For most people, RCDs and circuit breakers and circuit breakers are indistinguishable and they do not see the difference. Externally they are very similar, the inscriptions on the body are almost the same, there is a test button and the switch on in operation, but nevertheless they are different devices and let's understand the difference between RCD and a residual current device. In the material we will consider the purpose of both devices and their fundamental differences in important parameters.
Understanding the purpose of these devices and what is the difference between RCD and automatic circuit breaker will help you make the right choice when designing an electrical network of a private house or apartment.

Contents
What a residual current circuit breaker (RCD) does
The devices are similar in appearance, but there is a difference, as they perform different tasks. A circuit breaker monitors the current flowing through it and breaks the circuit (triggers) in the event of any leakage to ground after it. The maximum leakage current, above which the RCD will trip, is indicated on its case (10 mA to 500 mA).
The occurrence of differential current (the difference between the input and output of the RCD), can occur for various reasons, for example, a failure of household appliances or damage to the insulation of the cable, in which part of it begins to flow to earth.
Note! Where electrical current leakage occurs when the wiring insulation is damaged, the temperature of the wire increases, which can lead to a fire and a fire.
Read our article on how to check the quality of the insulation: How to use a megohmmeter to measure cable insulation resistance?
Note that in buildings with old electrical wiring, fires due to wiring fires are quite common.
A current greater than 30 mA is considered lethal for a person. Therefore, in the switchboards for the protection of outlet groups, install RCDs with current-breaking capacity 10 mA or 30 mA. RCDs with a larger rating of this parameter (for example, 100 or 300 mA) is called the fire protection circuit breaker and it is not needed for human protection, but to prevent a fire in the place of the damaged cable insulation.
It is important to understand that the RCD does not protect the network from overcurrents, this is the key difference between it and a circuit breaker. In the case of occurrence short-circuitit can burn out, but it will not trip (There is no leakage current to earth in a short circuit.). Therefore, it is not used alone, but must be installed In series with the circuit breaker.
Thus the main purpose of the RCD is to protect against human electrocution (if it leaks through the human body onto the ground) and the timely de-energizing of the network section with damaged wiring insulation.
Appointment of the automatic residual current circuit breaker (RCCB)
Differential circuit breaker is a versatile device that combines the functions of the circuit breaker and residual current device. This means that the automatic differential switch is able to provide protection against short-circuit, overload and current leakage.
The size of the circuit breaker for a single-phase 220 V network is equal to the size of a RCD or a two-pole circuit breaker (two modules). Therefore, in the panel They occupy the same space, but the differential circuit breaker has in addition to the functions of tracking current leakage, and operation on the thermal protection and exceeding the current limit. Therefore, in the absence of space in the switchboard, you should install differential circuit breaker instead of a combination of RCD + circuit breaker.
The automatic unit has two protections (two types of tripping devices):
- electromagnetic;
- Thermal.
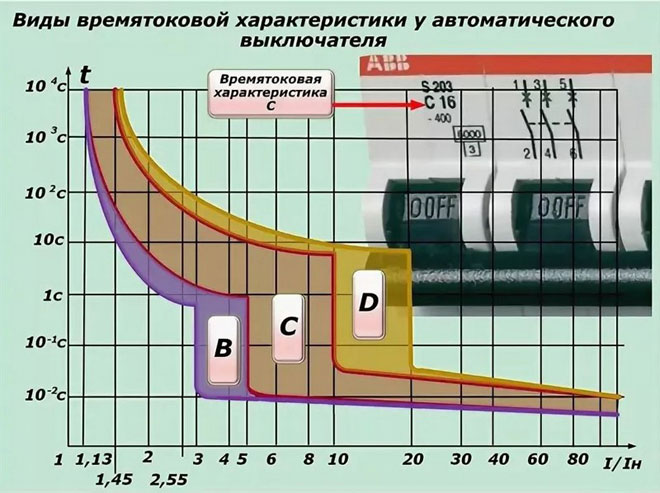
The electromagnetic release will trip when the current exceeds the rated current by a certain amount. This number depends on the type of differential breaker.
Note! For type "A" exceeds the rating will be 2-3 times, "B" - 3 to 5 times, "C" - 5-10 times the rating, "D" - 10-20 times more.
This is the instantaneous value of current, for example, in a short circuit or at high inrush current of powerful electrical equipment.
The thermal protection trips when the current flowing through the circuit breaker exceeds the rated value, a certain time. This time should be seen from the time-current characteristic of the particular circuit breaker. The greater the excess, the faster the circuit breaker will trip.
It is also worth noting that the cost of a circuit breaker is significantly higher than that of a RCD.
The difference between RCDs and differential circuit breakers
Let's analyze in detail the individual technical characteristics, what is the difference between RCD and differential circuit breaker and how you can use the advantages of each of them.
Let us note the main difference that RCD Does not provide network protection against overloads and short circuits. That is, it acts only as an indicator that monitors the leakage current.
If all appliances are included in the network at the same time and creates a deliberate overload, the protection device will not work, and the differential circuit breaker will immediately de-energize the network, preventing the emergence of fire and melting of the insulation.
Let's take a closer look at the devices themselves, and then it will become clear how to distinguish the RCD from the circuit breaker externally:
- marking of the rated operating current of the electromagnetic release - One of the key differences between RCDs and circuit breakers (It is the only one on the circuit breaker). The case must indicate the operating current (with a letter - C16, C32) and the leakage current. If only one parameter is indicated or without a letter, it is a RCD - the leakage current value and the switching capacity of the contacts are indicated on it.
- wiring diagram on the device - similar circuit diagrams are shown on the case, the RCD diagram is an oval indicating a differential transformer and electromechanical relay. On the diagram of the second device there are additionally thermal and electromagnetic trip units.
- The name on the side of the device - Not all units are labeled;
- abbreviation on the device - On devices of domestic manufacturers VD (differential switch) or AHDR (differential current circuit breaker.).

It is important to note that the reliability of operation differs little, the main differences lie in the timing of operation and operation of special trip units of the two types in the differential switch. The disadvantage of the latter is the impossibility of determining what caused the tripping: a mains overload, short-circuit or leakage.
The advantage of AADT is considered the combination in its case of two devices. In the switchboard there is additional space for a single-pole circuit breaker. However, in the event of a breakdown, full replacement will be required. The circuit breaker takes two places, because it must be connected in conjunction with the circuit breaker. This configuration simplifies the repair process in the event of failure - Only one component has to be exchanged.
Which device is better to choose
In general, it is not fundamental what to install - diphasomatic or separately RCD with a circuit breaker, the question will only be in the free space in the switchboard. The main thing correctly choose the rating and the value of the leakage current on the basis of the cross section and cable material, as well as selectivity the selectivity of the entire system as a whole.
In the selection process we recommend to pay attention to foreign manufacturers, because they are characterized by the best response time, reliability of elements and housings.
Here are some models that have proven themselves among users:
- Legrand in electronic-mechanical or electronic modifications;
- - Have a lot of advantages, are versatile;
- ABB - instantaneous disconnection in the event of a short circuit;
- IEK AD 12 - Keeps operability at reduction of voltage of electric network to 50 V;
- EKF AD 32 - is often used to connect boilers in the kitchen and bathroom.
So, the differences between the two devices are really there, both technically and externally. It is possible to assemble a working scheme with both options, but the choice is left to the designer of the electrical network of the house or apartment.
Related articles:






