In modern equipment often requires a timer, i.e. a device that will not work immediately, but after a period of time, so it is also called a delay relay. The device creates time delays for turning on or off other devices. It is not necessary to buy it in a store, because competently designed homemade time relay will effectively perform its functions.

Contents
Scope of application of the timer
Timer application areas:
- Regulators;
- sensors;
- automatics;
- various mechanisms.
All these devices are divided into 2 classes:
- Cyclic.
- Intermediate.
The first is considered an independent device. It gives a signal after a set time interval. In automatic systems, the cyclic device turns on and off the necessary mechanisms. With its help, the lighting is controlled:
- outdoors;
- in an aquarium;
- in a greenhouse.
Cyclic timer is an indispensable device in the "Smart House" system. It is used to perform the following tasks:
- Turning on and off the heating.
- Reminder of events.
- At a strictly specified time it switches on the necessary devices: washing machine, kettle, light, etc.

In addition to the above, there are other industries in which the cyclic delay relay is operated:
- science;
- medicine;
- robotics.
The intermediate relay is used for discrete circuits and serves as an auxiliary device. It performs automatic interruption of an electric circuit. The scope of application of the intermediate timer time relay begins where signal amplification and galvanic isolation of the electrical circuit are required. Intermediate timers are divided into types depending on the design:
- Pneumatic. Triggering of the relay after the arrival of the signal is not instantaneous, the maximum response time - up to one minute. It is used in the control circuits of machine tools. The timer controls actuators for step adjustments.
- Motorized. The time delay setting range starts with a couple of seconds and ends with tens of hours. Delay relays are part of overhead power line protection circuits.
- Electromagnetic. They are designed for DC circuits. They are used to accelerate and brake an electric drive.
- With clockwork mechanism. The main element is a wound-up spring. Adjustment time - from 0,1 to 20 seconds. They are used in relay protection of overhead power lines.
- Electronic. The principle of operation is based on physical processes (periodic pulses, charge, capacity discharge).
Schematics of various time relays
There are different versions of time relays, the scheme of each type has its own features. Timers can be made by yourself. Before you make a time relay with your own hands, you need to study its device. Schemes of simple time relays:
- on transistors;
- on microcircuits;
- for 220 V output supply.
Let's describe each of them in more detail.
Scheme on transistors
These transistors are the necessary parts:
- Transistor KT 3102 (or KT 315) - 2 pcs.
- Capacitor.
- A 100 kohm resistor (R1). Also 2 more resistors are needed (R2 and R3), which resistance will be chosen together with the capacitor depending on the response time of the timer.
- Button.
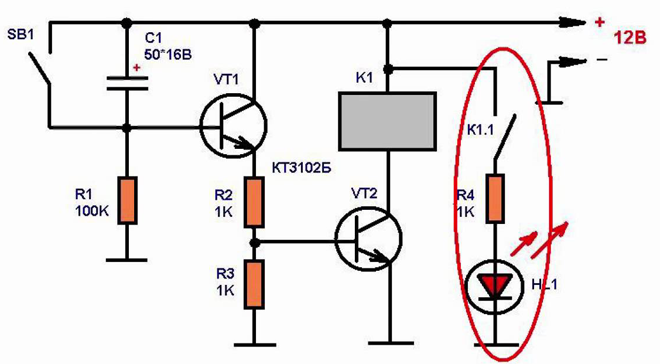
When you connect the circuit to the power supply the capacitor through resistors R2 and R3 and the emitter of the transistor will start to charge. The latter will open, so there will be a voltage drop across the resistor. As a result the second transistor will open, which will trigger the electromagnetic relay.
As the capacitance is charged, the current will decrease. This will cause the emitter current to decrease and the voltage drop across the resistor to a level that will cause the transistors to close and the relay to release. To restart the timer it is necessary to press the button briefly, which will cause a complete discharge of the capacitance.
In order to increase the time delay, the circuit on a field-effect transistor with an isolated gate is used.
IC-based
The use of chips will remove the need to discharge the capacitor and select the ratings of the radio components to set the required response time.
The required electronic components for a 12 volt timing relay
- Resistors rated 100 Ohm, 100 kOhm, 510 kOhm;
- Diode 1N4148;
- Capacitance of 4700 μF and 16 V;
- button;
- TL 431 microcircuit.
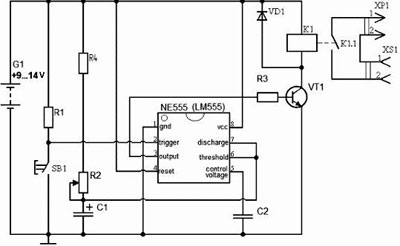
The positive pole of the power supply is to be connected to the pushbutton with one relay contact connected in parallel. The latter is also connected to a 100 Ohm resistor. On the other side the resistor is connected to a 510 and a 100 kOhm resistor. One of the pins of the latter goes to the microcircuit. The second pin of the chip is connected to the 510 kOhm resistor and the third is connected to the diode. A second relay contact is connected to the semiconductor device, which is connected to the executing device. The negative pole of the power supply is connected to a 510 kΩ resistor.
With a 220 V output power supply
The two schemes described above are designed for 12 V, i.e. are not suitable for heavy loads. It is possible to eliminate this disadvantage with the help of a magnetic starter installed at the output.
If the load is a low-power device (household lighting, a fan, a tubular electric heater), you can do without the magnetic starter. The role of the voltage converter will perform a diode bridge and thyristor. Parts needed:
- Diodes designed for a current of more than 1 A and reverse voltage not exceeding 400 V - 4 pcs.
- Thyristor VT 151 - 1 pc.
- Capacity of 470 nF - 1 pc.
- Resistors: 4300 kOhm - 1 pc, 200 Ohm - 1 pc, adjustable 1500 Ohm - 1 pc.
- Switch.
The contact of the diode bridge and the switch is connected to the 220 V power supply. The second contact of the bridge is connected to the switch. A thyristor is connected in parallel to the diode bridge. The thyristor is connected to the diode and the 200 ohm, 1500 ohm resistors. The second leads of the diode and the resistor (200 Ohm) go to the capacitor. In parallel to the last one a 4300 kohm resistor is connected. But it should be remembered that this device is not used for heavy loads.
Related articles:






