Operational remote monitoring of object position and quality is impossible without electronics. The latest developments in this area are RFID tags. They have a chip and memory, and are able to communicate the characteristics necessary for accounting at a distance using radio signals.

Contents
What is an RFID tag?
RFID is the radio frequency identification of objects. It is based on automatic reading or writing data stored in RFID transponders or tags, which is the same device sometimes called an RFID tag. Readers, readers, readers, and interrogators are used as readers.
A distinction is made between RFID standards:
- Near-field identification with the ability to read up to 20 cm;
- Intermediate identification, which allow to receive information at a distance of 0.2-5 m;
- Long-range identification that operates at a distance of 5-300 m.
The composition of tags includes:
- Integral circuit. Its task is to:
- store, process information;
- Modulate and demodulate the radio frequency signal.
- Antenna, through which by receiving and transmitting the signal the identification of objects is provided.
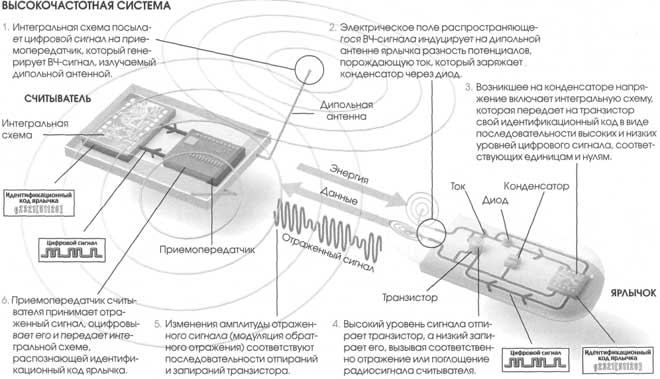
How does RFID work?
The object to be controlled is equipped with a tag. Then its primary radiofrequency identification is carried out - a portable or stationary reader is used. Control points are defined in which readers with antennas are placed.
The interrogator reads the data from the tag, caught in the electromagnetic field created by the scanner antenna. The information enters the system, where an accounting document is formed.
Classification of RFID tags
Radio-frequency identification tags are distinguished by some characteristics by which they are classified. These are:
- Power source. Passive RFID tags do not have it, active and semi-passive ones are equipped with a battery.
- The frequency at which the devices operate.
- Design.
- The memory type of the RFID tags.
According to the power supply
According to this indicator, the transponders can be:
- passive;
- active;
- semipassive.
Passive devices have no built-in power supply. They work on the electric current, which is induced in the antenna that receives the electromagnetic signal from the reader. Its power is sufficient for the functioning of the CMOS chip in the tag, issuing a response signal.
Tags of the passive type are made of silicon, polymer semiconductors. Each is provided with an identification number, has a non-volatile EEPROM-type memory. Their dimensions depend on the size of the antennas - the devices can be no larger than a postage stamp or as big as a postcard.
Low-frequency tags provide radio-frequency identification at a distance of 30 cm. Their commercial use is placing them in stickers (stickers), implanting them under the skin. Devices with radio-frequency exchange in the HF range are able to work at a distance of 1-200 cm; in the microwave and UHF range - 1-10 m.
Active devices have their own power supply that lasts up to 10 years. They differ in the range measured in hundreds of meters. The tags have a larger size and memory capacity.
The devices generate powerful output signals, which makes it possible to use them in environments aggressive for the radio-frequency signal - water, metals. They may contain additional electronics, sensors registering the temperature of perishable goods, atmospheric conditions, measuring lighting, vibration and humidity.
Semi-passive type of tags is similar to passive devices. The difference is the technology is equipped with a battery, which powers the chip. They have better characteristics, longer range. The latter depends on the sensitivity of the reader.
According to the type of memory used
According to this indicator, there are 3 types of RFID tags:
- RO. In devices with this memory you can write data only once - it is done during the manufacturing process. It is not possible to add additional information. Labels are used for identification purposes. They cannot be tampered with.
- WORM. Tags have an identifier, a block of memory in which data is written. Later they can be read out many times.
- RW. Tags with an identifier, a block of memory. The latter is used to write/read data, which can be repeatedly overwritten.
By operating frequency
RFID tags operate at different frequencies:
- 125 kHz (LF band). They are a passive type of device. They have a low cost. Due to their small size and physical parameters, they are used as subcutaneous tags when chipping people and animals. Disadvantage is the wavelength, which creates problems with reading and transmitting data at high range.
- 13.56 MHz (HF band). The systems are cheap, there are no licensing problems. They are environmentally friendly, deeply standardized, and come in a wide range of models. Tags of this group also have problems when reading information from long distances. This is especially evident in the presence of metal, high humidity. Mutual overlapping of signals during reading is possible.
- 860-960 MHz (UHF band). Devices allow the use of RFID technology at distances beyond the capabilities of the tags from the above groups. Many of the standards that ensure their work, provide anti-collision mechanisms to protect signals from mutual overlapping. Advantages of the devices include the presence of the immutable TID memory field, in which the product code and brand, as well as its identification number, are recorded at the manufacturing stage. The latter ensures password protection of the data on the tags from unauthorized writing and reading.
Reader readers
These are devices that automatically read or record the information that RFID cards store. They can function autonomously or be operated as an RFID-operated device with a connection to the accounting system at all times.

Readers can be:
- stationary;
- mobile.
Stationary readers are fixed on doors, walls, forklifts, stackers. They are fixed near the conveyor that moves the products, made in the form of locks that are inserted into the table.
This group of RFID readers has a large reading area, power. They are able to process data from dozens of tags at once. Interrogators are connected to PC, PLC, integrated into DCS. They register the movement, characteristics of objects, identify their position in space.
Mobile readers have a shorter range and often have no permanent connection to accounting and control systems. The data read from the cards are stored in the internal memory, and then they are reset to a computer.
Using
Radio-frequency identification systems are used in different spheres. Tags are placed on the goods in the store, that allows to control their movement, sale. They are used for the identification of people. Logistic systems and payment systems are suitable for using RFID technology. With its help, animals on farms, pastures are monitored.
Related articles: