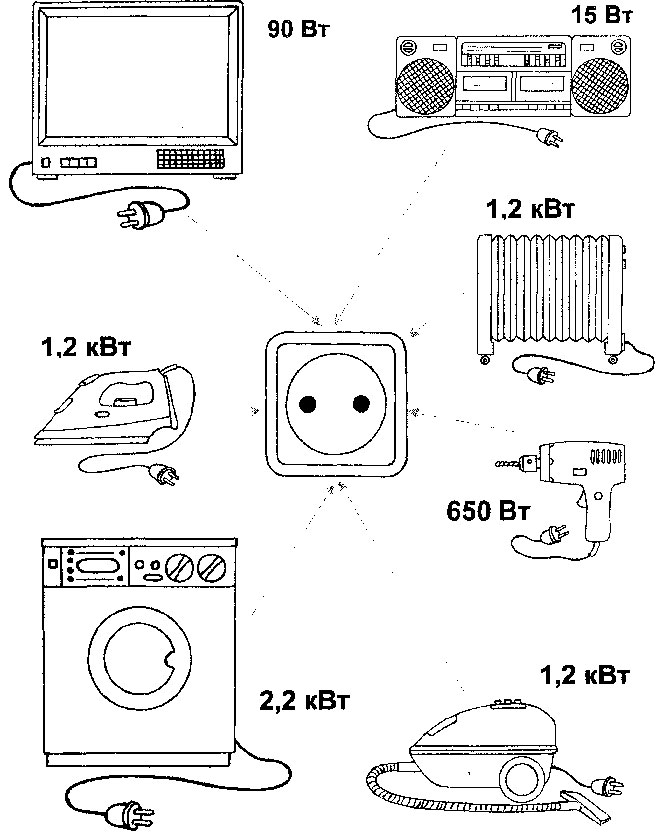
To describe the properties of electricity consumers, a parameter called the rated power is used. Its value is usually specified in the data sheet or marked on the product itself.
While the power of some electrical appliances and devices is indicated in "watts", the value "kilowatt" is used to indicate the technical parameters of more powerful electrical consumers.
When calculating the total power consumption of a network, installing switching and protection equipment, selecting the cross-section of wires, many are faced with the need to operate with one particular unit of measurement.
Contents
Introduction to Measurement
The generally accepted unit of measure for power is the watt (W). It usually describes the rate at which energy is being converted or consumed. By definition, power is the ratio of work (energy expended) to the time it takes to do the work. In turn, the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI) has always been the Joule.
The value "1 watt" in question corresponds to the work of one Joule produced in one second (J/s). In electrical engineering, for example, there are special wattmeters, which measure the power of an electric current or electromagnetic signal.
The unit gets its name from the Scottish-Irish inventor James Watt (Watt). This creator of the first steam engine first used it in describing the capabilities of a power machine. The Watt was put into circulation in 1882 and basically replaced the traditional units of calculation that had existed before: foot-pound-power-per-minute and tractive horsepower. The first unit of power corresponded to 2,260 watts. As for the second, it is still in use today: "metric horsepower" equals approximately 735 watts.
As a unit named after a scientist, it is subject to the rules of spelling originally adopted in the SI system. The name Watt is written with a lower case letter, and the designation W (W) is written with a capital letter, including in the designation of non-system units.
The use of the watt is not limited to the field of electrical engineering, it measures torque of power systems, the flow of thermal and acoustic energy, and the intensity of ionizing radiation.
One watt - is it a lot or a little? The transmitters of cell phones usually have a power of 1 watt. Incandescent light bulbs used in household fixtures consume 25, 40, 60, 100 watts, the TV and refrigerator 50-55, the microwave and vacuum cleaner 1000, and the washing machine 2500 watts.

Often in practice you need to convert watts to kilowatts or, conversely, convert kilowatts to watts.
Converting watts to kilowatts
To avoid writing lots of zeros or applying a 10³ multiplier, the unit of measure with the prefix "kilo" is used in the power designation. A kilowatt is a decimal multiple of 1000 watts. The phrase itself means that the digital value of power in watts is reduced by one thousand times. How do you convert from watts to kilowatts? Technically, you can do the conversion by moving the comma three positions to the right.
The following table gives examples of watts to kilowatts.
| kW | 1,75 | 0,12 | 2,01 | 0,0002 | 10,8 |
| W | 1750,0 | 120,0 | 2010,0 | 0,2 | 10800,0 |
Often it is necessary to do the reverse conversion. Knowing that a watt is a fraction and is 1/1000th of a kilowatt, the power value should be divided by a thousand. Technically, the conversion is achieved by moving the comma three digits to the left, after which we get the required number of watts in a kilowatt.
| W | 1600 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 10000,0 | 0,12 |
| kW | 1,6 | 0,005 | 0,02 | 10,0 | 0,00012 |
The difference between kilowatts and kilowatt-hour
In electrical engineering there is a value called kilowatt-hour, which is measured by electricity meters. Many people confuse the terms, not seeing any difference between the definition of "kilowatt" and "kilowatt-hour," considering the values as one parameter.
Despite the similarity of their names, they are completely different. The kilowatt hour is used to measure the amount of electrical energy produced or consumed per unit of time. Specifically, a kilowatt-hour refers to the energy consumed by a consumer of 1 kilowatt-hour for 1 hour. In contrast, a kilowatt is a unit of power that denotes the intensity of electricity generation or consumption.
Example: A recessed LED light is equipped with a 35 W LED bulb. As long as it will work for 1 hour it will consume 35Wh, for 2 hours 2x35=70Wh. In continuous operation for 5 days/120 hours our luminaire will consume 35x120=4200 W∙h or 4,2 kW∙h.
Relationship to basic and multiple power units
Watt is a derived power unit, so in practice it is sometimes necessary to define the value of a parameter in relation to the basic units of the International System of SI. In technical calculations, the following correspondences to the basic units are used:
- W = kgm²/s³;
- W = Nm/s³;
- W = W-A.
The parameter has universal application and is used equally in technical developments in a wide variety of fields.
In thermal engineering, the unit of measurement of heat power 1 cal/h is used, which is not part of the international SI system. Our considered value is related to it by the ratio: 1 W = 859.85 cal/hour.
Often, for ease of reference, a large amount of energy in a power plant or power package can be referred to as a watt with the prefix "mega" or "giga":
- A megawatt is denoted by MW/MW and corresponds to 106W;
- Gigawatt (abbreviated GW/GW) equals 109Watt.
On the contrary, in low-current information networks, electronic gadgets and modern radioelectronic equipment, power is measured in fractions of a watt:
- A milliwatt (mW, mW) is 10-3 Watt;
- A micro-watt (µW) is 10-6 W.
Using these ratios, you can always convert most parameters to the required power units.
Related articles: