Time relays are designed to implement a preset sequence of turning on and off various devices, circuit elements, alarms. With the help of time control devices are formed by the specified delays of switching and control. Most of the designs of time control devices provide for adjustment of the duration of the on or off interval. Depending on the design of the time relay, the adjustment can be done mechanically, electronically or programmatically.

Contents
Operating Principle of Time Relays
The general principle of the time relay is to provide a time delay for switching a contact group on, off, or over. Implementation of the delay depends on the design features of the device. Common differences in the different types of relays is in the switching of the executive part. According to this feature, two groups of relay devices are distinguished:
- with a delayed shutdown;
- with a delay on.
Many relays allow to change the type of switching or have both.
The principle of timing and contact control depends on the design of the relay, but the general algorithm is as follows:
- At start-up, the contact group is actuated, organized according to the type of switching (for time relays with delayed switching the contacts are closed);
- at the same time the time delay mechanism is wound up (the clock generator in electronic devices is started);
- after a set interval, the contact group reverses its state.
The three-position relay differs in a more complex algorithm of operation. The sequence of operation is as follows:
- Circuit open.
- Start. The circuit is closed, the countdown starts.
- The circuit ends. Circuit closed.
In cyclic devices, the above sequence is repeated many times.

The timing is started manually or automatically by direct closure of the power contacts or via an electromagnet acting on the mechanism.
The time relay with delayed activation works in the same way.
Types and classification
The following types of time interval timing devices are used, according to which they are classified
- pneumatic;
- motor;
- electromagnetic;
- clock (anchor);
- electronic.
The next difference lies in the value of the supply voltage of the controlling electromagnet, which carries out the initial actuator or mechanism and the electromagnet, which controls the switching of output terminals. The most widespread types of time relays are as follows voltage:
- 12 V DC voltage;
- 24 V DC;
- 220 volt AC.
Time relays for 380V are used in three-phase networks with delta connection.
The operating voltage is different from the switching voltage, which depends on the design and capacity of the contact groups. The operating voltage is necessary for the function of the device and must be within strictly defined limits. The minimum switching voltage limit is not limited. If the permissible values are exceeded, there may be a breakdown between the contacts.
The same requirements are imposed on the switching current, exceeding the permissible value fraught with the risk of burning and sintering of contact groups, the occurrence of electric arcs at the moment of opening.
The operating voltage is dictated by safety requirements. It is taken into account that the higher the power of the control solenoid, the higher the current consumption of the solenoid. The most widespread are 24 volt time relays, because in this case there is the most advantageous combination of voltage and current consumption of the relay.
In cars, time relays with a supply voltage of 12 V are used, because this is the most common value of the on-board network of the car. For example, time relays for control of windshield wipers and direction indicators. Contact groups of these devices are highly reliable, have a large margin on the value of current to avoid burning, as the safety of traffic on the roads depends on faultless operation.
All these types allow the production of multichannel time relays. In such a case, switching of circuits is performed by several independent groups of contacts. In simple designs, the groups are triggered simultaneously, in complex - depending on the programmed algorithm.
A great variety in the number of groups and algorithm of operation is provided by electronic devices. Circuits designed with the use of microcontrollers have small dimensions, which are limited only by the type and size of actuating elements that switch the load.

The reliability of the devices and mechanisms depends on the compliance of the design with the requirements. Selection of a time relay is the selection of the type that meets all the requirements, including:
- operating voltage;
- switching voltage and current;
- duration of time intervals;
- accuracy of time intervals setting;
- operation on or off;
- on and off adjustment.
Cyclic time relays
This type of time relay automatically and continuously generates set intervals of time. If you ask why cyclic type relays are needed, we can say that they are most commonly used in automatic lighting control systems (street lighting, livestock farms, aquariums, etc.).
Electromagnetic
Electromagnetic devices are also called electromagnetic delay time relays. They have a simple design and are used in relay automation devices. The electromagnet winding additionally contains a short-circuited coil in the form of a copper cylinder, which prevents the rapid rise and fall of the magnetic flux, resulting in the armature of the moving system moving with a delay. The delay time for actuation is 0.07 to 0.11 seconds, and for release is 0.5 to 1.4 seconds. Disadvantages:
- Impossibility of delay time correction;
- operating only with direct current.
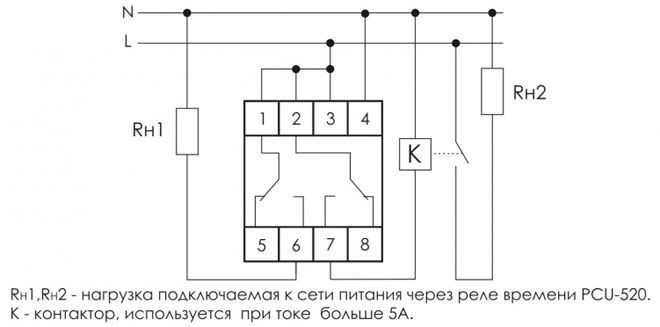
Pneumatic
The retarder in this design is a pneumatic damper, which is supplied with air through a calibrated hole. Its flow cross-section is regulated by a needle with a special screw.
Advantages: Does not require a power supply
Disadvantages:
- Low timing accuracy (over 10%);
- Sensitivity to air contamination.
Motor
Represents a synchronous motor which, through a reducer, transmits rotation to a shaft with contact groups. May include an electromagnetic clutch that disengages the motor shaft and gearbox. The holding time ranges from a few seconds to tens of hours.
Disadvantages:
- Low timing accuracy;
- ability to operate only in a narrow temperature range;
- The need for regular cleaning and lubrication of the mechanism.
With clock and anchor mechanism.
Built on the principle of mechanical watches. In industry, a current winding is used to wind the spring. Thus, the higher the current in the winding, the more the spring is compressed and the faster the movement moves. They are characterized by a low accuracy of time setting. Setting the mechanical relay is similar to adjusting the alarm clock.
Electronic
The most common class of devices. They are made on the electronic components. As the time setting element used clock frequency generator, or synchronization from the mains frequency.

They are characterized by the widest frequency tuning limits. The minimum interval is units of microseconds, and the maximum - days, months and years. The frequency steps are adjusted electronically (by means of switches) or programmatically (by changing the built-in program coefficients or through the interface from external equipment).
The hour, day or week relay is often an option in electronic clocks.
Electronic timing relays offer the widest range of control circuit options, including multi-channel versions or cyclic operation.
Semiconductor keys or electromagnets with different groups of contacts are used as the executive part to switch the relay load.
Advantages of electronic devices:
- The widest setting range of shutdown;
- the minimum size and weight;
- high reliability;
- the highest accuracy of setting time intervals.
Exposure accuracy depends only on the frequency stability of the master oscillator. The use of oscillators on quartz elements with thermal stabilization can achieve accuracy of thousandths of a percent.
DisadvantagesDisadvantages: The need for external power supply to operate the electronic components of the circuit.
Time relay circuits are of great variety. Among them there are both the simplest and complex ones based on microcontrollers.
Applications
Time relays are used in applications where it is necessary to observe strictly the intervals between switching on and off equipment, to provide signals at preset intervals.
The need to use one or another type of device is dictated by local conditions and requirements for their parameters.
Electronic devices are capable of replacing all of the above, provided there is an external power supply.
Related articles:






