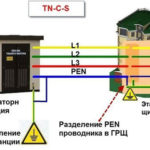
A fuse is an element of the power system that performs a protective function. Unlike a circuit breaker it needs to be replaced after each trip. The fusible link, which will burn out if the rated current exceeds the allowable current, must be selected according to the load on the mains.
Contents
Working principles and purpose of fuses
The pure metal (copper, zinc, etc.) conductor inside the fuse insert is the core of the fuse.copper, zinc, etc.) or an alloy (steel). Circuit protection is based on the physical property of metals to heat up when current flows. Many alloys also have a positive coefficient of thermal resistance. Its effect is as follows:
- when the current is below the nominal value provided for the conductor, the metal heats evenly, having time to dissipate heat, and does not overheat;
- A high current will cause the conductor to heat up, and the fuse, designed for a certain value of current, will collapse.

This property is based on the melting of a thin wire placed in an electric fuse. Depending on the application, the shape and cross-section of the conductor can vary from thin wire in household and automotive appliances to thick plates designed for a current force of several thousand amperes (A).
The compact part protects the electrical circuit from overloads and short circuits. If the permissible mains current is exceeded (i.e. the rated current) the insert will break and the circuit will be interrupted. Its operation can be restored only after replacing the element. When there is a defect in the connected equipment, the fuses will blow immediately after the faulty device is switched on, allowing the integrity of the device to be preserved and indicating the presence of the problem. If a short circuit occurs in the mains, the protective device is triggered in the same way.
Graphic designation in a diagram
According to the uniform system of design documentation in Russia, in circuit diagrams the fuses are indicated by a rectangle with a straight line inside it. Its ends are connected with 2 parts of the circuit before and after the protective device.
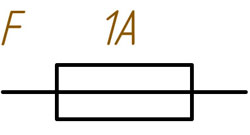
Other designations can also be found in the documentation of imported devices:
- Rectangle with separated parts at the ends (IEC standard);
- Cable wavy line (IEEE/ANSI).
Types and types of fuses
For application in electric circuits different types and varieties of fuses are used. Produced in Russia products differ in the type of construction:
- filled with the marking PN-2; PPN, NPN, etc.;
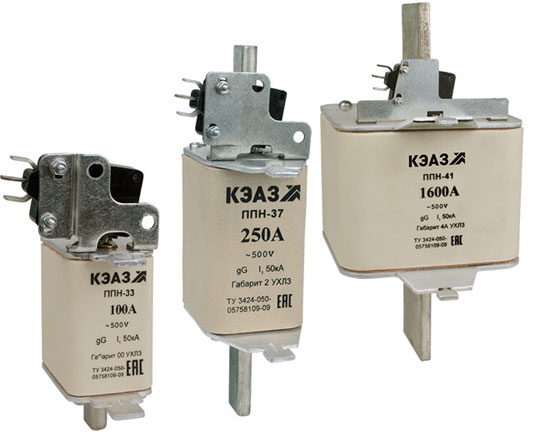

- unfilled (PP-2).
The concept of fullness is related to the presence of a substance inside certain types of inserts that extinguishes the electric arc that occurs at the moment the conductor burns out. The circuit will be open only after it has disappeared. This is why PP-filled flasks contain silica sand. The unfilled ones are capable of releasing gases that extinguish the arc. This occurs when the insert body material heats up.
In addition to types, a distinction is made between types of PP:
- Low-current are used in low-power household appliances with a current consumption of up to 6A. These are cylindrical inserts with contacts at the ends.
- Fork-length wiring terminals are often installed in automobiles. The name is due to the appearance: the contacts are on one side of the body and are inserted into the sockets, like a plug into a socket.
- Plugs - common in single-phase networks, electrical plugs for the meter. The rated current of such plugs is 63 A, they are designed for simultaneous connection of several household appliances. The burnout insert in such a fuse is inside a ceramic case with a cartridge, 1 contact remains outside and the other is connected to the contacts of the plug. When the load is exceeded, the part burns out, completely de-energizing the apartment. The power supply can be restored by replacing the insert with a new one.
- Tubular PP resembles a plug insert in structure, but its attachment is made between 2 contacts. The type of such a fuse is unfilled, and the body is made of fiber, which emits gas when heated strongly.
- The blade fuses The knife fuses have a rating of 100 - 1250 A and are used in networks that require a high current carrying capacity (For example when connecting an appliance with a powerful motor.).
- QuartzFused with quartz sand are used in networks with voltages up to 36 kV.
- Gas-generating, collapsible and non collapsible. When burning varieties PSN, PVT is a powerful release of gas, accompanied by a clap. The SS is used for networks with voltage of 35-110 kV. The rated current of such a PP is up to 100A.
Depending on the total load on the network, different types of CCs are installed - more powerful ones are installed in special transformer booths, they can withstand the current that meets the needs of a residential area or an enterprise. Low-power ones are installed in meters: they protect individual apartments. Old household appliances can also be fitted with a PP (low current), but modern appliances contain these elements rarely.
Choosing the fuse insert
The choice of the fuses is made taking into account their nominal values, time-current characteristics and total network load (total power of all operating elements). The rated current of a fuse is that which the fuse link will be able to withstand before breaking. This value is indicated on the fuse case (e.g. marking of 63 A for household cork fuses).
The time-current characteristics are calculated from special charts. They must be taken into account for electric motors whose starting current exceeds the operating current by several times. When using several electric motors (at the enterprise), the starting current of the most powerful one is calculated.
The total (maximum) load power of the network is the sum of all operating currents of the devices (indicated in the instructions and on the housing). If an electric motor is included in the mains, its starting current is also taken into account, divided by the factor k = 2.5 (for soft start and squirrel cage rotor) or 2-1,6 (for heavy starting or phase locked rotors ) or 2-1.6 ( for squirrel cage rotors ).).
You can calculate the desired rating using the formula: I np>1/k (I common + I start). When calculating, note that the rating of the sensor must always be greater than the value obtained from the current calculation.
To avoid time-consuming calculations, use the table to find the rated current of the fusible link.
| W | 10 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 250 | 500 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 | 1600 | 2000 | 2500 | 3000 | 4000 | 6000 | 8000 | 10000 |
| А | 0,1 | 0,25 | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
First row (Windicates the wattage printed on the housing of the fuse, and the second line (А) is the fuse rating. For an apartment network, you will have to add up the values in watts of all home appliances and find a suitable number in the table, but it would be better to use circuit breakers.
Calculation of the wire diameter of the fuse
Complex calculations are made in order to temporarily repair a burnt insert, if there is no possibility of replacing it. In order for the network to be protected from overloading, the thickness of the wire used to install the "bug" must match the rating of the destroyed insert. For the network of a city apartment, where you install PP rated 63A, you can use a copper wire with a diameter of 0.9 mm.
If you need to repair another protective device, you need to determine the rating of the PP (indicated on the housing), and then determine the correspondence of the available copper wire:
- measure its diameter;
- cube this number and take the square root of the value;
- multiply this number by 80.
The result should be approximately equal to the PP rating indicated on the case.
When repairing, the selected wire is wound around the contacts of the burned insert, connecting them together. The bug is inserted into the socket on the fuse body.
If the wire melts again, it means that the fault is in the protected appliance or in the mains of the apartment and they must be repaired. Do not use a thicker wire as this could cause a fire.
Functionality Check
Modern car fuses sometimes have a built-in burnout indicator. It tells the owner that the part needs to be replaced. In low-current fuses, the wire is visible through the transparent housing. But part of the sensor is opaque and has no indicators.
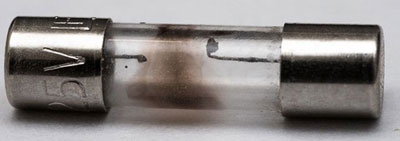
If it is not possible to visually detect a broken conductor inside the sensor, it can be determined with a multimeter. Before you check the fuse with the tester, you must select the minimum resistance value (Ohm). Place the stylus of the tester to the contacts of the sensor and determine the reading of the device:
- if the resistance value is zero or close to 0, conclude that the insert is functional;
- if the tester shows 1 or the sign of infinity, then the sensor is burned out.
If the tester has a sound device, you can simply test the fuse by placing the styli to the contacts. The sound of the tester indicates that the element is working.
Related articles: