Since the invention of electric light there has been a question about the regulation of brightness. At first, this was done using mechanical devices, blocking part of the beam (curtains, etc.). This was cumbersome and inconvenient. Then potentiometers and adjustable transformers were used for this. This was unreliable and uneconomical. As solid-state power electronics developed, it became possible to create compact devices to change brightness without excessive energy consumption.
Contents
Dimmer as a device for regulating the intensity of illumination
The name of such devices comes from the English to dim - dim. When the device works, you can set the desired level of lighting or create color effects, including dynamic, as well as achieve some energy savings.
From the user's point of view, changing the light intensity is done by manipulating the controls of the fixture - rotary knob, "more or less" buttons, remote control, etc.
From the point of view of a lighting system designer (even a small home one) it is necessary to have a deeper understanding of the processes that lead to changes in the brightness of a lighting fixture.
Principle of dimming
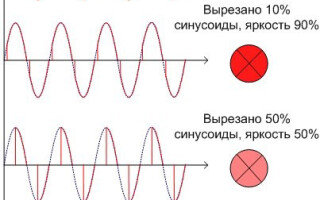
With lamps that operate on AC circuits, dimming is done by reducing the current by "cutting out" part of the sine wave.
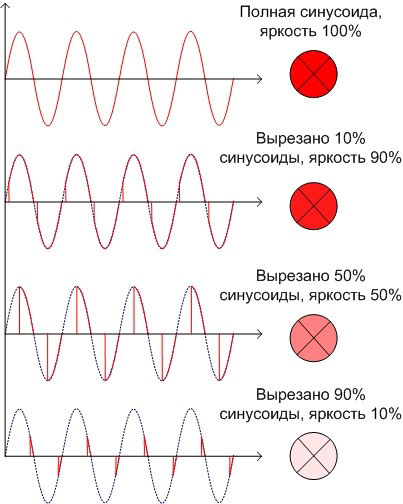
The more of the voltage cut out, the less current through the lamp. The brightness is averaged out due to the inertia of the lamp filament and human vision.
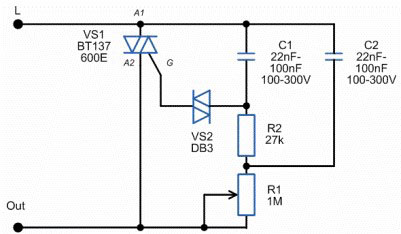
Classic dimmers are made according to the above scheme (small variations are possible). The key is triac - It opens and closes at a given moment of time after the voltage passes through zero. The later the triac opens, the smaller part of the sinusoid goes to the consumer. This torque is adjusted with a potentiometer.
Which lamps can work in combination with a dimmer
A dimmer, made according to a classic circuit, regulates the average current through the light fixture, so it is ideal for changing the light level of incandescent lamps и halogen lamps. Fluorescent lamps are arranged on a different principle, so they do not work together with dimmers, except for special lighting fixtures with a special design and the label "Dimmable".
Adjusting the brightness of LED lamps has its own peculiarities. Many LED lights are equipped with a current stabilizer (driver). It keeps the current through the LEDs stable, despite changes in input voltage. That is, it performs the opposite function to the dimmer. Therefore, dimming is not possible in this case. An exception are lamps whose driver input circuits are supplemented with special circuitry. Such lamps are marked Dimmable.
Another option - the current in the luminaire is limited by a resistor (such a solution is used in LED strips, etc.). Here is also a problem - it is extremely undesirable to include LEDs in AC circuits.
The weak point of LEDs is their low resistance to reverse voltage. When you turn on such a luminaire in a domestic circuit, it will fail very quickly, despite the fact that it is designed for 220 volts. These lights should be connected to a DC circuit, and the brightness is regulated by PWMThe brightness is adjusted by the PWM method, where the positive polarity voltage is applied.
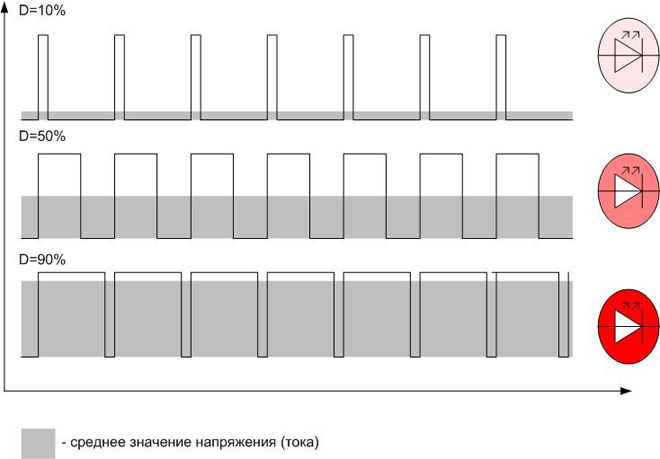
LED light output is averaged due to the inertia of human vision. LED strips (and other similar lighting fixtures) need a special dimmer that works on the principle of PWM.
Important! All LED strips are dimmable. The Dimmable label, implying the existence of non-dimmable strips, is a marketing ploy.
Types of dimmers and their connection diagram
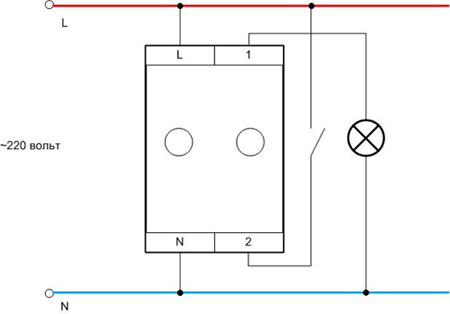
Dimmers with mechanical manual control are made according to a classic scheme and are turned on like a light switch in the gap of the phase wire (usually dimmers have a built-in switch). They are even available in the form factor of household light switches to simplify installation and mounting.
 The simplest dimmers turn lights off when the knob is turned from the minimum light position to the extreme position (until it clicks). The disadvantage of such a system is that after switching on, you need to re-set the desired light level each time. More advanced devices adjust the light level by turning the knob, and turn the light on and off by pressing the knob. In this case, the brightness level does not change.
The simplest dimmers turn lights off when the knob is turned from the minimum light position to the extreme position (until it clicks). The disadvantage of such a system is that after switching on, you need to re-set the desired light level each time. More advanced devices adjust the light level by turning the knob, and turn the light on and off by pressing the knob. In this case, the brightness level does not change.
Light dimmers with a higher comfort level (sensor, remote control, audio control, etc.) are connected both to the phase wire and to the neutral conductor. This is due to the need to supply power to the internal control circuitry. If the dimmer is controlled by a computer (mainly for creating light effects on LED tapes), a separate power supply from the mains is provided for it.
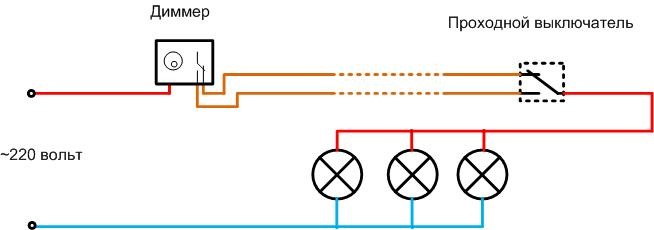
Separately we should consider the connection diagram of the pass-through dimmer. This is a dimmer that can work in a system with a loop-through switch. Such switching devices are located, for example, at two ends of a long corridor. The lights can be switched on when you enter the corridor and off when you leave, irrespective of the position of the other switch.
If this system is supplemented by a dimmer, the light level can be changed. The dimmer is installed on one side only - if installed on two sides, the result of double slicing a single sine wave will be unpredictable.
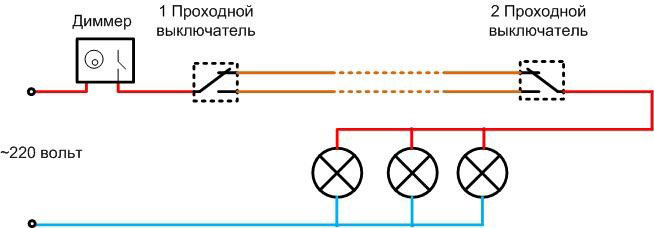
If you equip the dimmer with its own group of changeover contacts, you get a pass-through dimmer. It allows you to turn lights off and on regardless of the position of the other device and adjust the brightness.
It is worth mentioning and portable dimmers. They are used for floor lamps, table lamps, etc. Such a dimmer is plugged into a socket, and already in his socket you can connect the lamp and adjust its level of light.

For lighting rooms without permanent residence (porches, warehouses, etc.) are designed and used modular dimmers.
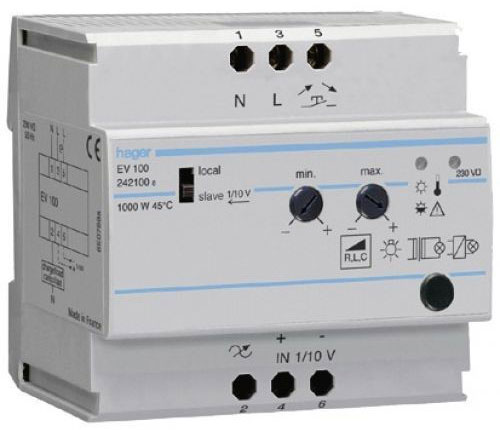

They have a regulator unit and the on-off switch are separated in space. The main module is usually located in the electrical switchboard and is included in the general power supply system. The remote switch is mounted in any accessible place - at the entrance to the room, on the control panel, etc.
The dimmer is set on the body of the main unit. The required brightness of the lamps is set during adjustment. Such a regulator can be turned on manually or automatically - in this case it is supplemented by a motion sensor, capacitive relay, etc.
Such dimmers (except for models of the Economy class) have additional functions, such as a smooth rise and fall of the light level, etc.
There are modular regulators to create Master-Slave systems. The level and algorithm of operation are set on the master device, the others repeat the settings, which are transmitted via communication lines.
Typical wiring mistakes
If the dimmer is connected to the luminaire and the brightness cannot be adjusted or the lamp does not shine at all, the first thing to check is compatibility (or better to check it before installation when you buy it). If the luminaire may not be dimmable or dimmable, you should look for the Dimmable marking on it. When choosing a dimmer, you need to determine what load it is designed for - this is also you can This can also be determined by the marking.
| Letter marking | Symbol | Load type | Compatible lamps |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | Active (ohmic) | Incandescent | |
| C | Capacitive reactive | With electronic ballast (electronic transformer) | |
| L | Reactive of inductive nature | Low-voltage halogen lamps with a conventional transformer |
In addition, the lighting system may not work due to common mistakes in the installation - switching the device instead of breaking the phase wire to break the neutral, etc. To avoid this, the usual care in installation is needed.
Also errors of choice can be related to the power of the load - each dimmer has its own limit. You should buy devices with a margin of 15...20% on the power of the luminaire. If you follow this simple rule, the dimmer will work long and reliably.
Related articles: