Circuit breakers (RCD) - is an electrical current protection apparatus responding to leakage currents (differential currents). Leakage currents are defined as fault currents flowing between the mains conductors and "ground". Depending on the magnitude of the differential current, a circuit with a RCD can prevent a person from being struck by electricity or prevent a fire from occurring due to faults in the wiring.

Contents
Wiring diagrams for RCDs in single-phase networks
Industry produces circuit breakers designed to work in a single-phase or three-phase network. Single-phase devices have 2 poles, three-phase - 4. In contrast to circuit breakers, neutral conductors must be connected to the disconnecting devices in addition to the phase conductors. The terminals to which the neutral conductors are connected are designated by the Latin letter N.
To protect people from electric shock, the most commonly used RCDs react to 30 mA leakage currents. In damp rooms, basements, children's rooms, devices set to 10 mA are used. Disconnecting devices designed to prevent fires have a trip threshold of 100 mA and above.
In addition to the threshold, the protective device is characterized by the rated switching capacity. This term refers to the maximum current that the disconnecting device can withstand for an unlimited amount of time.
An important prerequisite for the reliable operation of residual current protection is the earthing of the metal housings of electrical apparatus. Earthing of the TN can be made by a separate wire or via the earthing contact of the mains socket outlet.
In practice, there are two ways of incorporating RCDs into an electrical circuit:
- RCD connection scheme with individual protection;
- Circuit of the group protection of consumers.
The first method is most often used for the protection of high-power consumers. It can be applied to electric stoves, washing machines, air conditioners, electric heating boilers or water heaters.
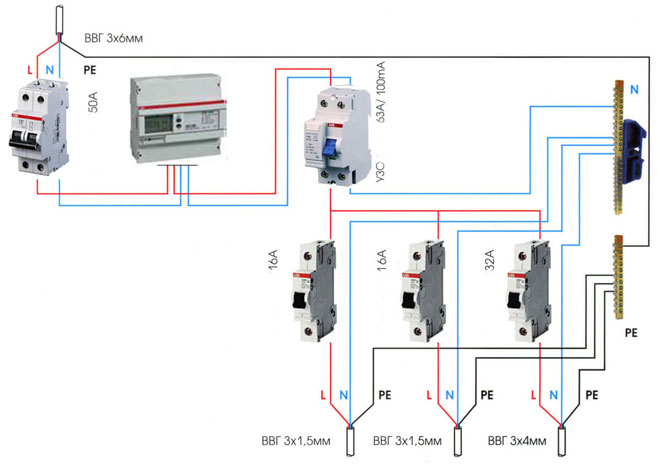
Individual protection involves simultaneous connection of a RCD and a circuit breaker, the scheme is a serial connection of two protective devices. They can be placed in a separate box in the vicinity of the electrical receiver. Selection of the tripping device is based on the rated and differential currents. It is best if the rated breaking capacity of the protective device is one step higher than that of the circuit breaker.
For group protection, a group of circuit breakers supplying different loads is connected to the RCD. In this case, the circuit breakers are connected to the output of the residual current device. Connecting RCDs in a group arrangement reduces costs and saves space in distribution boards.
In a single-phase network, the connection of one RCD for several consumers requires the calculation of the rated current of the protective device. Its load capacity must be equal or greater than the sum of the ratings of the connected circuit breakers. The choice of the trip threshold of the differential protection is determined by its purpose and the hazard category of the premises. The protective apparatus can be connected in the switchboard in the staircase or in the switchboard inside the apartment.
The wiring diagram of RCDs and circuit breakers in the apartment, individual or group, must comply with the requirements of the Electrical Installations Code (Rules for Electrical Installations). The rules unambiguously prescribe earthing of electrical installations protected by RCDs. Failure to comply with this condition is a gross violation and can lead to negative consequences.
Wiring diagrams for RCDs in three-phase networks
Urban dwellings are usually powered by a three-wire single-phase network. The previous section described how to connect a RCD in an apartment.
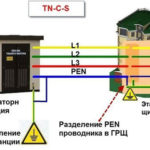
Suburban houses and homeowners often consume much more electricity. They are often connected to a three-phase network. Electric heating boilers, powerful water heaters for hot water can be used in a country house. In the outbuildings are often organized workshops, equipped with machine tools for various purposes.
Many powerful loads are designed for 380 V. They must be powered by wiring that consists of five conductors - three phase conductors, a neutral conductor and a protective earth conductor. Many locations use obsolete four-wire systems that do not have a separate grounding conductor. In this case, in order to use a three-phase RCD, the owners have to make their own grounding loop and lay the grounding network.
If earthing is present, the installation of RCDs in a three-phase network is no different from the connection of single-phase protective earthing devices. Wiring diagrams and criteria for selecting protection devices remain the same.
In case there is a power value of the three-phase load supplied from the network of 380 V, the rated current can be calculated by the formula:
I = P /1,73 U,
where I - rated current; P - power of three-phase load; U - voltage of three-phase network.
Mistakes in the connection of RCDs
Beginner electricians and home craftsmen often do not know how to connect RCDs and circuit breakers. When connecting differential current protective devices, the following rules must be strictly followed:
- RCDs must be connected in series with circuit breakers;
- The electrical equipment to be protected must be earthed.
Despite the simplicity of the rules, repeated mistakes are common. Many craftsmen believe that disconnecting devices must be triggered when a person touches parts of electrical equipment that have been energized as a result of an insulation fault. This is a misconception. It is not the touch of a person that triggers the protection, but the moment the insulation is broken. Therefore, protective earthing is used in conjunction with RCDs.
The second common and dangerous mistake is the use of "grounding". In this case, the neutral conductor is connected to the body of the electrical equipment to be protected. This arrangement is dangerous because if the neutral conductor breaks, there is a possibility of a phase on the equipment being protected.
Another common mistake is to connect neutral conductors supplied by different protective devices. Such a connection necessarily leads to the occurrence of leakage currents and tripping of protection devices.
Installing RCDs
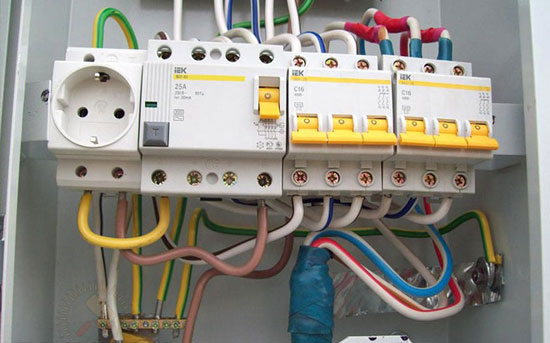
Deciding how to connect a RCD or circuit breaker rarely causes difficulties. Modern protection devices are available in standard modular enclosures and are mounted on a DIN rail. They are equipped with convenient latches for mounting on the rail. To connect the conductors they use screw terminals or spring clips that allow screwless installation.
Manufacturers offer switchboards for DIN-rail indoor and outdoor installation. Such devices have an aesthetic appearance and allow quick installation in a city apartment and in an individual private house.
Related articles: