One of the key concepts in the field of electricity is selectivity. It is no secret that the safety of electrical networks is extremely important, and you can provide it in different ways. Selectivity - is a special function of relay protection, which avoids breakdowns and increases the service life of devices.
Contents
General concept of selectivity
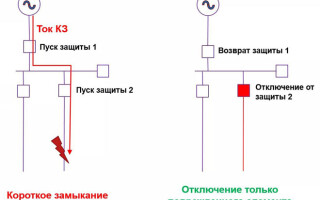
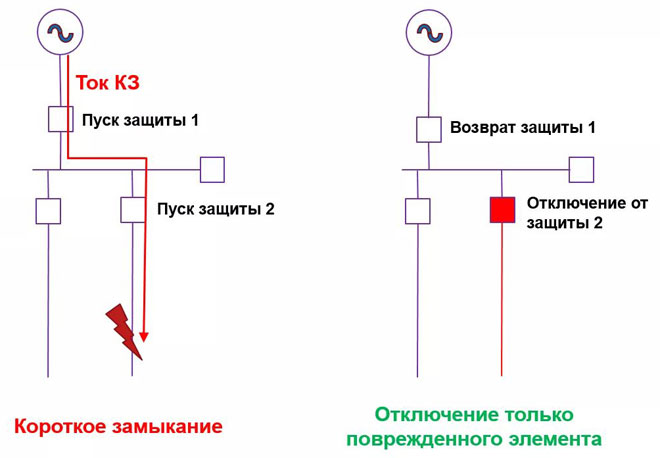
As already mentioned, the selectivity is understood as a feature of relay protection. It is defined by the ability to discover the faulty element in the whole power network and disconnect the faulty section rather than the whole system.
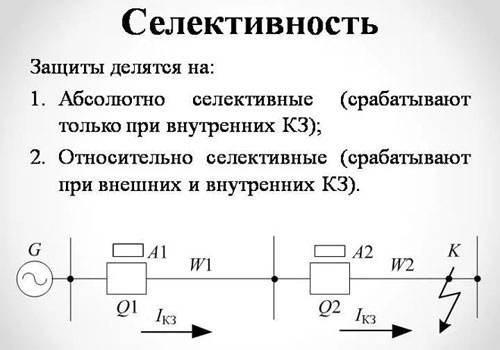
Selective protection can be absolute and relative.
- Absolute protection implies that the fuses are activated precisely in the section of the network where the short circuit or breakdown occurred.
- The relative selectivity causes the tripping of circuit breakers that are also near the point of failure, if the protection in those sections has not tripped.
Main functions
The key tasks of the selective protection are to ensure uninterrupted functioning of the electrical system and to prevent mechanisms from burning down when there are threats. The only prerequisite for the correct operation of this type of protection is considered to be the consistency of protection units among themselves.
As soon as an emergency situation occurs, the faulty section is instantly detected by the selective protection and disconnected. At the same time, serviceable places continue to work, and the disconnected ones do not interfere with them in any way. The selectivity significantly reduces the load on the electrical installations.
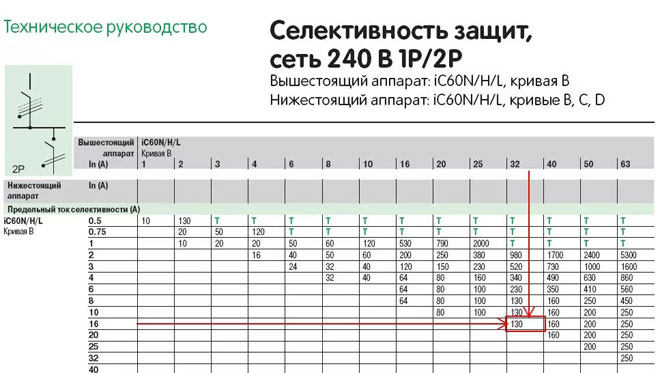
The basic principle of this type of protection is to equip circuit breakers with a rated current that is less than that of the device on the input. Together they can exceed the rating of the group circuit breaker, but individually - never. For example, if a 50 amp bushing is installed, the next unit should not have a rating greater than 40 amps. The unit closest to the point of emergency will always trip first.
ATTENTION! The choice of circuit breakers, including those for protection with absolute selectivity, depends on their rating and tripping characteristics, which are marked B, C and D. Often the devices that protect the electrical system are different types of circuit breakers, fuses, RCDS ..
Thus, the main functions of selective protection can include:
- ensuring the safety of electrical appliances and workers;
- rapid identification and disconnection of the area of the electrical system where the breakdown occurred (and the working areas do not stop functioning);
- reduction of negative consequences for working parts of electromechanisms;
- reduction of load on component mechanisms, prevention of breakdowns in the faulty zone;
- guaranteeing a continuous work process and a constant high level of power supply.
- supporting the optimal operation of this or that installation.
Types of selective protection
Total and partial
Full protection is designed to connect devices in series. In case of an accident, the protection unit that is closest to the point of failure will be triggered as quickly as possible. Partial selective protection is much like full protection, but operates only up to a certain value of current.
Temporal and time-current selectivity
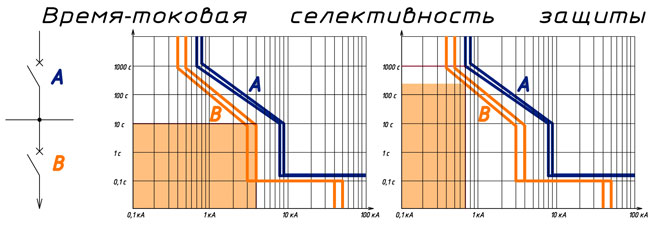
Temporal selectivity is when devices connected in series have identical current characteristics and a different trip time delay (when increasing in series from the problem area to the power source). Temporal protection is used so that the circuit breakers can back each other up in case of failure. For example, the first one should work after 0.1 second, if it is faulty, after 0.5 seconds the second one will start, and if necessary the third one will work after 1 second.
Time-current selectivity is considered the most complex. It uses the equipment of 4 groups - A, B, C and D. Each of them has a personal reaction to the electric current and disconnection at the necessary moment. The best protection is achieved in group A, which is used mainly for electric circuits. The most popular type of units is C, but experts do not advise installing them everywhere and ill-considered.
Current selectivity
This variety is similar in method to the temporary, but the difference is that the main criterion is the limit value of the current mark. The current values are lined up in descending order from the power source to the load objects.
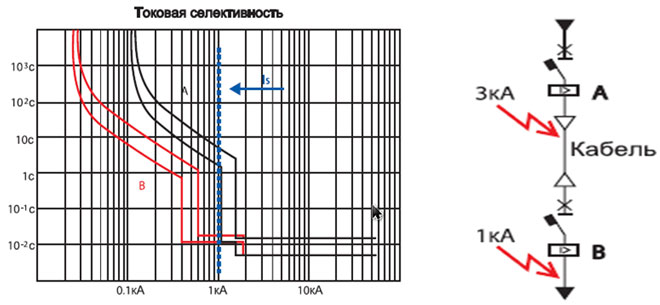
If a short circuit occurs near circuit breaker A, the B end protection must not operate and the circuit breaker itself must remove the voltage from the device. For current selectivity to guarantee total selectivity, it is necessary to have a high resistance between both circuit breakers. It is obtained by means of:
- An extended power line;
- The insertion of a transformer winding;
- the insertion of a smaller cross-section wire in the gap.
Power
This scheme involves the rapid selectivity of auto-switches. In this case Short-circuit currents (short-circuit currents) do not have the possibility of reaching their maximum values.
These "rapid-fire" circuit breakers operate for literally a couple of milliseconds. Due to the high dynamism of the loads, it is extremely difficult to agree on the real time-current parameters of the protections.
The average user has no way to trace the characteristics of this type of selectivity. The manufacturer is obliged to provide them in the form of graphs and tables.
Zone selectivity
Such schemes are often used in industrial facilities. This is not only a very complex, but also an extremely expensive way of protection. To apply zone selectivity you need to buy special tracking devices.
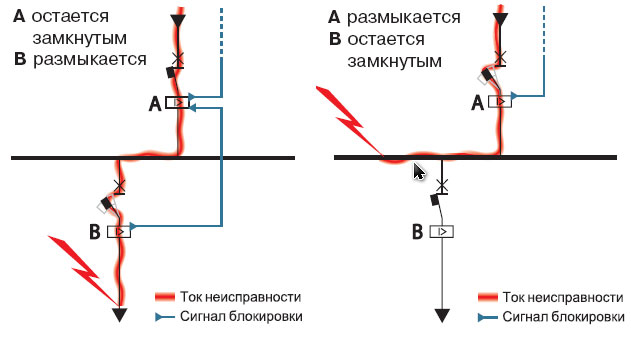
All the data obtained during the operation of the devices are concentrated in the control center. It determines which circuit breaker should be activated for tripping.
In these devices, electronic release units are used. Their scheme of operation is as follows: when an emergency occurs, the lower device sends a signal to the one above. If after 1 second the lower device has not tripped, the second device takes over.
Calculation of the selectivity of circuit breakers
Protection devices are in most cases not some tricky devices, but the standard and well known circuit breakers. In order to ensure correct selectivity, you just need to choose the right parameter settings. The operation of such units is based on the following condition:
Ic.o.last ≥ Kn.o.* I k.pred, where:
- Ic.o.lest - current at which the protection begins to operate;
- I k.pred. - short-circuit current at the end of the protection zone;
- Kn.o. - reliability coefficient, which depends on a number of settings.
To calculate the selectivity for time-controlled devices, you can use the following scheme:
tc.o.last ≥ tc.pre.+ ∆t, where:
- tc.o.last and tc.pre. - are the time intervals at which the circuit breakers trip in order of proximity to the power supply;
- ∆t is the time step of selectivity.
Selectivity map
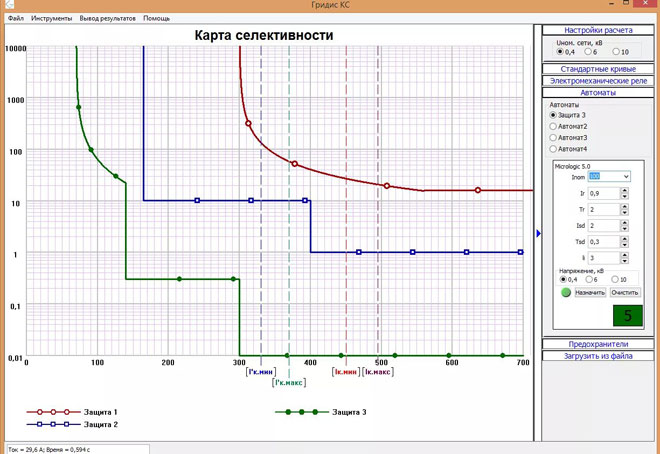
In order to provide the highest level of protection for circuit breakers, a selectivity map or a visual representation thereof is required. The map is a kind of chart that shows all the sets of current parameters in the power grid.
To create a correct selectivity map, the following points must be adhered to:
- electrical installations must be connected to a single power source;
- It is necessary to choose the scale correctly so that all the calculated points can be accommodated on it;
- in addition to the qualities of the circuit breakers, the maximum and minimum values of short-circuit in the points of the system should be indicated.
The parameters of the units are mapped in turn, which is determined by the order in which they are connected. In order to build the schemes correctly, it is necessary to apply the axes with the key values. A properly drawn map is the key to easy comparison of the parameters of protection devices and the overall selectivity.
PAY ATTENTION! To make a map faster, it is worth using a special program. It can be easily found on the "World Wide Web".
Conclusion
Often, current or time selectivity is used in domestic power grids. The best way to do this is to install a series of RCD installationwhere there is one common circuit breaker and several more are located on the loop. Selective protection contributes to the correct and uninterrupted functioning of the equipment.
Related articles: