It's not just touching an uninsulated wire that poses a high voltage electrical hazard. A power line wire snapped during a storm or thunderstorm is just as dangerous. Within a certain radius of a live wire there is a strong electric field that is dangerous to humans. The insidiousness of the phenomenon is that it cannot be seen or felt beforehand, it does not emit any sound or smell. However, once broken off, the cable poses a serious danger of being struck by step voltages.

Contents
What is step voltage
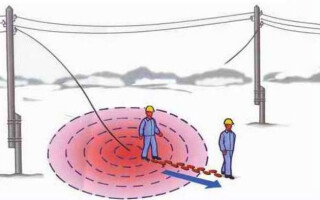
When a ground fault occurs, the cable radiates electricity. The current does not go anywhere, but creates a spreading area on the ground surface within a certain radius. Step voltage is a phenomenon that occurs between points in the zone of activity near an electric wire with a large current. The conditions under which the step voltage occurs are when the high voltage cable touches the ground or other surface. Causes of occurrence are as follows:
- Breakage of power line cable or local wire;
- Accident at a substation;
- Lightning striking an overhead line pole;
- Short circuit of high-voltage wires.
In the event of a break in an electrical substation, a staged automatic disconnection system is activated. First, the line is de-energized, but after some time the current to the damaged cable is reapplied. In some cases the cause of the fault is eliminated automatically: The overhead conductor can be blocked by branches or birds. Therefore, even a de-energized cable is a potential step voltage hazard.
Maximum radius of impact
The radius of step voltage is directly related to the voltage applied to the severed wire. Electricity over 360 volts is a potential hazard to humans. At the minimum value, an area of step voltage closer than 3 meters to the source of electricity is particularly dangerous. When the value rises to 1,000 volts, an area up to 5 meters is considered dangerous.
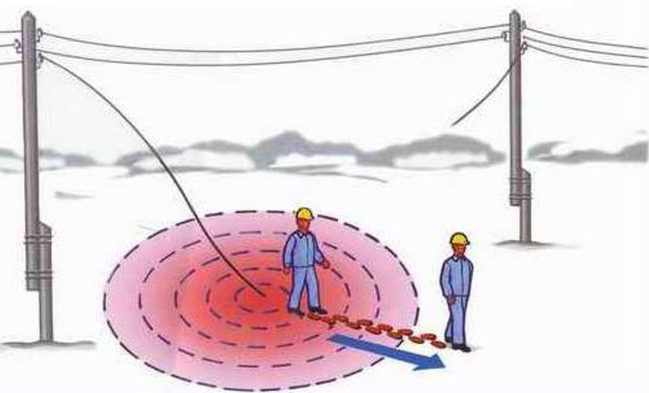
When a power line breaks or an accident at a substation, the current source is much higher than 1,000 volts. In this case, the impact radius reaches 8 meters. At higher currents, the danger zone is much greater than this value, but the current at a distance of 12-15 meters from the source is not fatal. The safe electrical value for step voltage is 40 volts. At a distance of 8 to 20 meters from the source, the step voltage rarely exceeds this value.
The greatest striking power occurs when a person has one foot on the wire and the other foot (80 cm) away. In this case, the distance between the feet plays no less a role than the distance from the source. It is at this distance that the potential difference between the two points arises, causing an electric shock to a person.
The level of danger increases considerably in wet weather. For example, wet asphalt or soil is a better conductor than dry ground. It has a higher resistance. Therefore, you should be as careful as possible when it is raining or swampy.
Rules for moving in a step voltage area
The best way to avoid becoming a victim of step voltage is to avoid the danger of being struck. This requires extreme caution, especially in wet weather and limited visibility. When crossing power lines in windy conditions, make sure there are no broken wires. In addition to cables that have fallen to the ground, sources wrapped around poles or trees pose a danger. If it is found, you should go around the wire 10-15 meters away. In case the cable has fallen directly near the person, it is necessary to remain calm and follow the following algorithm:
- Stand up straight on your two feet, bringing your heels together as much as possible;
- Locate the closest path away from the potential voltage source, avoiding obstacles;
- Gently make a turn in the desired direction;
- Move away from the source with as few steps as possible;
- After leaving the danger zone, contact the emergency department immediately to eliminate the hazard.
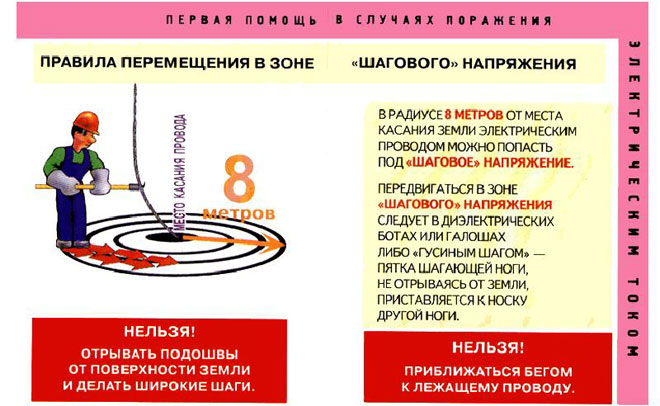
The most effective way to get out of the danger zone is to move in goose steps. This means that the front heel practically touches the toe of the back foot, the foot is moved to the length of the foot when stepping. In this way the distance between the feet is kept to a minimum, which is not enough to cause dangerous tension.
This method of movement takes a lot of energy, but it is the safest. You should move as quickly as possible, but without rushing or panic (according to statistics, panic is the cause of 80% of accidents during any emergency). Running or trying to jump out of the danger zone is strictly prohibited.
You can gradually increase the step interval by a few centimetres, but it is recommended to do it at a distance of 5-7 metres from the source of danger. Signs of step tension are tingling in the limbs, with a larger value of tension - cramps, sharp pain. In exceptional cases, paralysis of the legs is possible. Spasm of the limbs is especially dangerous, because it causes involuntary contraction of the muscles and may lead to a fall (after which it is almost impossible to leave the dangerous area independently).
Another effective, but forbidden for safety reasons, is jumping on one leg. Making contact with the ground with only one limb in this case is completely safe, but if you fall on the other leg or arm, there is a risk of life-threatening injury.
How to get a person out of the step-in zone
If a person falls within a dangerous radius of the source, it is advisable to get out on one's own. However, if the person cannot leave it by himself, he must be pulled out. This should be done in the same way as when leaving the zone: by small steps. It is necessary to wrap your hands with dry clothes, in the best case - with insulating materials, and then slowly pull the person out in small steps.
Clothing with insulation: rubberized boots and gloves can help when stepping out of a live area. It is this type of clothing that is used by workers maintaining power lines and EMERCOM services for troubleshooting and hazards.

After leaving the danger zone
The first thing to do is to assess your condition (or the condition of the rescued by providing first aid to the injured person). Usually after the exit the person feels normal, but in some cases there are problems with health. It is necessary to focus and assess your condition, pay attention to your heart and lungs. According to WHO statistics, 20% of people have problems with these organs after independently exiting the step electricity zone. After that, it is necessary to contact the EMERCOM to eliminate the danger, and if you suspect a bad health condition, call an ambulance. It will not be superfluous to pass a medical examination for several days.
Related articles: