Alloy under the interesting name of nichrome has chromium and nickel in its composition. A number of unique properties of the alloy and a huge usefulness allow it to be widely used in industry, and be in demand in the market. Even despite its high cost.

Contents
What is nichrome?
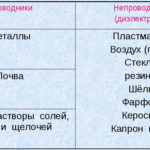
Nichrome is a corrosion-resistant alloy consisting of 2 metals - nickel and chromium, and additives (manganese, sulfur, aluminum, phosphorus, iron, etc.). The alloy is temperature resistant up to +1300 ⁰C and its plasticity allows it to be used for the production of electric heating and resistive elements, different rolls and wires (filaments). Depending on its composition, nichrome is divided into certain grades.
Characteristics and properties of nichrome wire
The production of nichrome wire is limited to two main grades: X15H60 и X20H80. The characteristics and properties of each grade are different.
X20H80 Characterized by:
- Composition of 25% chromium, 75% nickel, 1% iron.
- resistivity 1.13 Ohm-mm2/m (for wire over 3 mm in diameter).
- The operating temperature is 1250-1300 ⁰C.
X20H80 has a density of 8,500 kg/m³ and a specific heat capacity of 0.44 kJ/(kg-K).
X15H60 is inferior to X20H80 in terms of technical characteristics:
- operating temperature - 1000-1100 ⁰C;
- composition - 18% chromium and 60% nickel;
- Specific heat capacity - 0.46 kJ/(kg-K);
- density 8200-8500 kg/m³;
The specific resistance of this grade is 1.12 Ohm-mm2/м.
The low iron content of X20H80 allows the yarn to show resistance to corrosion and wear. In contrast to X15H60, which is more susceptible to corrosion. However, this grade serves the production of samples whose cross section is more ductile and smaller.
REFERENCE. As an additive element, both grades can include aluminum, manganese, titanium, silicon, iron and zirconium. Meanwhile, the presence of iron increases the magnetic properties of the alloy.
Where nichrome wire is used

Plasticity, resistance to aggressive substances and high yield strength find the use of nichrome in industrial production and a number of industrial applications, where electric heating furnaces are widely used. The alloy is also used in electric furnaces where the temperature of heating is extremely high.
The wire is also used in other areas:
- in homemade welding machines;
- In ovens for drying and firing;
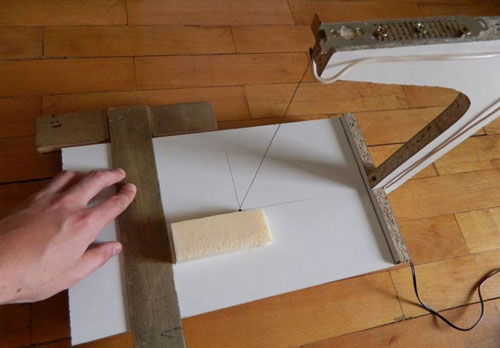
- For machines slicing foam plastic;
- in the heating system of car windows and mirrors;
- in devices where an increased degree of reliability is required, etc.
Such a property of the alloy as strength has provided nichrome wire a place in all environments where chemicals, heat and high temperatures are a necessity.
Advantages of the alloy
Advantages of the alloy include:
- Heat resistance and toughness;
- excellent electrical resistance;
- ductility;
- weldability;
- easy processing of the product;
- resistant to high temperature deformation (above 400 ⁰C) and pressure;
- non-magnetic alloys.
In addition, nichrome has more than one mechanical quality in the form of advantages. And low weight.
How do you define nichrome?
Nichrome, as a material of a slightly silver or white color, is not easy to recognize. In addition, it often has a dark gray tint associated with an oxide (oxidative) film.

However, it is possible to determine the appearance of the material by signs:
- A dark green film on the surface;
- The turning of the wire into a spiral after heating.
The latter sign indicates that the nichrome is highly resistant to deformation.
WARNING .. To preserve the quality characteristics of nichrome wire will help the regime of alternating long and short-term use of the thread.
Where to find nichrome wire?
The easiest way to find nichrome wire is to go to a special store (vape shop). However, nichrome wire is not cheap there, and you have to pay a decent amount of money for one meter.
There are other options where you can find nichrome wire:
- radio markets;
- soldering irons;
- hair dryers;
- Fan heater;
- an electric stove with an open coil;
- Internet.
The possibility of detecting metal at a radio market is not too great, compared to a soldering iron (working or malfunctioning). A soldering iron can be found in a garage, or in a "Fix Price" store, where the product costs pennies. To find what you are looking for, the device must be disassembled and the wire must be pulled out. As a rule, the nichrome wire in the soldering iron is thin. To determine its cross-section will help winding 10 turns on a pencil. The length of the wound wire reaches up to 2.5 m.
Variants with a hair dryer and a heater will cost more. The hardest thing to get the wire out of the electric stove.
To avoid going to the market and looking for nichrome wire in the store, you can find information on the Internet about selling the metal, or things that contain it.

By the way, nickel in the alloy composition affects the price of the wire.
What can be substituted?
Heating elements in electrical appliances often need to be replaced. Usually, the working coil serves as a substitute for the nichrome filament. It can easily be found in kettles, electric stoves, irons and other appliances.
Another option for replacement is stainless material. It has long been proven in the home that stainless steel has the same resistance as nichrome, plus it outperforms the latter in terms of oxidizability.
Peculiarities of soldering
Features soldering Nichrome are as follows:
- The use of tin-lead materials PIC 50 and PIC 1 for soldering.
- Careful preparation of flux.
- Proper treatment of the working surface.
Before soldering, the working surface is cleaned with sandpaper, and treated with cotton soaked in an alcoholic solution of copper chloride. Next, flux is applied, and the process begins.
IMPORTANT. Flux is prepared by mixing several elements: 100 g of technical Vaseline, 5 g of glycerin and 7 g of zinc chloride powder.
When tinning nichrome with copper leads is better to use 2-3 g of citric acid. This is enough to serve one wire. To remove the acid, you need to put the wire on rosin, dip it, and use the soldering iron for further work.
Related articles: