protective earthing - is a system designed to prevent human exposure to electric current through intentional connection to ground of enclosures and non-current carrying parts of equipment which can be energized. Grounding systems can be natural or artificial.
Contents
What is earthing and why do I need it?
Earthing devices are the intentional connection of electrical type conductors between different points in an electrical system.
The purpose of grounding is to prevent human exposure to electric current. Another purpose of protective grounding is to conduct the voltage from the body of the electrical installation through the grounding device to earth.
The main purpose of grounding is to reduce the potential level between the point that is grounded and the ground. This lowers the amperage to the lowest level and reduces the amount of damage caused by contact with parts of electrical devices and installations in which a ground fault has occurred.
What is neutral?
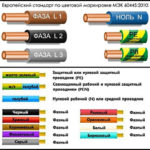
Neutral - is a neutral protective conductor that connects the neutrals of electrical installations in three-phase electrical networks. It is used to neutralize electrical installations.
The step-down substation, where the transformer plant is located, is equipped with its own grounding loop. This circuit consists of a steel bus and bars, buried in a special way in the ground. A cable with 4 wires is laid to the sources of consumption from the substation to the switchboard. When a power consumer needs power from a three-phase circuit, all 4 cores must be connected. When different loads are connected to the cores, there is a neutral shift in the system and the neutral conductor is used to prevent this shift. It helps distribute the load symmetrically over all phases.
What are PE and PEN conductors?
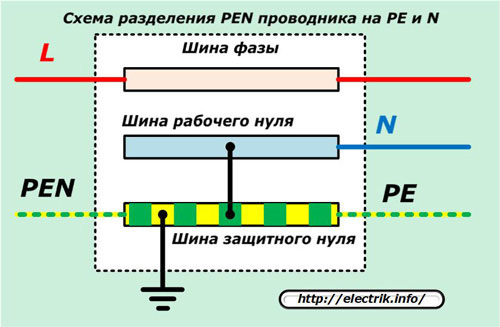
PEN conductor - is a conductor that combines the functions of a protective earth conductor and a working earth conductor. It comes from the substation and separates into PE and N conductors, directly at the consumer.
The PE conductor - is a protective earth conductor that we use, for example, in an apartment in a grounded outlet. The PE conductor is used to ground devices, installations and appliances where the voltage level does not exceed 1 kV.
This type of grounding is only used to ensure safety. This grounding provides a continuous connection between all exposed and external parts. The mechanism ensures that the current flows to ground which has arisen due to an electrical current flowing to the enclosure of any device.
The PEN conductor (combination of a protective earth conductor and a working earth conductor) is used when a TN-C type earthing system is used.
Types of artificial grounding systems
In the classification of grounding systems are natural and artificial types of grounding.
Artificial type grounding systems are:
- TN-S;
- TN-C;
- TNC-S;
- TT;
- IT.
Types of grounding - deciphering of names:
- T - grounding;
- N - connection of a conductor to the neutral;
- I - isolation;
- C - combination of functional and neutral protective conductor options;
- S - separate use of wires.
Many people are interested in what is called a working ground. It is also called functional grounding. The answer to this question gives paragraph 1.7.30 PUE. This is the grounding of the points of current-carrying parts of the electrical installation. It is used to ensure the function of electrical appliances or installations, and not for protective purposes.
Many people are also concerned about what protective grounding is. It is the process of grounding devices to ensure electrical safety.
Systems with a TN grounding system with a deaf-earthed neutral
These systems include:
- TN-C;
- TN-S;
- TNC-S;
- TT.
According to clause 1.7.3 of the PUE, TN-system is a system in which the neutral point of the power supply is solidly grounded and the exposed conductive parts of the installation are connected to the solidly grounded neutral point of the power supply by means of zero protective conductors.
The TN includes elements such as:
- the midpoint earthing conductor, which relates to the power supply;
- the external conductive parts of the device;
- the neutral conductor;
- combined conductors.
The source neutral is solidly grounded and the external conductors of the installation are connected to the solidly grounded midpoint of the source by means of protective type conductors.
You can make a ground loop only in electrical installations with a capacity not exceeding 1 kV.
TN-C system
In this system the neutral protection and neutral operating conductors are combined into one PEN conductor. They are combined throughout the system. The full name is Terre-Neutre-Combine.
Among the advantages of the TN-C are only the easy installation of the system, which does not require much effort or expense. The installation does not require improvement of already installed cable and overhead power lines, which have only 4 conductors.
Disadvantages:
- Increased likelihood of electrocution;
- Linear voltage may appear on the body of the electrical installation during a circuit interruption;
- High probability of losing the grounding circuit if the conductor device is damaged;
- This system protects only against short circuits.
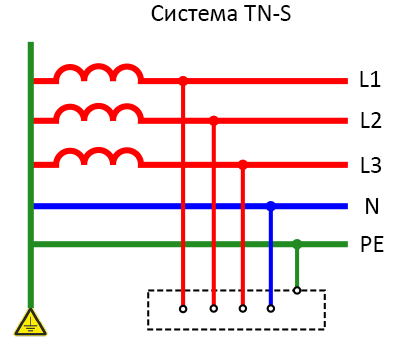
TN-S system
The peculiarity of the system is that electricity is supplied to consumers via 5 conductors in a three-phase network and via 3 conductors in a single-phase network.
A total of 5 conductor sources depart from the grid, 3 of which serve as the power phase and the remaining 2 are neutral conductors connected to the neutral point.
Design:
- PN is the neutral that is involved in the circuitry of the electrical equipment.
- PE is the deaf-earthed conductor that performs a protective function.
Advantages:
- ease of installation;
- low cost of purchase and maintenance;
- high degree of electrical safety;
- no need to make a loop;
- possibility to use the system as a current leakage protection device.
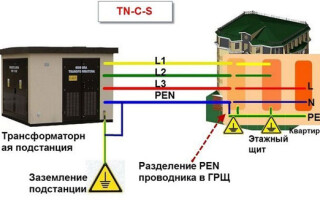
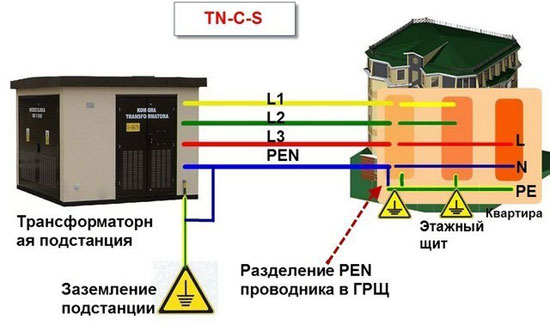
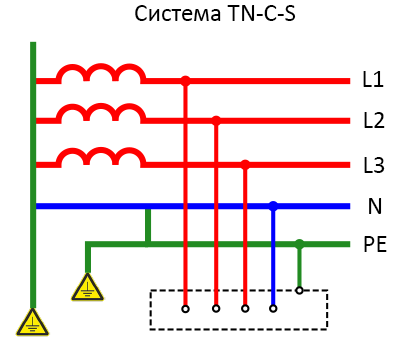
TN-C-S system
The TN-C-S system involves splitting the PEN conductor into PE and N at some point in the circuit. Usually the separation takes place in the switchboard in the house, and before that they are combined.
Advantages:
- A simple lightning protection mechanism;
- availability of protection against short circuits.
Minuses of use:
- weak level of protection against zero conductor burnout;
- the possibility of a phase voltage;
- high cost of installation and maintenance;
- the voltage cannot be switched off by the automatics;
- no protection against electric current in open air.
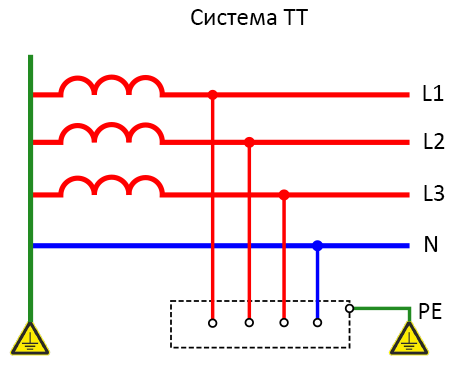
TT system
TT system is designed to provide a high level of safety. It is installed in power plants with a low level of technical condition, for example, where bare wires are used, electrical installations that are located outdoors or are attached to poles.
TT is mounted in a four conductor circuit:
- The 3 phases that supply voltage are offset at an angle of 120° to each other;
- 1 common zero performs the combined functions of a working and protective conductor.
Advantages of TT:
- high level of resistance to deformation of the wire leading to the consumer;
- short circuit protection;
- the possibility of using on electrical installations of high voltage.
Disadvantages:
- Complicated lightning protection device;
- Inability to trace the phase of short circuit.
Systems with isolated neutral.
In the transmission and distribution of electric current to consumers, a three-phase system is used. This makes it possible to provide symmetry and equal current distribution of the load.
Such a device creates a mode that provides for the use of transformer boxes and generators. Their neutral points are not equipped with a ground loop.
The isolated type of neutral is used in the power supply circuit when the secondary windings of transformer installations are connected in a delta circuit and when there is no power supply during emergencies. Such a network is a substitute circuit.
The isolated neutral facilitates the breakdown of the insulation coating in the event of a short-circuit and the occurrence of a short-circuit on the other phases.
IT System
The IT system with voltages up to 1000 V provides grounding through a high resistance level and is equipped with a power supply neutral.
All external elements of the electrical installation, which are made of conductive materials, are earthed. The advantages include low current leakage during single-phase mains faults. Installation with such a mechanism can function for a long time, even in emergency situations. There is no difference between the potentials.
Disadvantage: current protection does not operate during a ground fault. During operation in single-phase short-circuit mode, the probability of electrocution by touching the second phase of the installation increases.
Related articles: