A residual current device (RCD) prevents fires due to electrical leakage and also reduces the risk of electric shock. This device is popular for both apartment and private home installations. And RCD for an apartment built with modern technology is a must.

Contents
Designation of RCDs and principle of operation
It is important to understand that this device protects against excessive current, not against overvoltage and short-circuits. At the same time, a circuit breaker protects the electrical system in your home, and a circuit breaker can ensure that the risk of electrocution is reduced.
The RCD is not designed for short-circuit protection, so it is imperative that you connect a circuit breaker to it. Before you decide which RCD to choose, you need to know its design and principle of operation.
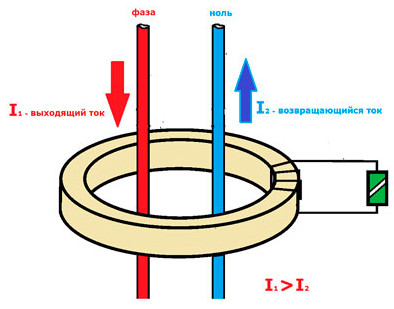
Inside the case there are several coils. One coil is connected to the phase, the other to the neutral wire. Current passing through the coils creates magnetic fields. Since they are directed in opposite directions, they destroy each other. If the current flowing through one of the coils is stronger than it should be, an excessive field is formed which directs it to the third coil. When the third coil starts to work, the RCD protection triggers as intended and shuts off the electricity in that area of the house.
Based on the principle of operation of the device, the question of how to choose the right RCD for the house and apartment is decided.
The main characteristics of the device
In order to determine which RCD is the best, when buying it, it is necessary to consider all the parameters and technical characteristics.
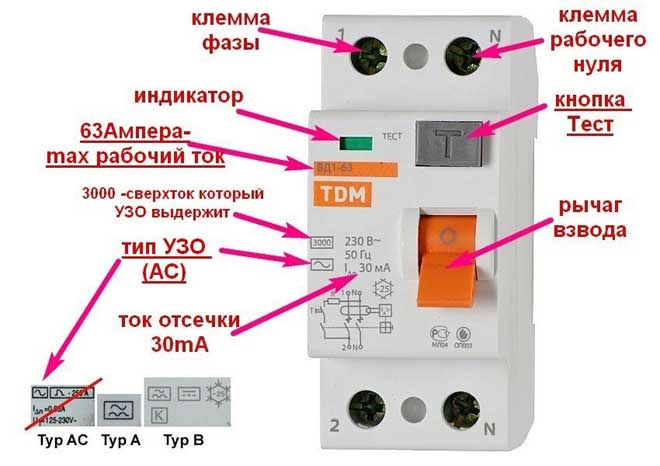
After the information about the manufacturer and the brand name, the case is marked with data about the performance characteristics and ratings, such as:
- Name and series. The word "RCD" does not necessarily have to appear in the inscription, many manufacturers call it "RTD" (differential current circuit breaker).
- The value of the rated voltage. It should be single-phase (220 V) or three-phase (330 V) at a standard frequency of 50 Hz. If the device is chosen for a private home, then take the one that is designed for three-phase voltage.
- Rated operating current is the maximum value that the protective device is able to handle. There are devices for 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80 and 100A.
- The rated differential current is the leakage value at which the protection trips and automatically shuts off the power. This value can be 6 mA, 10 mA, 30 mA, 100 mA, 300 mA and 500 mA.
There is a marking on the body, which tells about the additional characteristics:
- The rated rated short-circuit current value is the maximum short-circuit current at which the RCD can continue to function normally, provided an autoswitch is installed in addition to it.
- Tripping time of protection. This is the time interval from the occurrence of the leakage until it is eliminated, during which the protection trips. The maximum value is 0.03 s.
- Obligatory scheme of the device.
How to choose RCDs by parameters
RCDs should be selected by paying attention to its rated and differential tripping current.
The rated current is the current for which the power contacts are designed to work. In the case of its increase, they can fail. The differential is the tripping current of the circuit breaker, that is, the leakage.
Before choosing a RCD, it is useful to know its price, quality and performance and compare these three parameters. Since it may be difficult for non-professionals to choose RCDs in terms of power and quality, experts advise to make a table of parameters of favorite devices and use it to choose the device with the best characteristics.
Rated current
When selecting according to the rated current, you should know that the device is always put in series with a circuit breaker to protect the power contacts from overload and short-circuit. If one or the other occurs, the device will not trip because it is not designed to do so. Therefore, it must be protected by a circuit breaker.
The next thing to look at: the rated current must be at least the same as the rating of the breaker, or better yet, be one step higher.
Differential current
There are two important things to remember:
- For electrical safety purposes, always choose a differential tripping current of either 10 mA or 30 mA. For example, one electrical appliance can be supplied with a 10 mA RCD. At the entrance to the house, a device with this value may trip too often, because the electrical wiring in the apartment has its own leakage limits.
- All other RCDs, which have a differential current above 30 mA, are used for fire purposes. But if you install a 100 mA RCD at the input, a 30 mA RCD should be installed in series with it for electrical safety purposes. In such a case, it would be wise to install a selective RCD at the inlet so that it will trip with a short time delay and allow a device with a lower rated current to operate.
Product type
All of these devices are classified into 3 types based on the form of current leakage:
- AC type device. This device is common because of its more affordable price. It triggers only when a sinusoidal current leakage occurs.
- Type "A" device. Designed to trip when an overcurrent is instantaneous or gradual, which has a variable sinusoidal and pulsating constant form. This is the most demanded type, but it is characterized by higher cost due to the ability to control both direct and alternating current.
- Type "B" device. Most often used to protect industrial premises. In addition to triggering to sine and pulsating waveforms, it also responds to the rectified form of constant leakage.
In addition to these basic three types, there are 2 more:
- Type "S" selective device. Turns off not immediately, but after a set interval of time.
- Type "G". The principle is the same as the previous one, but there the time delay for tripping is slightly shorter.

Design
By design, there are 2 types of RCDs:
- electronic - operating from an external network;
- Electromechanical - not dependent on the network, for its operation does not need power supply.
Manufacturer
An equally important criterion is the choice according to the manufacturer. It is up to the buyer to decide which RCD company to choose. The following options are recommended:
- Legrand;
- ABB;
- AEG;
- Siemens;
- Schneider Electric;
- DEKraft.
Among the budget models, the highest quality is at Astro-UZO and DEK.
Related articles:






