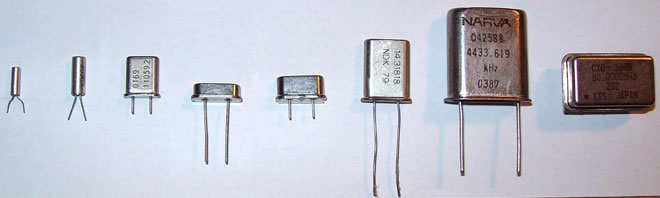
Quartz resonator is an electronic device based on the piezo effect, as well as mechanical resonance. It is used by radio stations, where it sets the carrier frequency, in clocks and timers, fixing in them an interval of 1 second.

Contents
What it is and why you need it
The device is a source that provides high-precision harmonic oscillations. It has, in comparison with counterparts, a greater efficiency of work, stable parameters.
The first examples of modern devices appeared in radio stations in 1920-1930 as elements with stable operation, able to set the carrier frequency. They:
- replaced the crystal resonators operating on segnaetium salt, which appeared in 1917 as a result of Alexander M. Nicholson's invention and were notable for their instability;
- they replace the former coil-capacitor circuit which was not very efficient (up to 300) and was affected by temperature changes.
A little later quartz resonators became an integral part of timers, clocks. Electronic components with an intrinsic resonance frequency of 32768 Hz, which in a binary 15-bit counter sets the time interval equal to 1 second.
The devices are used today in:
- quartz clocks, giving them accuracy regardless of ambient temperature;
- Measuring instruments, guaranteeing them a high accuracy of readings;
- sea echo sounders used in surveys and mapping the bottom, fixing reefs, shoals, finding objects in the water
- circuits corresponding to frequency synthesizing reference oscillators;
- circuits used in wave indicating SSB or telegraph signal;
- radios with a DSB signal at an intermediate frequency;
- bandpass filters Superheterodyne type receiverswhich are more stable and more robust than LC filters.
The devices are made with different housings. They are divided into lead wires, used in volumetric mounting, and SMD, used in surface mounting.
Their operation depends on the reliability of the switching circuit, which affects:
- frequency deviation from the required value, the stability of the parameter;
- aging rate of the device;
- load capacitance.
Properties of the quartz resonator
Superior to previously existing analogues, which makes the device indispensable in many electronic circuits and explains the scope of the device. This is evidenced by the fact that in the first decade since its invention more than 100,000 units of the device have been produced in the United States (not counting other countries).
Among the positive properties of quartz resonators, explaining the popularity, the demand for devices:
- good quality factor, the values of which - 104-106 - exceed the parameters of previously used analogues (have quality factor of 300);
- small dimensions, which can be measured in fractions of a millimeter;
- resistance to temperature, its fluctuations;
- long service life;
- ease of manufacturing;
- possibility to build high quality cascade filters without manual tuning.
Quartz resonators also have disadvantages:
- external elements allow frequency tuning in a narrow range;
- have a fragile structure;
- do not tolerate excessive heat.
The principle of operation of a quartz resonator
The device works on the basis of the piezo effect, which appears on a plate of quartz, and low-temperature. The element is cut from a single crystal of quartz, observing a given angle. The latter determines the electrochemical parameters of the resonator.
The plates are coated on both sides with a layer of silver (platinum, nickel, gold are suitable). Then they are firmly fixed in the case, which is sealed. The device is an oscillating system that has its own resonant frequency.
When the electrodes are exposed to alternating voltage, the quartz plate, which has piezoelectric property, bends, compresses, shifts (depends on the type of crystal processing). At the same time a counter EMF appears in it, as in an inductor coil in an oscillating circuit.
When a voltage is applied at a frequency that coincides with the plate's natural oscillation, resonance occurs in the device. At the same time:
- The quartz element has an increase in the amplitude of oscillation;
- the resistance of the resonator is greatly reduced.
The energy required to maintain oscillation, in the case of equality of frequencies is low.
The designation of the quartz resonator in the circuit diagram
The device is designated similarly to a capacitor. Difference: between the vertical segments is placed a rectangle - the symbol of a plate made of quartz crystal. The sides of the rectangle and the capacitor covers are separated by a gap. Nearby in the schematic there may be a letter designation of the device - QX.
How to test a quartz resonator
Problems with small devices occur if they receive a strong shock. This happens when devices containing resonators in their design fall. The latter fail and require replacement for the same parameters.
Checking the resonator for performance requires a tester. It is assembled according to a scheme based on a transistor KT3102, 5 capacitors and 2 resistors (the device is similar to a quartz oscillator, assembled on a transistor).
It is necessary to connect the device to the base of the transistor and the negative pole in the connections, protecting the device with a protective capacitor. The power supply of the switching circuit is constant 9V. Plus is connected to the input of the transistor, to its output - through a capacitor - a frequency meter, which captures the frequency parameters of the resonator.
The scheme is used when tuning the oscillation circuit. When the resonator is good, it produces oscillations when connected, which lead to the appearance of an alternating voltage at the emitter of the transistor. And the frequency of the voltage coincides with the similar characteristic of the resonator.
The device is defective if the frequency meter does not register the occurrence of frequency or detects the presence of frequency, but it is - either much different from the nominal, or when heating the case with a soldering iron changes greatly.
Related articles: