12 to 220 V voltage converters are used wherever there is a need to connect electrical devices which consume standard AC current to a source of alternating voltage. In many cases, this network is not available. The use of an autonomous gasoline generator requires compliance with the rules of its maintenance: continuous monitoring of the operating fuel level, ensuring ventilation. The use of converters in conjunction with car batteries allows you to solve the problem in the best way.
Contents
Designation and principle of operation
What is a voltage converter. This is the name of the electronic device that changes the magnitude of the input signal. It can be used as a device that increases or decreases its value. After conversion, the input voltage can change both its magnitude and frequency. Such devices that change the DC voltage (convert it) into an AC output signal are called inverters.

Voltage converters are used both as an autonomous device supplying AC power to consumers, and can be part of other products: systems and uninterruptible power supplies, devices to increase DC voltage to the required value.
Inverters are harmonic voltage generators. A direct current source with a special control circuit creates a mode of periodic switching of polarity. As a result, an alternating voltage signal is formed on the output contacts of the device, to which the load is connected. Its magnitude (amplitude) and frequency are determined by the elements of the converter circuit.
The control device (controller) sets the frequency of switching of the source and the form of the output signal, and its amplitude is determined by the elements of the output stage of the circuit. They are designed for the maximum power consumed by the load in the AC circuit.
The controller is also used to control the output signal, which is achieved by controlling the pulse width (increasing or decreasing the pulse width). Information about changes in the output signal value on the load comes to the controller through the feedback circuit, on the basis of which the control signal is formed in the controller to maintain the necessary parameters. This method is called PWM (pulse width modulation) signals.
Power output switch circuits of 12V voltage converter can use powerful compound bipolar transistors, semiconductor thyristors, field-effect transistors. Controller circuits are made on microcircuits, which are ready-to-operate devices with necessary functions (microcontrollers), specially designed for such converters.

The control circuit provides the key sequence to provide the inverter output with the signal required for the normal operation of the consumer devices. In addition, the control circuitry must ensure the symmetry of the half-wave output voltage. This is especially important for circuits that use step-up pulse transformers at the output. For them, the voltage constant component that can appear if the symmetry is broken is unacceptable.
There are many variants of voltage inverter circuits (VIC), but there are 3 basic ones:
- Non-transformer bridge IN;
- Transformer with a zero conductor;
- Bridge circuit with a transformer.
Each of them finds application in its field depending on the power supply used in it and the required output power to power the consumers. Each of them must have protection and signaling elements.
The protection against undervoltage and overvoltage of the DC source determines the range of operation of the inverters "by input". The over-voltage and undervoltage AC output protection is necessary for the normal operation of the consumer's equipment. The operating range is set according to the requirements of the load used. These types of protection are reversible, i.e. when the equipment is restored to normal operation can be restored.
If the protection has tripped due to a short circuit in the load or an excessive increase in output current, a thorough analysis of the cause of the event is necessary before continuing to operate the equipment.
The 12V inverter is the most suitable for creating a local power system. The availability of a large number of cars and 12-volt DC batteries allows them to be used to supply user requests. Such networks can be created in a variety of places, starting from your own car. They are mobile and do not depend on the parking place.
Varieties of 12 to 220 volt converters
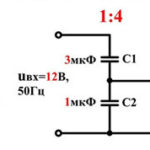
Simple converters from 12 to 220 are designed for small power consumers. Requirements for the quality of the output supply voltage and the shape of the signal are low. Their classic circuits do not use PWM microcontrollers. The multivibrator, assembled on I-NE logic elements, generates electrical pulses with a frequency of 100 Hz. A D-trigger is used to create an antiphase signal. It divides the frequency of the master oscillator by 2. The counter-phase signal in the form of rectangular pulses is generated at the direct and inverse outputs of the trigger.
This signal via buffer elements on logic elements NOT controls the output circuit of the inverter, which is built on key transistors. Their power determines the output power of the inverters.
Transistors can be composite bipolar and field effect transistors. The drain or collector circuits include half of the transformer's primary. Its secondary winding is designed for an output voltage of 220 V. Since the trigger has divided the frequency of the 100 Hz multivibrator by 2, the output frequency will be 50 Hz. This value is necessary to power the vast majority of domestic electrical and radio equipment.
All circuit elements are powered by the car battery with additional stabilization and high-frequency noise protection elements. The battery itself is also protected from them.
The schemes of simple transducers do not include protection and automatic control elements. The frequency of the output signal is determined by the choice of capacitor and resistor resistance, included in the circuit of the oscillator. As the simplest short-circuit protection in the load, a fuse is used in the circuit supplying the circuit to the car battery. It is therefore necessary to always have a spare set of fuses.
More powerful modern DC to AC converters are made by other circuits. PWM controller sets the operating mode. It also determines the amplitude and frequency of the output signal.
The 2000W converter circuit (12V+220V+2000W) uses a parallel connection of power active elements in its output stages to obtain the required output power. With this circuit design the currents of the transistors are summed up.
But a more reliable way to increase the power parameter is to combine several DC/DC converters as input to a common DC/AC (direct current/alternating current) inverter whose output is used to connect a heavy-duty load. Each DC/DC converter consists of an inverter with a transformer output and a rectifier for that voltage. There is a DC voltage of about 300 V on the output terminals. They are all connected in parallel on the output.
It is difficult to get more than 600 W of power from one inverter. The whole circuit of the device is powered by the battery voltage.
Such circuits are provided with all kinds of protection, including thermal protection. Temperature sensors are mounted on the surfaces of the heatsinks of the output transistors. They produce a voltage that depends on the degree of heating. The threshold device compares it with the one set at the design stage and gives a signal to stop the operation of the device with the corresponding alarm. Each type of protection is equipped with its own signaling device, often audible.
Additional forced cooling is used by means of an air cooler installed in the housing, which automatically activates at the command of the corresponding thermal sensor. In addition, the case itself is a reliable heat sink, since it is made of corrugated metal.
According to the form of the output voltage signal
Single-phase voltage converters can be divided into two groups:
- With a pure sine wave output;
- With a modified sinusoidal output.
In the first group of inverters, a high-frequency converter creates a constant voltage. Its value is close to the amplitude of the sinusoidal signal, which is required at the device output. In the bridge circuit, the constant voltage is extracted from this voltage by pulse width modulation of the controller and a low-pass filter, which is very close to a sinusoidal shape. The output transistors open several times in each half period for a time varying according to the harmonic law.
A pure sine wave is required for devices that have a transformer or motor as an input. Most of today's devices allow power supply with voltages whose shape approximates a sine wave. Products with switched-mode power supplies have particularly low requirements.
Transformer devices
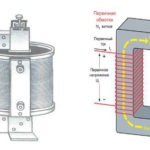
Voltage converters can contain transformers. In inverter circuits, they are involved in the operation of the master blocking generators, which produce pulses that are close to rectangular in shape. As part of such a generator a pulse transformer is used. Its windings are connected in such a way as to create a positive feedback, resulting in creation of undamped oscillations.
The magnetic core is made of an alloy, which has a high magnetic bandwidth. This allows the transformer to operate in an unsaturated mode. Various types of ferrite, permalloy have these properties.
Transformer blocking generators have been replaced by multivibrators. They use a modern element base and have a higher frequency stability than their predecessors. Furthermore, multivibrator circuits change the operating frequency of the oscillator in a simple way.
In modern models of inverters the transformers work in the output stages. Through the lead from the center point of the primary winding to the collectors or drains of the transistors used in them, the supply voltage from the battery is applied. The secondary windings are calculated, using a transformation ratio, to the AC voltage of 220 V. This value is used to power most domestic consumers.
Related articles: