Conductors and dielectrics are physical substances that have different degrees of electrical conductivity and react differently to the effects of an electric field. Opposing material properties are widely used in all areas of electrical engineering.
Contents
What are conductors and dielectrics
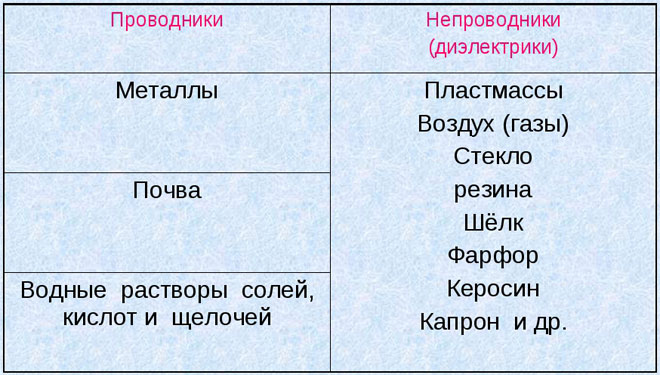
Conductors - are substances with free electric charges, capable of moving directionally under the influence of an external electric field. Such features are possessed by:
- Metals and their melts;
- natural carbon (hard coal, graphite);
- electrolytes - solutions of salts, acids and alkali;
- ionized gas (plasma).
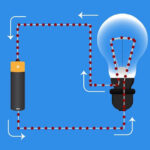
Main property of materialsFree charges - electrons in solid conductors and ions in solutions and melts, moving through the entire volume of the conductor conducts electric current. An electrical voltage applied to a conductor creates a conduction current. Specific resistance and electrical conductivity are the main indicators of a material.
The properties of dielectric materials are the opposite of conductors electricity. Dielectrics (insulators) are made up of neutral atoms and molecules. They do not have the ability to move charged particles under the influence of an electric field. Dielectrics in an electric field accumulate uncompensated charges on their surface. They form an electric field directed inside the insulator, polarization of the dielectric occurs.
As a result of polarization, the charges on the dielectric surface tend to reduce the electric field. This property of electrical insulating materials is called the dielectric permittivity of the dielectric.
Characteristics and Physical Properties of Materials
The parameters of conductors determine their field of application. The main physical characteristics:
- specific electrical resistance - characterizes the ability of the substance to prevent the passage of electric current;
- temperature coefficient of resistance - a value that characterizes the change in the index depending on the temperature;
- thermal conductivity - the amount of heat that passes through a layer of material per unit of time;
- contact potential difference - occurs when two dissimilar metals come into contact, is used in thermocouples for measuring temperature;
- tensile strength and elongation - depends on the type of metal.
When cooled to critical temperatures, the specific resistance of a conductor tends to zero. This phenomenon is called superconductivity.
The properties that characterize a conductor are:
- Electrical - resistance and electrical conductivity;
- chemical - interaction with the environment, corrosion resistance, ability to connect by welding or soldering;
- physical - density, melting point.
The peculiarity of dielectrics is to resist the influence of electric current. Physical properties of electrical insulating materials:
- dielectric permittivity - the ability of insulators to polarize in an electric field;
- specific volumetric resistance;
- electrical strength;
- tangent of the angle of dielectric losses.
Insulating materials are characterized by the following parameters:
- electrical - breakdown voltage value, electrical strength;
- physical - thermal resistance;
- chemical - solubility in aggressive agents, moisture resistance.
Types and classification of dielectric materials
Insulators are divided into groups according to several criteria.
Classification by aggregate state of matter:
- solid - glass, ceramics, asbestos;
- liquid - vegetable and synthetic oils, paraffin, liquefied gas, synthetic dielectrics (silicon and organofluorine compounds, coolant, freon);
- gaseous - air, nitrogen and hydrogen.
Dielectrics may be of natural or artificial origin, of organic or synthetic nature.
Organic natural insulating materials include vegetable oils, cellulose, rubber. They are characterized by low thermal and moisture resistance, rapid aging. Synthetic organic materials - various types of plastic.
Inorganic dielectrics of natural origin include: mica, asbestos, muscovite, phlogopite. The substances are resistant to chemical attack and withstand high temperatures. Artificial inorganic dielectric materials are glass, porcelain, and ceramics.
Why dielectrics don't conduct electric current
The low conductivity is due to the structure of the dielectric molecules. The particles of matter are tightly bound together, unable to leave the boundaries of the atom and move throughout the volume of the material. Under the influence of the electric field, the atomic particles are capable of slightly loosening - polarizing.
Depending on the mechanism of polarization, dielectric materials are divided into:
- non-polar - substances in different aggregate state with electronic polarization (inert gases, hydrogen, polystyrene, benzene);
- polar - have dipole-relaxation and electron polarization (various resins, cellulose, water);
- Ionic - solid dielectrics of inorganic origin (glass, ceramics).
Dielectric properties of a substance are not constant. Under the influence of high temperature or high humidity, electrons are detached from the nucleus and acquire the properties of free electric charges. In this case, the insulating properties of the dielectric decreases.
A reliable dielectric is a material with a low leakage current that does not exceed a critical value and does not interfere with system operation.
Where dielectrics and conductors are used
Materials are used in all spheres of human activity which use electric current: in industry, agriculture, instrument making, electric networks and household appliances.
The choice of conductor is determined by its technical characteristics. Products made of silver, gold and platinum have the lowest specific resistance. Their use is limited to space and military purposes because of their high cost. Copper and aluminum are not as good conductors, but their relative cheapness has led to their widespread use as wires and cable products.
Pure metals without impurities conduct current better, but in some cases it is necessary to use conductors with high resistivity - for production of rheostats, electric furnaces, electric heating devices. Alloys of nickel, copper, manganese (manganine, constantan) are used for this purpose. Electrical conductivity of tungsten and molybdenum is 3 times lower than that of copper, but their properties are widely used in production of electric lamps and radio devices.
Solid dielectrics - materials that ensure the safety and smooth operation of current-conducting elements. They are used as an electrical insulating material, preventing current leakage, insulate conductors from each other, from the body of the device, from the ground. An example of such a product are dielectric gloves, about which is written in our article.
Liquid dielectrics are used in capacitors, power cablesThe materials are used as a filling and impregnation agent in circulating cooling systems of turbine generators and high-voltage oil circuit breakers. The materials are used as filling and impregnation.
Gaseous insulating materials. Air is a natural insulator that also provides heat dissipation. Nitrogen is used in places where oxidation processes are unacceptable. Hydrogen is used in powerful generators with high heat capacity.
Coordinated operation of conductors and dielectrics ensures safe and stable operation of equipment and power supply networks. The choice of a particular element for the task depends on the physical properties and technical parameters of the substance.
Related articles: