example of the difference between the two types of signals can be a comparison of the old wired telephone and modern cellular communications.
Wired telephony does not always work well even within the same locality. A call to the other end of the country is a test of vocal cords and hearing. You have to shout and listen to the answer. Noises and interference are filtered out with our ears, the missing and distorted words we think up ourselves. Even though the sound is bad, it is there.
The sound in cellular communication is perfectly audible even from the other hemisphere. The digitized signal is transmitted and received without distortion. But it is not without flaws either. If there are glitches, the sound cannot be heard at all. Letters, words and entire phrases drop out. It is good that this is rare.
It's about the same with analog and digital television. Analog uses a signal prone to interference, of limited quality and has already exhausted the possibilities of development. Digital does not distort, provides sound and video of excellent quality, and is constantly being improved.

Advantages and disadvantages of different types of signals
Since its invention, analog signal transmission has been greatly improved. And served for a long time transmitting information, sound and image. Despite many improvements it retained all its disadvantages - noise and distortion in the transmission of information. But the main argument for the transition to another system of data exchange was the ceiling quality of the signal transmitted. Analog cannot hold the volume of modern data.
Improvements in recording and storage methods, especially for video content, have left the analog signal in the past. The only advantage of analog data processing so far is the widespread and cheap availability of the devices. In all other respects, analog is inferior to digital signal.
Examples of digital and analog signal transmission
Digital technology is gradually overtaking analog technology and is already widely used in all areas of life. Often we just don't notice it, but digital is everywhere.
Computing
The first analog computers were created in the 30s of the twentieth century. They were rather primitive devices for specialized tasks. Analog computers appeared in 1940s, and were used widely in 1960s.
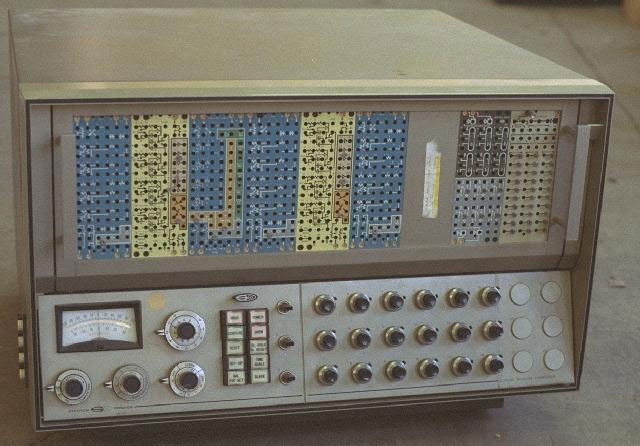

They were constantly improved, but as the amount of information to be processed gradually gave way to digital devices. Analog computers are well suited for automatic control of production processes, because of the immediate response to changes in incoming data. But the speed is low and the amount of data is limited. Therefore, analog signals are only used in some local networks. It is mainly the control and management of production processes. Where the initial information is temperature, humidity, pressure, wind speed and similar data.
In some cases, the help of analog computers is resorted to when solving problems, where the accuracy of data exchange calculations, is not important as for digital electronic calculating machines.
At the beginning of the 21st century the analog signal yielded to the digital technologies. In computing, mixed digital and analog signals are used only for data processing based on some chips.
Sound recording and telephony
Vinyl record and magnetic tape are two prominent representatives of the analog signal for sound reproduction. Both are still in production and are in demand by some connoisseurs. Many musicians believe that only by recording an album on tape can you achieve a lush, real sound. Melomaniacs like to listen to discs with characteristic noises and crackles. Since 1972, tape recorders with digital recording on magnetic tape were produced, but they were not popular due to their high cost and large size. They are only used in professional recording.

Another example of analog and digital signals in sound recording is mixers and sound synthesizers. Digital devices are mostly used, and the use of analog devices is caused by habits and prejudices. It is believed that digital recording has still not achieved that all-encompassing music transmission effect. And it is inherent only in analog signals.
Whereas young people, can't imagine music without MP3 files stored in the memory of phones, flash drives and computers. And online services provide access to their repositories with millions of digital recordings.
Telephony has gone even further. Digital cellular communications have all but superseded wired communications. The latter remained in government agencies, health care institutions and similar organizations. Most can no longer imagine life without a cell and how to be tied to the wire. Cellular communication, the basis of data transmission in which a digital signal reliably connects subscribers around the world.

Electrical measurements
Digital data processing and transmission is firmly rooted in electrical measurements. Electronic oscilloscopes, volt and ammeters, multimeters. All instruments where information is displayed electronically use a digital signal to transmit the measurement. In the home, this is most often encountered in the form of stabilizers and voltage relays. Both devices measure the mains voltage, process and transmit the digital signal to the display.
Increasingly, digital technology is also used to transmit electrical measurement data over long distances. Digital equipment is installed in substations and dispatcher control rooms to monitor the performance of electrical networks. Analog devices are popular only in switchboards, directly at the measuring points.

Another wide application of the digital signal is electricity metering. Households often forget to to look at their meter readings and enter them into a personal cabinet or transmit them to the power supply company. Digital electricity metering systems save you the trouble. The readings go straight into the metering system. Therefore, there is no need for the subscriber to constantly communicate with the supplier, you can sometimes go to a personal office and check the data.
Analog and digital television
Mankind has been living with analog television for many years. Everyone is used to simple and straightforward things. First on the air, then cable a little better quality. A simple antennaand a TV set and a mediocre quality picture. But video recording and storage technology has gone far ahead of the analog signal. And it can no longer fully transmit a modern movie or TV program. Only digital television can provide quality, stability and a good signal level.
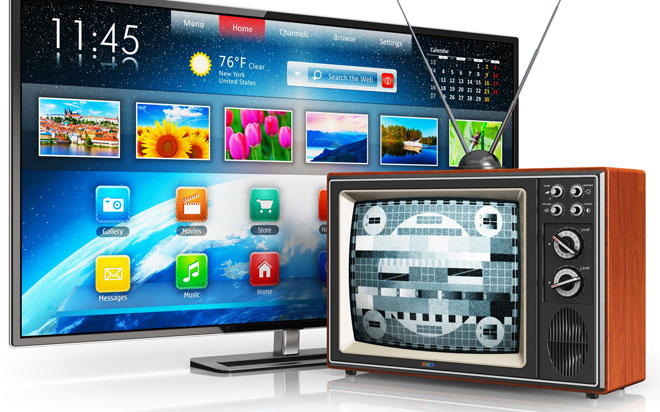

There are so many advantages of digital television. The first and very big advantage is the signal compression. Due to this, the number of available channels has increased. Just improved the quality of video and audio transmission, without that just can not be transmitted to modern TVs with big screens. Along with this came the ability to display information about the broadcast, the next TV program, and so on.
Along with the pluses came a small problem. To receive a digital signal you need a special tuner.
Features of Terrestrial Television
To receive an on-air digital signal you need a T2 tuner, otherwise known as a receiver, decoder or set-top box DVB-T2. Most modern LED TVs are originally equipped with such devices. Therefore, their owners have nothing to worry about. If you turn off analog TV, you only need to reconfigure the channels.
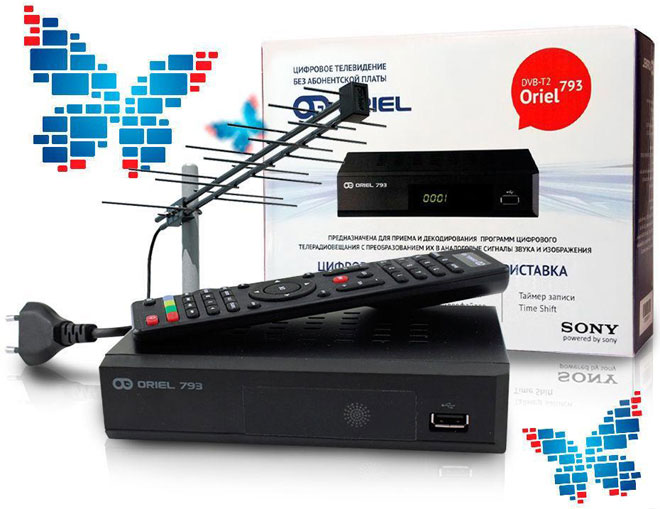

There are no problems for owners of older TVs without a built-in T2 tuner. Here everything is simple. You need to buy a separate DVB-T2 set-top box, which will receive the T2 signal, process it and transmit the ready picture to the screen. The set-top box can be easily Connect the set-top box to any television set.
Digital signal is used in all large areas of life. Television is no exception. Don't be afraid of the new. Most televisions are already equipped with what you need, and for older televisions you need to buy an inexpensive set-top box. Especially since it is easy to configure the device. And the picture and sound quality is better.
Related articles: