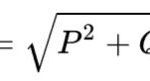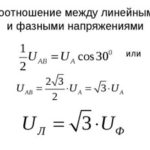The characteristics of electrical equipment are power and current consumption. If only one of these values is specified, then you need to convert amperes to kilowatts. These conversions are needed to determine the ratings of circuit breakers and select the cross-section of supply conductors, calculate and design the power supply system, and record the electricity consumed.
All the necessary concepts for calculations are available in the school physics course, except for the nuances of using reactive loads. How many amperes in a kilowatt is determined for DC and AC the same way, provided active consumers are used. An inductive or capacitive load requires a power factor to be considered. There are several formulas for how to convert amps to kilowatts, and they do not require complex calculations.
Translation for 220 volt networks
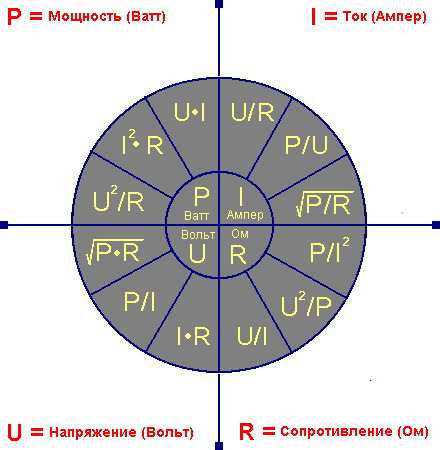
The power formula combines the supply voltage, current and power consumption:
P=U-I
In circuits with reactive loads, where inductive and capacitive loads are present, the active power value is corrected by entering a power factor into the expression:
Pa=U-I-cosø
The conversion of amperes to kilowatts for single-phase circuits is made by substituting the initial values into the formulas given. The first is used in the case of an active load and the second in the case of a reactive load (electric motors). By substituting current and voltage in volts and amperes, the power is obtained in watts. For high-power loads, it is customary to convert watts to a more convenient value:
1000 watts = 1 kW.
These are the basic rules for converting electrical quantities.
380 volt power lines.
The conversion of current values into power for a three-phase network does not differ from the above, only you need to take into account the fact that the current consumed by the load is distributed over the three phases of the network. The conversion of amperes to kilowatts is done taking into account the power factor.
In a three-phase network, you need to understand the difference between phase voltage and line voltage, as well as line and phase currents. There are also two possible ways of connecting the consumers:
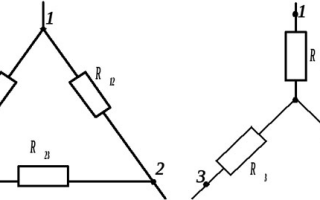
- Star. Uses 4 wires - 3 phase wires and 1 neutral (neutral) wire. Using two wires, phase and neutral, is an example of a single-phase 220 volt network.
- Triangle. 3 wires are used.
The formulas for how to convert amps to kilowatts for both types of connection are the same. The only difference is in the case of a delta connection to calculate separately connected loads.
Star connection
If you take the phase conductor and the neutral conductor, there will be a phase voltage between them. The line voltage is the voltage between the phase conductors and is greater than the phase voltage:
Ul = 1.73-Uf.
The current flowing in each of the loads is the same as in the mains conductors, so the phase and line currents are equal. If the load is uniform, there is no current in the neutral conductor.
The conversion of amperes to kilowatts for star connection is made according to the formula:
P=1.73-Ul-Il-cosø
Delta connection
With this type of connection, the voltages between the phase wires are equal to the voltages at each of the three loads, and the currents in the wires (phase currents) are related to the line currents (flowing in each load) by the expression:
Il = 1.73-If.
The translation formula is the same as the one given above for "star":
P=1.73-Ul-Il-cosø
This translation is used when selecting fuses to be installed in the phase conductors of the supply network. This is true when using three-phase consumers - electric motors, transformers.
If single loads connected in delta are used, the protection is placed in the load circuit, and the phase current value is used in the formula for the calculation:
P=3-Ul-If-cosø
Inverse conversion of watts to amperes is done using inverse formulas, taking into account the connection conditions (type of connection).
The calculation can be avoided by a translation table, which contains the values for the active load and the most common value cosø=0.8.
Table 1. Conversion of kilowatts to amperes for 220 and 380 volts, corrected for cosø.
| Power, kW | Three-phase alternating current, A | |||
| 220 В | 380 В | |||
| cosø | ||||
| 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | |
| 0,5 | 1.31 | 1.64 | 0.76 | 0.95 |
| 1 | 2.62 | 3.28 | 1.52 | 1.90 |
| 2 | 5.25 | 6.55 | 3.,4 | 3.80 |
| 3 | 7.85 | 9.80 | 4.55 | 5.70 |
| 4 | 10.5 | 13.1 | 6.10 | 7.60 |
| 5 | 13.1 | 16.4 | 7.60 | 9.50 |
| 6 | 15.7 | 19.6 | 9.10 | 11.4 |
| 7 | 18.3 | 23.0 | 10.6 | 13.3 |
| 8 | 21.0 | 26.2 | 12.2 | 15.2 |
| 9 | 23.6 | 29.4 | 13.7 | 17.1 |
| 10 | 26.2 | 32.8 | 15.2 | 19.0 |