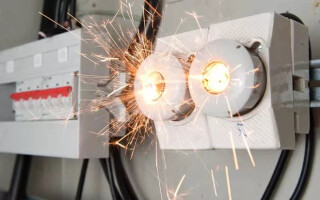
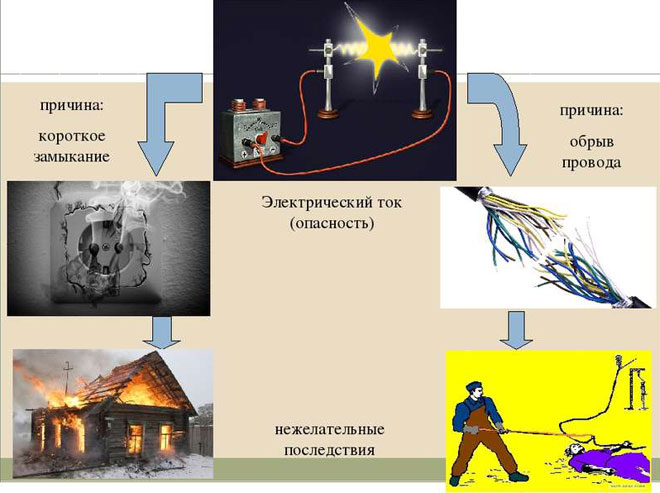
A short-circuit current is a rising electrical impulse of the shock type. It can cause wires to melt and some electrical devices to malfunction.
Contents
Why does a short circuit occur?
Short circuit currents occur in the following cases:
- When the voltage level is high. A sudden spike occurs, the voltage level begins to exceed the allowable limits, there is a possibility of electrical breakdown of the insulating coating of the conductor or circuitry of the electrical type. Current leakage occurs and arc temperature rises. The short-circuit voltage creates a short-term arc fault.
- When the insulation coating is old. This short circuit occurs in residential and industrial buildings where the wiring has not been replaced. Any insulation coating has a life expectancy that is depleted over time by environmental factors. Failure to replace the insulation in a timely manner can cause a short circuit.
- When exposed to external mechanical influences. Grinding the protective sheath of a wire or removing its insulation coating or damaging the wiring will result in fire and short-circuits.
- If foreign matter enters the circuit. Dust, debris or other small objects on the wiring harness may cause a short circuit in the mechanism.
- When lightning strikes. The voltage level rises and the insulation coating of the wire or circuit is punctured, causing a short in the circuit.
Why are short circuits called short circuits?
Let's look at the definition of a short circuit, which stands for short circuit. It is the joining of any 2 points (having different potentials) that are in an electrical circuit. The connection is not provided by the normal operation of the circuit, which leads to critical currents at the point where these points are combined.
Such a short circuit is called a short circuit because it is formed by bypassing the device, i.e. by taking a shortcut.
In simple terms: the positive and negative conductor are connected (short circuit), which causes the resistance value to become 0. Resistance is necessary for the normal functioning of the mechanism, and its absence causes a failure in the voltage source, which leads to a short circuit.
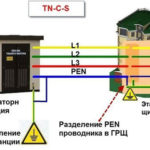
A short circuit is any connection of conductors of different potentials to each other or to ground. A short circuit occurs only if such a connection is not planned by the design of the appliance or machine in question. For example, the connection between any points of different phases or the union of a phase and 0, when a destructive current that exceeds all critical values of the electrical circuit of the device is formed.
What are the dangers?
The consequences of a short circuit can be as follows:
- The voltage level in the electrical circuit drops. This can lead to failure and burning of the electrical device or malfunctioning of the device.
- Damage of mechanical and thermal type: circuit breakage, damage to wiring or individual wires, sockets and switches.
- Depending on the power of the short circuit, the wiring and nearby materials and objects may catch fire.
- Destructive electromagnetic effect on telephone lines, computers, televisions and other electrical appliances.
- Danger to life. If a person is near the source of the short circuit at the moment the short circuit occurs, he or she may get burned.
- The functioning of the electrical supplying systems is disturbed.
- Depending on the parameters of the short circuit, malfunctions of underground utilities are possible in the electromagnetic effect.
Many people are interested in the question of how to calculate how much current is equal in a short circuit. To do this, use Ohm's law: the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage at its ends and inversely proportional to the total resistance of the circuit.
Calculation of short-circuit is carried out according to the formula: I= U/R (I - current, U - voltage, R - resistance).
Types of short circuits and their causes
There are such types of short circuits as:
- Single-phase short circuits. A fault on power lines when 1 of the phases of an electrical system is shorted to ground or to an element that is connected to ground. The fault may be caused by improper grounding.
- Two-Phase Short Circuit. A type of fault that occurs between 2 phases with different potentials in a power circuit. Caused by a wire insulation failure. It can also be the simultaneous connection of 2 phases, not with each other, but to earth.
- Three phase short circuits (symmetrical). Short circuit of 3 phases to each other. This can be caused by mechanical damage to the insulation coating, by overheating and breakdown in the insulation, or by wires getting stuck together.
- Inter-twist. This type of short circuit is typical for electric machines. In this case, the turns of the stator winding mechanism, transformer or rotor device are shorted with each other.
- Short-circuiting to the metal body of an appliance or system. Such a short circuit occurs when the wiring insulation on the metal case is broken.
Short Circuit Protection Options
As a protection against the occurrence of a short circuit, you can use:
- Electrical type reactors that will limit the current;
- paralleling the electrical circuit;
- Disconnection of sectional circuit breakers;
- transformers of step-down type with low-voltage split winding;
- fast-acting switching devices that have the option of limiting current flow;
- fusible safety elements;
- installation of circuit breakers;
- timely replacement of the insulation coating of wires and regular inspection of wiring for defects;
- Relay protection devices that will shut down damaged portions of the circuit.
Circuit breakers can only be installed on the entire system, not on individual phases and the neutral circuit. Otherwise, during a short circuit, the neutral circuit breaker will fail and the entire electrical system will be energized because the phase circuit breaker will be energized. For the same reason, it is not recommended to install a wire with a smaller cross-section than the circuit breaker can allow.
The use of this phenomenon
This phenomenon has found its application in arc welding, the principle of which is based on the interaction of the rod with the metal surface. The surface is heated to the melting temperature, due to which a new strong connection appears, i.e. The welding electrode is short-circuited to the ground.
Such short-circuit modes operate for a short period of time. At the moment of welding, a non-standard current charge occurs at the junction of the rod and the surface, due to which a large amount of heat is released. It is enough to melt the metal and create a welding seam.
Short circuit is also used in the field of industrial automation, it is used to create information systems that reflect the parameters of current signal transmission.
Useful short circuit is used in electrodynamic sensors. For example, in induction vibrometers, seismic receivers. Short-circuit provides an opportunity to further reduce the number of oscillations of the moving system.
Short-circuit mode can be used when combining cascades in electronics, when the output of the first active component operates in short-circuit mode.
Related articles: