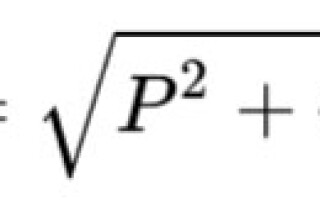All of us are daily confronted with electrical appliances, it seems that without them, our life stops. And each of them has a power in the technical manual. Today we will understand what it is, learn the types and methods of calculation.
Contents
Power in an AC circuit
Electrical appliances plugged into electrical circuits operate in an alternating current circuit, so it is under these conditions that we will look at power. First, however, let's give a general definition of the concept.
Power - A physical quantity representing the rate at which electrical energy is converted or transmitted.
In a narrower sense, electrical power is said to be the ratio of the work done in a period of time to that period of time.
If we paraphrase this definition less scientifically, we say that power is a certain amount of energy consumed by a consumer in a certain period of time. The simplest example is an ordinary incandescent light bulb. The rate at which a light bulb converts the electricity it consumes into heat and light is its wattage. Accordingly, the higher the initial rate of the light bulb, the more energy it will consume and the more light it will give off.
Since in this case there is not only the process of converting electricity into some other process (light, heat, etc.).light, heat, etc.), but also the process of oscillation of the electric and magnetic field, there is a phase shift between current and voltage, and this must be taken into account in further calculations.
When calculating power in an alternating current circuit, it is customary to distinguish between active, reactive and total components.
The concept of active power
The active (useful) power is that part of the power which is used to directly convert electrical energy into other forms of energy. It is designated by the Latin letter P and measured in Watt (Watt).
Calculated by the formula: P = U⋅I⋅cosφ,
where U and I are the rms value of voltage and current respectively, cos φ is the cosine of the phase angle between voltage and current.
IMPORTANT! The previously described formula is suitable for the calculation of circuits with circuits at 220VHowever, heavy duty machines normally use a circuit with 380 volts. If this is the case, multiply this by the root of three or 1.73.
The concept of reactive power
Reactive "harmful" power is the power generated during the operation of electrical appliances with inductive or capacitive loads, and reflects the electromagnetic fluctuations that occur. Simply put, it is the energy that is transferred from the power supply to the consumer and then fed back into the grid.
It is naturally not possible to use this component in the case, moreover, it harms the power supply network in many ways, so they usually try to compensate for it.
This value is denoted by the Latin letter Q.
REMEMBER! The reactive power is not measured in usual watts (Wattbut in volt-ampere reactive (WAR).
Calculated by the formula:
Q = U⋅I⋅sinφ,
where U and I are RMS voltages and currents respectively, sinφ is the sine of the phase angle between voltage and current.
IMPORTANT! This value can be either positive or negative in the calculation, depending on the phase motion.
Capacitive and Inductive Loads
The main difference between reactive (capacitive and inductive) loads are inherently capacitive and inductive loads that store energy and feed it back into the grid.
An inductive load first converts the energy of an electric current into a magnetic field (during half a half-period), and then converts the energy of the magnetic field into electric current and transmits it to the mains. Examples are asynchronous motors, rectifiers, transformers, electromagnets.
IMPORTANT! With inductive loads, the current curve always lags behind the voltage curve by half a half period.
A capacitive load converts the energy of an electric current into an electric field and then converts the energy of the resulting field back into an electric current. Both processes again run for half a half period each. Examples are capacitors, batteries, synchronous motors.
IMPORTANT! During a capacitive load, the current curve is ahead of the voltage curve by half a half period.
Power factor cosφ
Power factor cosφ (which reads cosine phiis a scalar physical quantity reflecting the efficiency of electrical energy consumption. Simply put, the cosφ coefficient shows the presence of the reactive part and the magnitude of the resulting active part relative to all power.
The cosφ factor is found through the ratio of the active electrical power to the total electrical power.
NOTE! In a more accurate calculation, nonlinear distortions of the sinusoid should be taken into account, however, in normal calculations they are neglected.
The value of this factor can vary from 0 to 1 (if the calculation is carried out as a percentage, then from 0% to 100%). From the calculation formula it is not difficult to understand that the greater its value, the greater the active component, and therefore the better the performance of the device.
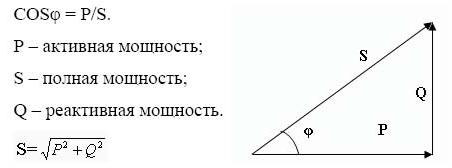
The concept of total power. The power triangle
Total power is a geometrically calculated quantity equal to the root of the sum of the squares of the active and reactive powers, respectively. It is denoted by the Latin letter S.
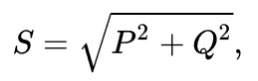
You can also calculate the total power by multiplying the voltage and current, respectively.
S = U⋅I
IMPORTANT! The total power is measured in volt-amperes (VA).
The power triangle is a convenient representation of all the previously described calculations and relationships between active, reactive, and total power.
The cathetuses represent the reactive and active components, while the hypotenuse represents the total power. According to the laws of geometry, the cosine of the angle φ is equal to the ratio of the active and total components, i.e. it is the power factor.
How to find the active, reactive and total power. Calculation example
All calculations are based on the previously mentioned formulas and the power triangle. Let's look at a problem that is most common in practice.
Usually, electrical appliances are labeled with the active power and the cos ϕ value. With these data it is easy to calculate the reactive and total components.
To do this, divide the active power by the cosφ and obtain the product of current and voltage. This will be the total power.
Then, from the power triangle, we will find the reactive power equal to the square of the difference between the squares of the total and the active power.
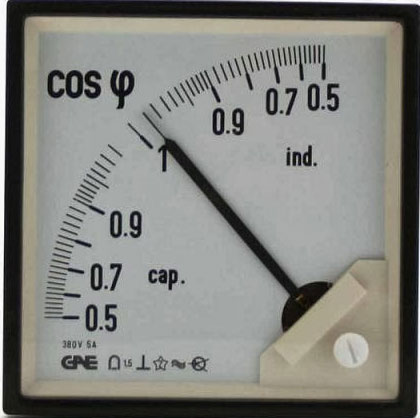
How cosφ is measured in practice
The value of cos ϕ is usually stated on the labels of electric appliances, however, if it is necessary to measure it in practice, a special device, a a phasometer. Also a digital wattmeter can easily cope with this task.

If the resulting cosφ is low enough, it can be compensated practically. This is done mainly by including additional devices in the circuit.
- If it is necessary to correct for the reactive component, then a reactive element should be included in the circuit, acting in the opposite direction to the already functioning device. To compensate the operation of an induction motor, for example an inductive load, a capacitor is connected in parallel. For the compensation of the synchronous motor an electromagnet is connected.
- If it is necessary to correct nonlinearity problems, a passive cosφ corrector is introduced into the circuit, for example a high inductance choke connected in series with the load.
Power - this is one of the most important indicators of electrical appliances, so to know what it is and how it is calculated, it is useful not only for schoolchildren and people who specialize in technology, but also for all of us.
Related articles: