To control liquids in pipelines special shut-off valves are traditionally used. According to the established order, it is made in the form of valves (cocks), closing or opening manually. Today, instead of the usual valves are increasingly installed modern shut-off devices that work on the principle of electromagnetic induction.

Contents
What is a solenoid solenoid valve
A solenoid valve - is a classical electromechanical unit, the main purpose of which is the operational control of the flow of liquid or gaseous media. Thanks to this device it is possible to partially or fully automate this process. The final decision to open or close the solenoid is made by the operator or the logic of the controller.
When at the control panel, the operator presses the "open" button, thereby applying voltage to the solenoid coil. The latter retracts the valve stem by means of the current flowing through it, putting the valve in the "Open" mode (when the valve type is normally closed). To perform the reverse action, the operator only needs to press the "Close" button. Then the coil is de-energized and the stem, under the action of the return spring, takes its normal safety position.
Purpose and application of solenoids

The main purpose of solenoids and similar devices is to redirect or block the movement of fluids in pipelines of various types and applications. In domestic conditions they are used in automobiles, in ordinary water supply systems, as well as in heating networks and in irrigation systems for summer cottages. In industry, these devices are installed to regulate the flow of technical liquids and gases transported through a branched pipe network, control shut-off valves.
They can also be installed in equipment where automatic valve control is required depending on the operating conditions. In this case the solenoid kit can be supplied with a special kip sensor, sensitive to leakage, for example. In this case, if a leakage is detected, the alarm signal from the sensor is sent to a special controller which, after processing the information, issues a command to close the valve.
Design and principle of operation of solenoid valve
A typical solenoid valve includes:
- a body molded from durable and wear-resistant materials;
- an inductive coil with solenoid;
- disc or piston directly controlling the fluid flow;
- a spring damper.
The inductor coil, which is the main working element of the electromagnet, is encapsulated and encapsulated in epoxy resin, completely isolated from the external environment. This reliable sealing prevents water, which is a good conductor of current, from getting into it.
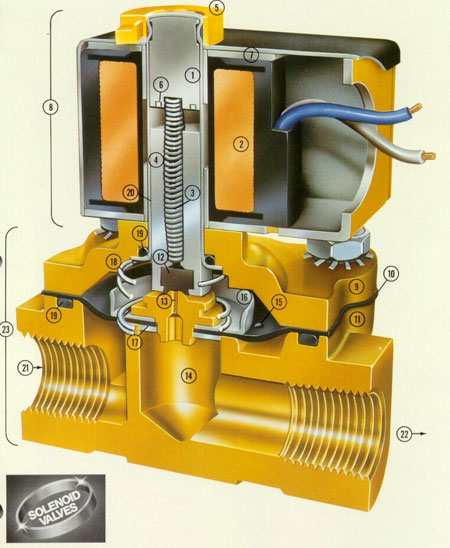
The principle of operation of the solenoid valve is based on the electromagnetic effect, well known from school physics. According to it, when an electromagnetic field appears in all the metal parts in the area of its action, the same type of field is induced by induction. Magnetized objects begin to interact with the initial field structure, attracting or repelling from its carrier.
In the device under consideration, the initial influence is created by the electromagnetic coil, and the secondary field is "induced" in the solenoid (in the moving part of the system). When an impulse is applied, the solenoid with the control rod attached to it moves and closes/opens the channel with the fluid (gas) flowing through it.
Types of solenoid solenoid valves
The described devices are classified according to the following main characteristics:
- the material on the basis of which the body is made;
- design features of the valve;
- its position when the coil is de-energized (de-energized);
- operating principle;
- features of connection to pipelines.
Important! On the correct choice of the valve according to some of these features depends on whether it will work for a long time in the environment with the specified parameters.
The body of these products is made of traditional brass, plastic or stainless steel. The right choice of material largely determines whether the valve can be used in critical environments. For domestic water heating systems any of the above varieties is suitable.
Valves are divided into piston, diaphragm and spool valves according to their design features. The cheapest and sufficiently reliable option is the spool device, which copes well with its functions. Therefore, such valves are traditionally installed in the home.
According to the position of the piston rod with the piston when the electromagnet is disconnected from the power supply, they are divided into the following types:
- closed in the normal state (NC);
- open (NO);
- Having two stable positions.
In the first case, when the coil is de-energized, the core with the valve due to the elasticity of the return spring reliably closes the pipeline channel. In the second case, when the voltage is disconnected, the opposite effect occurs. Under the action of the same spring, the stem is completely retracted into the coil, and the channel remains open. In the third case, the valve can be in both positions (closing the channel or leaving it free) in the initial state when the voltage is removed. It all depends on the circuit used to turn it on.
On the principle of actuation (its functionality) all such valves are divided into one-way, two-way and three-way. The first type has only one operating spigot connected to the pipeline. Such designs are usually used as a safety valve, serving to get rid of excess steam or water.

Their three-way counterparts have three connecting spigots, allowing them to be used to divert the flow of liquid media. The most common type of solenoid valves are two-way valves. They have two spigots on both sides and are installed directly in the pipe break. According to the connection features, solenoid devices are divided into socket valves, as well as flanged and socket valves.
The different valve designs also differ in the material used for the seal and the shut-off diaphragm. According to this characteristic, they can use:
- fluoride elastomer;
- ethylene propylene elastomer (EPDM);
- rubber backing.
Additional information: Domestic devices used to shut off the flow of water in pipelines usually use the second type.
This is because the synthetic EPDM material is resistant to the damaging effects of salts and works well at low temperatures.
How to connect the electromagnetic valve
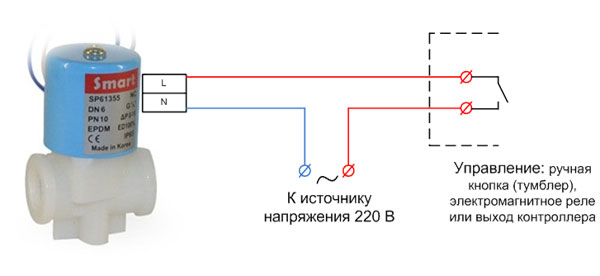
Before installing and connecting the electromagnetic valve, it is important to consider that this mechanism very poorly "tolerates" hydraulic shocks, often occurring in pipelines with dense liquids. If it is not properly protected, it will not last very long. The function of such protection is performed either by a pressure reducing valve, which allows to reduce the pressure at the time of impact, or by rubber tubes mounted directly in front of the device to be protected.
In addition, the following important points must be taken into account:
- Before installing the solenoid valve, preparatory work is carried out, which consists in cleaning the pipes and marking them;
- The installation site should be chosen such that there is always easy access to the valve (in case of replacement or repair);
- installation is carried out with the solenoid completely disconnected from the mains.
Important! It is advisable to install a coarse filter in front of the solenoid valve to trap small dirt particles.
The mechanical installation and the electrical connection process includes the following steps in the sequence shown below:
- First, the body of the device is installed by means of flanges with sealing gaskets in the pipe break.
- Then the electrical part, represented by a magnetic coil with three contacts, is connected.
- To two of them are connected + and - 24 V DC voltage, or phase and zero for 220 V solenoids, and the third contact is earthing.
To connect the ground to the valve body, a thick copper conductor is used, which is attached by welding to the mounted protective circuit.
Related articles:






