If you paid attention to this article, you probably wondered not long ago - "What is RCDs and what is their purpose?" We will try to answer this question in as much detail as possible. Well, first of all, let's say that the abbreviation RCD stands for disconnecting device.

Contents
What is a RCD in electricity
Despite the fact that these days, electrical wiring is as protected as possible from human contact and the unfortunate consequences, there is no escaping from leaks. Here is where the RCD will be an indispensable assistant. The device will instantly react to the increased current value in the leakage point and cut off the power supply.
RCD - is one of the main "cogs" in the protective automatics of today's electrical networks. The device switches electrical circuits and protects them from currents that flow through unwanted conductive paths under standard conditions. This will increase the chances that your home or business will be protected from fires and no one will be injured by a current discharge.
Note that this apparatus has the function of switching circuits on or off. In other words, it can make their switching. Accordingly, the device is a switching device.
Why install RCDs
Many consumers have heard about the existence of such a miracle apparatus as RCD, but not everyone knows what it is needed for. It is possible to understand the general principles of operation of the unit even without having a deep knowledge of electricity. Until recently, RCDs were not used in homes. But these days, things have changed, and now devices are increasingly common in apartments, so it is worth learning more about them.

As previously mentioned, RCDs are installed to prevent current leaks that lead to wiring fires and fires. In addition, the RCD will protect you from electric shock, which can lead to significant health problems or, God forbid, death if you come into contact with uninsulated wires and conductive sections of electrical equipment.
CAUTION! RCD is different from the circuit breakers that protect the wiring from overloads and short circuits, its purpose is to significantly improve the protection of people.
Operating Principle of RCDs
The functioning of the device is based on fixing the leakage current to "ground" and disconnecting the power grid in case of such an emergency. The presence of the leakage device registers only the difference between the currents that left the device and those that came back.
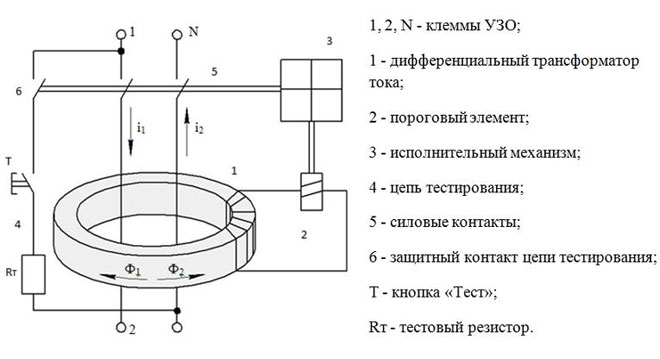
If there is nothing wrong with the power grid, the currents are identical in magnitude, but different in direction. As soon as a leakage occurs - for example, if you touch a 100% uninsulated wire - some of the current goes to ground through another circuit (in this case through the human body). As a result, the current returning to the RCD through the neutral will be less than the current going out.
The same happens if one of the electrical appliances has damaged its insulation. Then the case or another part is energized. By touching them, a person creates another circuit "to ground". In this case, some of the current will move through it, that is, the balance will be destroyed.
Of course, if the insulation is damaged, the branch circuit can also appear without the participation of the human body. In this situation, the device will also respond 100% and save the network section from unfortunate consequences like overheating and fire.
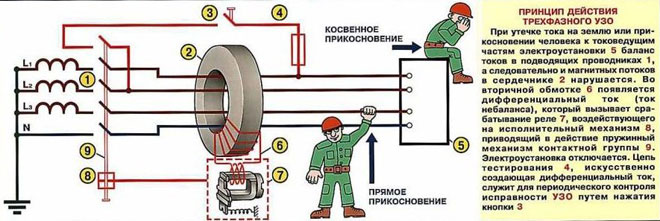
When is it necessary to install a RCD?
The device is indicated for installation when there is a need to protect group lines supplying power to plug-type receptacles for portable electrical appliances. A RCD must be installed if the circuit breaker or fuse does not provide an autoswitching time of 0.4 seconds with a rated voltage of 220 V because of the small currents short-circuit currents.
TAKE NOTE! We recommend the use of differential circuit breakerwhich is a single RCD device with an autoswitch that reliably protects against overcurrent and leakage.
In addition, it is recommended to install a RCD if you have people in your family who "like" to handle electrical wiring carelessly. The simplest case is when a person drills into a wall while leaning barefoot on a radiator and touches the phase wire. It flies through the chain "metal body of the drill - arm - chest - leg - battery" and leads to terrible consequences: paralysis of the heart or respiratory failure (sometimes all together). If you have a RCD installed, it will instantly "know" that some of the current has not returned, and immediately cut off the power. Yes, an electric shock will occur, but the discharge will be minimal.
When will the RCD not help?
However, you should not consider the RCD a panacea for all electrical problems. The device is not smart enough to understand exactly what is included in the electrical circuit - a light bulb or a person. It will only trip if there is a leak.
RCD does not save from overvoltage, including pulsed, as well as from low voltage, which "kills" electric motors - in the refrigerator, washing machine and so on.
The unit also does not protect against short circuits. This task is performed by a circuit breaker or circuit breaker or a residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) does this job..
How many RCDs do I need to install?
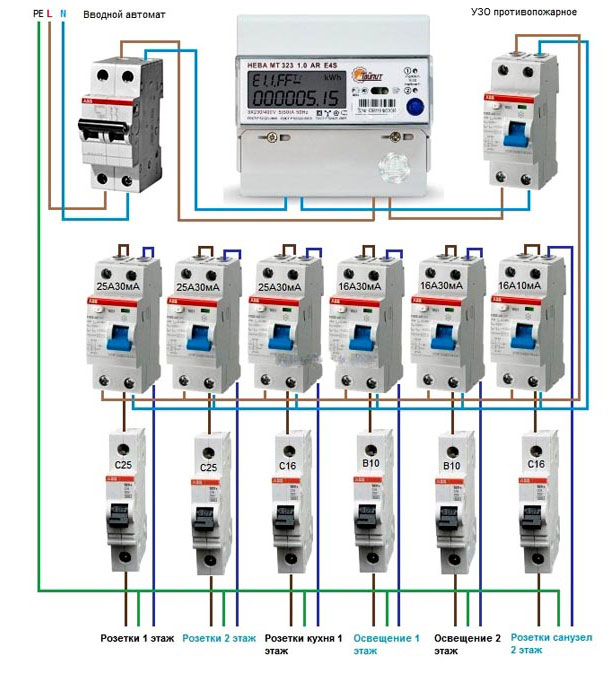
To determine the exact number of RCDs required for a particular room, you will need an expert who can make the appropriate calculations. For example, in a one-room apartment, most likely, one such device designed for a leakage current of 30 mA will be enough. But a four-room apartment with 15 groups of outlets will need at least five RCDs, as well as one device for each lighting group, electric stove and water heater.
It is usually assumed that one group of electrical appliances - a protective device 30 mA plus one fire RCD 100 or 300 mA.
NOTE! To control the wiring as a whole, at the entrance to a private home is recommended to install one general RCD with a rated breaking current of 300 mA in addition to the calculated.
When it is not advisable to install a RCD?
Sometimes it simply does not make sense to install the device. One such situation is the presence of old and decrepit wiring. The RCD's ability to detect leaks can be a headache if the device starts to trip unpredictably (Which is what happens with bad wiring). In this case, the best solution would be to put RCDs not in the electrical circuit of the apartment as a whole, but in places where there is a high risk for the use of outlets.

There is also no point in buying a low-quality RCD. In today's market you can find not only original devices, but also the widest range of fakes of unknown origin. Many of these devices are made "at the knee around the corner". The use of such devices is absolutely inadmissible and unreasonable. Before buying, carefully study the technical documentation and quality certificates of the unit to be purchased.
It makes no sense to install the device in lines that provide voltage to stationary equipment and fixtures, as well as in the general power grid.
Device
The design of the RCD implies the presence of:
- leakage sensor;
- Polarized magnetic relay.
The operation of the device is based on laws based on incoming and outgoing electricity in closed circuits with extremely large loads. This indicates that the current should have only one value, regardless of the phase of passage.
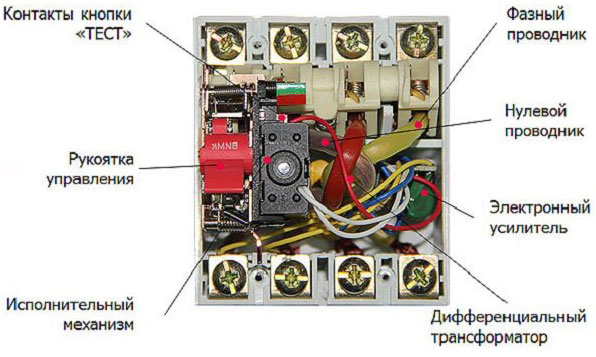
There are three magnetic coils inside the device. Phase passes through the first and zero through the second. The current creates magnetic fields at the input and output of the coils of the device.
If everything works as it should, the mutual fields cancel each other out. If one of the coils is out of balance, that is, a current leak forms, it will cause the third coil to act, which has a relay to cut off the power.
The main technical characteristics are
Each RCD has a specific set of technical parameters that should be studied before purchase:
- manufacturer;
- model name;
- operating current - the current limit that the device can commutate;
- mains parameters (voltage and frequency);
- Leakage current - the maximum leakage current to which the RCD reacts
- RCD type;
- operating temperature range;
- rated rated short-circuit current;
- RCD device scheme.
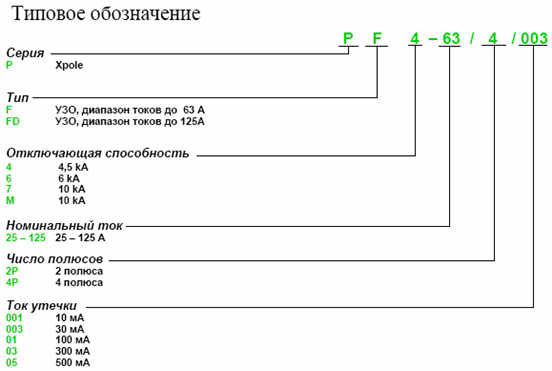
Marking deciphering
The marking is applied to the case of RCDs, which makes the choice of the right model more convenient and easy. First of all, the manufacturer is indicated, but there is also other important information:
- "RCD" or "RCD" - means that it is a ground fault interrupter;
- 16А - the maximum current for which the contacts of the product and other internal elements are designed;
- In 30mA - is the leakage current at which the RCD will trip;
- 230V and 50Hz - the voltage and frequency at which the unit operates;
- S - RCD selective;
- "~" sign - means that the unit trips for AC leakage.
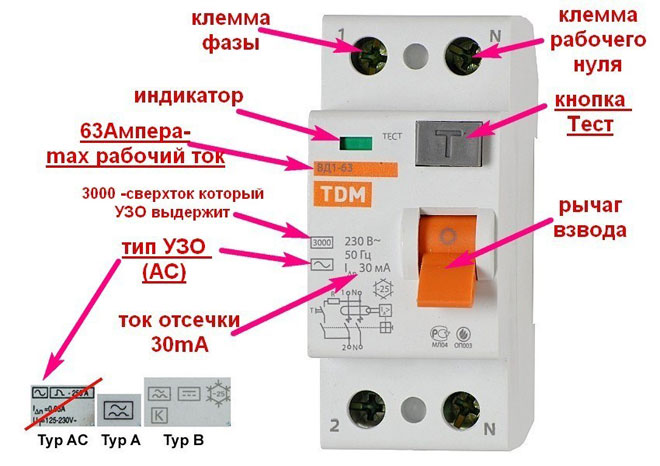

In addition, there are inscriptions near each contact for proper RCD connection:
- N (at the top) - The neutral conductor coming in is connected to this contact;
- 1(from above) - the incoming phase conductor is connected here;
- 2 (from below) - the phase conductor to the load is connected here;
- N (from below) or no letter - the neutral conductor to the load is connected here.
To to choose the RCD.which is ideal for your electrical system, it is necessary to understand the markings in detail, even if this task is very laborious and tedious.
Types and types
Modern manufacturers offer a variety of types and kinds of RCDs. The two most popular types of units in terms of their internal design in the electrical goods market are electromechanical (are independent of the amperage) and electronic (depend). Selective and fire protection devices are also distinguished.
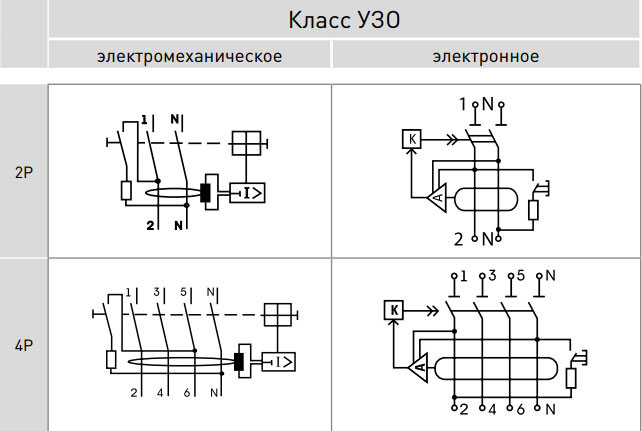
Electromechanical
Electromechanical RCDs are widely popular in use and are used in AC electrical circuits. What is the reason for this? Because when a leak is detected, such a device will trip, preventing unfortunate consequences even at the most minuscule voltage.

This type of RCD in many countries is considered a standard of quality and the one that is mandatory for widespread use. No wonder, because this RCD will work even in the absence of zero in the network and can save someone's life.
Electronic
These RCDs are easy to find at any construction market. Their difference from electromechanical RCDs is that they have an amplifier board inside that needs power to operate.

However, such RCDs, as has already been said, have a huge disadvantage - it is not certain that they will work in case of current leakage (it depends on the mains voltage). If the zero is burned out, but the phase remains, the risk of electrocution is not eliminated.
WARNING! We are talking about the advantages and disadvantages of RCDs in general, not specific models. If you are very "lucky", you can become the owner of a poor quality RCD, both electromechanical and electronic.
Selective
The main difference between selective RCDs from their "brothers" - the presence in the scheme of the function of delayed tripping circuit which feeds the load, i.e. selectivity. Often this parameter does not exceed 40 ms. Therefore, we conclude that selective devices are not suitable for protection against shock at direct contact.

Another feature of selective units is a good resistance to current and voltage spikes (The probability of false alarms is almost zero).
Fire protection
As the name implies, such RCDs are used in power supply systems of apartments and houses to prevent fires. However, they are not able to protect people since the leakage current they are designed for is 100 or 300 mA.

Usually these units are installed in metering panels or in floor distribution boards. Their main task is:
- protection of the incoming cable;
- The protection of the consumer lines, in which the differential protection is not installed;
- As an additional stage of protection (If the apparatus below it suddenly failed to work.).
Number of poles
Since RCDs operate on a comparison of currents that pass through the differential body, the number of poles at the unit coincides with the number of current-carrying conductors. In some cases, the RCD can be used with 4 poles for two- or three-wire service.
Do not forget to leave free phase poles in reserve. The unit will safely do its job not completely, but partially, which, in general, is not profitable from a financial point of view, but it is possible.
Conclusion
With each passing day in our lives there are more and more household appliances. Accordingly, the risk of current leakage increases, which sometimes even leads to death. If it doesn't kill you with an electric shock, it can cause serious health problems or a fire. There is only one answer to all of these problems - a ground fault circuit interrupter. We strongly advise you to install it in your home, as they say, out of harm's way.
Related articles: