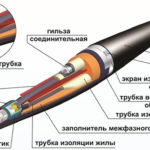
After performing electrical wiring, the issues of safety and protection of the connection during the further operation of the wiring become paramount. In the process of laying electrical networks, special attention should be paid to the observance of technology and quality standards when laying and connecting cables, because these sections of electrical wiring are the most vulnerable. Various categories of insulation and heat shrink tubing are used to prevent burnout and emergencies.
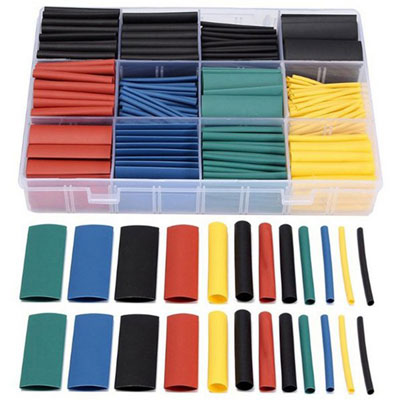

Heat shrink tubing is an elastic product made of thermoplastic material subject to heat shrinkage. That is, the length and diameter is affected by temperature, the source of temperature can be hot water, air or fire.
A distinctive feature of the tubes is the increased transverse compression value compared to longitudinal compression. This means that the diameter of the heat-shrinkable tubing can be reduced by several times (from 2 to 6), and the maximum increase in length is 20%.
Contents
General information and application of heat shrink tubing
Heat shrink tubing is manufactured in the factory from a special heat shrinkable material, which changes its dimensions several times depending on the degree of temperature increase. The surrounding elements - water, flame, air - have an effect on the product. If one end is heated, the size of the heat shrink tube will increase only at that end, while the other end will remain in the same dimensional range. If the diameter is reduced, the wall thickness of the thermopolymer increases proportionally, which also increases the insulating characteristics of the heat shrink tubing for electrical wiring insulation.
Heat shrink tubing TUT is able to shrink in size under the influence of temperature and cover the wire. TUT is used in the following applications:
- performing electrical installation work in order to provide reliable electrical insulation. Heat shrink wrap has many advantages compared to conventional electrical tape, especially when there are a large number of connections;
- Labeling cables and wiring - in this case, heat shrink tubing is used as a sleeve
- providing corrosion protection for connections in many areas;
- a means to ensure mechanical stability of working mechanisms. For example, heat shrink tubing is often used on conveyor rollers and rollers;
- in production, heat shrink tubes provide reliable protection of joints from the aggressive effects of external factors, including precipitation.
Advantages and disadvantages
Heat shrink tubing has the following advantages:
- Due to the tight fit, it does not shift when exposed to mechanical impact;
- the use and installation of heat shrink tubing is a simple task that can easily be done by yourself;
- a wide choice of materials and diameters of heat shrink tubing;
- after shrinking, the heat-shrink tubing TUT acquires additional strength and rigidity at the joint;
- When choosing which is better - heat shrink or electrical tape, unambiguously heat shrink has advantages in terms of technical characteristics and longer life.
The disadvantages include factors such as:
- the impossibility of re-use, because under the influence of temperature, the diameter has changed, and it is impossible to remove the TUT without damage;
- Cost is higher than that of duct tape.
Types of heat shrink
Types of polymer heat shrink tubing TUT are distinguished on the basis of the method of production and the material used:
- Polyolefin. They are made of chemically or radiographically bonded polyethylene with dyes, plasticizing components and fire retardants added. Most of the tubes are manufactured according to this technique and they are designed for the temperature range of -50 up to 125 degrees Centigrade. The material is also resistant to benzene and oxidizing agents for short-term contact;

- elastomers based on synthetic rubber. Characteristic differences are temperature resistance up to 175 degrees and oil and gas resistant properties, but the price is often too high, which holds back the growth of popularity;

- heat shrink for wires made of thermoplastic polyvinyl chloride. The material provides a high level of insulation, but a small range of operating temperatures from -20 to 80 degrees;

- polyester has a high level of chemical resistance and resistance to mechanical damage. The material is ideal for manufacturing thin-walled products;
- fluoropolymer - requires complex technological processing, provides unique chemical and physical characteristics;

- silicone products - are plasticity and non-toxic, but not resistant to organic solvents.
They are also classified by the method of installation:
- adhesive shrink tubing, in which a layer of adhesive is applied on the inner side, providing a high degree of tightness and tightness of the fit. This type also provides protection against moisture ingress;
- TUT without adhesive layer for standard connections, where there is no need to ensure tightness.
According to the color distinguish decorative TUT for additional decorative effect, and transparent standard heat shrink is recommended for use in places where you want to check the tightness of the connection.
Depending on the wall thickness there are: thin, medium and thick walls.
For specific tasks, special types of shrink wrap are produced with additional functions, for example, shrink wrap with solder, with corrugated surface, high electrical density, specific cold shrink material and others.
Characteristics and differences
The main parameters, which are characterized by heat shrinkable tube, are:
- thermal resistance;
- Shrinkage coefficient in the range from 200 to 600%;
- diameter of heat-shrinkable tubing before and after temperature effect;
- oil resistance;
- chemical inertness;
- Ability to withstand voltage up to 1000 V;
- gasoline resistance;
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- flame retardant properties;
- shrinkage temperature and working range.
The products can be produced in round, oval and compressed form, which does not affect the installation. Note that thin-walled heat-shrink tubing is mostly manufactured in oval or flattened shapes.
Diameter before and after
Heat shrink tubing for wires changes its dimensions as the temperature rises. For this reason, the manufacturer specifies the size before and after heating in the name. For example, if the name indicates TUT NG 40/20, then 40 mm is the inside diameter before shrinkage, 20 mm - after. When connecting cables with different cross-sections and diameters, shrinkage with larger coefficients is required.
The amount of shrinkage must also be taken into consideration when choosing the length of the products. In high-quality tubes shrinkage along the length is not more than 5-7%, while the Chinese about 20%.
When selecting large diameter heat shrink tubing, it is necessary to pay attention to both shrinkage parameters. The higher the shrinkage, the thicker the walls of the tube become after heating, which results in a much higher density and strength of the connection. Thick-walled products have optimum shrinkage rates.
Shrinkage coefficient
The shrinkage coefficient implies that the products are characterised by longitudinal shrinkage. This parameter varies from 2:1 to 6:1, which means it has the ability to shrink 2 to 6 times from the original shape. The coefficient means the ratio of the initial diameter to the diameter after shrinkage.
Tubes with a higher ratio are more expensive because the manufacturing process is more complex. Tubes with a 4 to 1 ratio are considered more versatile than 2 to 1.
Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is of no small importance, TUTs are available in
- thin-walled;
- with medium walls;
- thick-walled.
The wall thickness must be chosen on the basis of the application and the function assigned to the heat shrink tubing.
Non-combustible heat shrink tubing
Significant importance is given to the material of manufacture, because it is the material that has the characteristics required of the product. For example, variants with flame retardants are characterized by self-extinguishing, and their names indicate the value of NG.
However, it is impossible to say that it does not burn at all. In the absence of an open flame, the product itself is extinguished. This happens because of the effects of flame retardants, which displace oxygen in the seat of fire.
Note that when the room is used VVG HG wiring, then the insulation should be made with similar heat shrink tubing. Heat-resistant and non-combustible heat-resistant tubing will reliably prevent the occurrence of fire, thus minimizing the risk of accidents.
Color matching
Colored decorative heat shrink tubing is convenient for marking because a small ring of a prominent shade is placed on the insulation at the end of the cable. Here are the basic rules for using colored tubes:
- in the wiring of DC circuits, red is used on the plus and black on the minus;
- on grounding wires - yellow-green shade;
- In three-phase electrical circuits, red, yellow and green colors are used for the phases.
Due to the wide range of colors, heat shrinkable tubes can be used as a decorative material.
Installation Rules
Before answering the question of how to use heat shrink tubing, we note that for this process it is recommended to have specialized equipment - a heat shrinking machine. On it, the required shrinkage temperature is set to facilitate the procedure. As an option, you can use a lighter or put the tube in boiling water.
Here is a sequence of steps and rules for using the THA:
- It is recommended that thick wall or large diameter tubing be preheated with a heat gun to half the temperature specified in the parameters for shrinkage before installation. Thin walled tubing does not need to be preheated;
- Cut the proper length of the THT tube with scissors, being careful to remove any burrs or scored edges to prevent tearing during use;
- Stretch the tubing and pull it into place;
- heat up to the specified temperature, but do not exceed the limit in order to avoid deformation. Hot air should be directed from one end to the other or heated from the center to the edges;
- let the tube cool down, and then the process is finished.
So, installing the heat shrink tubing is not a difficult task, the main thing is not to exceed the temperature and heat evenly. If deformation or mechanical damage is detected, the tube must be replaced with a new one.
Related articles: