Chokes, that is, inductive resistances are used in AC circuits to limit load current. Such devices ensure considerable energy saving, prevent overloading and excessive heating.
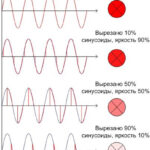
A choke is a type of inductor coil whose main purpose is to delay the effect of current on a specific frequency range. And a sharp change in the current in the coil is not possible, because the law of self-induction works, as a result of which an additional voltage is created. Let's consider in detail the principle of operation, types and purpose of chokes.
Purpose
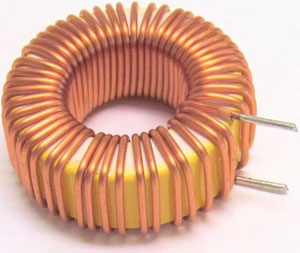
Many people are interested in what a choke is and what it looks like. The device is made in the form of an iron transformer, the only difference is the presence of one winding. The coil is wound on a core of transformer steel, with the plates separated and not in contact with each other in order to reduce eddy current.
The electronic choke is characterized by a high inductance level of up to 1Gn, the coil effectively counteracts current variations in the electrical circuit. When the current is decreasing, the coil maintains it, and in case of a sharp increase the coil provides limitation and prevention of a sharp spike.
When considering why a choke is needed, the following purposes should be mentioned:
- reducing interference;
- smoothing of electric current pulsations;
- storage of energy in the magnetic field;
- separation of circuit parts at high frequency.
So why do we need a choke? Its main purpose in the electric circuit is to delay on itself the current of a particular frequency range or to accumulate energy in the magnetic field.
The importance of the choke can be explained by the fact that fluorescent discharge lamps (e.g. household lights, street lamps) do not function without a choke. It acts as a limiter of the voltage applied to the electrodes of the discharge lamp.
Also throttling devices form the starting voltage required to create an electrical discharge between the electrodes. This ensures that the fluorescent lamp is turned on. The starting voltage is designed for only a fraction of a second. Thus, the choke is the device responsible for turning on the lamp and its stable operation.
Function Principle
The electronic reactor has a simple configuration and an easy-to-understand operating principle. It is a coil of electrical wire, which is wound on a core of special ferromagnetic material. The operating principle is based on the self-induction of the coil. When considering the design of the choke, it becomes clear that it works like an electrical transformer, only with one winding.
The core and the ferromagnetic plates are insulated to prevent Foucault currents which cause significant interference. The coil has a large inductance, and directly acts as a protective guard against sudden mains voltage surges.
However, this design is considered low-frequency. AC current in household networks fluctuates over a wide range, so the fluctuations are divided into three categories:
- Low frequencies between 20Hz-20kHz;
- ultrasonic frequencies between 20 kHz and 100 kHz;
- ultra-high frequencies over 100 kHz.
High-frequency devices do not have a core, instead plastic frames or standard resistors are used. And the choke itself in this case has a multi-layer winding configuration.
In the process of calculations and making schemes, how to connect the choke, its parameters and characteristics of the network in which it is necessary to maintain the operation of lamps are taken into account. Particular attention must be paid in the connection to the stage at which the lamp begins to glow, when the gas medium is required to be penetrated by the discharge. At this point, a high voltage is needed, and after that the device acts as a voltage limiting element.
Main characteristics
For the most part, chokes have substantial dimensions. To make the devices compact without compromising performance, the inductor coil is replaced by a stabilizer, which is essentially a powerful transistor. The result is an electronic choke. However, this type of device is a semiconductor, so it should not be used in high-frequency devices.
An electronic choke must be chosen according to several parameters, the main of which is considered to be the inductance, measured in Gn. Also important technical characteristics of devices are:
- resistance, which is taken into account at constant current;
- voltage variation within the permissible limits;
- Magnetizing current - the nominal value is used.
Choosing a device, first of all, it is necessary to be guided by the purposes and tasks for which the choke is needed in the circuits of electric circuits. The use of magnetic cores in electric chokes makes it possible to ensure compactness of devices while maintaining the same inductance values. Ferrite and magnetodielectric compositions, due to low capacitance, can be used in a wide range of frequencies.
Varieties of Chokes
The following types of electrical chokes are distinguished, based on the types of lamps in which they are used:
- single-phase - suitable for household and office lighting systems that operate from 220 volts;
- three-phase - designed for 220 and 380 volts. Such chokes are suitable for DRL and DNAT lamps.
Electronic chokes may belong to one of the categories, depending on where they are installed:
- recessed or open-ended. They are mounted in the lamp housing, which provides protection from external factors;
- closed - they are hermetically sealed and moisture-proof. Such devices can be installed outdoors in open areas.

Depending on the purpose, chokes are divided into types:
- AC. They are used to limit the voltage in the network, for example, at the time of starting an electric motor or pulsed RCEP;
- saturation. Mainly installed in voltage regulators;
- smoothing - to reduce pulsations of rectified current;
- magnetic amplifiers. Such inductors involve a magnetizing core due to the presence of direct current in the network. By adjusting its parameters, it is possible to change the values of inductive resistance.
Chokes can remain functional for a long period of time if used properly. The device is designed to limit sudden spikes in voltage, which allows you to secure both devices and the entire network.
Related articles: