With the development of technology and the emergence of energy-saving lamps on sale, more and more people are thinking about whether it is worth overpaying for energy-saving lamps, and how much better than the usual incandescent bulbs. To answer this question, you need to understand what characteristics are important for light sources and how they differ in different types of lamps.
Contents
Differences in design and operating principle
Tungsten filament light source was first patented in the 1890s by the Russian scientist A.N. Lodygin. Such lamps work on the principle of incandescence of the filament of a special tungsten alloy to very high temperatures, which inevitably leads to glow. Structurally, such a device consists of a glass bulb with a chemically inert gas inside (e.g. a mixture of nitrogen and argon), a tungsten filamentfilament), molybdenum filament holders with other elements to hold the filament and electrical conductors with a base at the bottom of the lamp.
Such lamps are widely used in all spheres of human activity, but they are gradually being replaced by modern and efficient LED lighting devices.

LED lamps were discovered back in the early 20th century, but were first used in practice only in 1962, when an American scientist from the University of Illinois, Nick Holonyak, obtained crystals with a red glow. The principle of LED luminescence is in the electro-hole transition, which is characteristic of semiconductor elements. When electric current flows in the forward direction through the LED, photons are emitted and a glow appears.
With the development and improvement of technological processes, the production of LEDs is no longer expensive and LED lamps have become widespread, rapidly displacing incandescent lamps from the market. All this is because such devices have a high efficiency and at low power have a large luminous flux.
To understand what is the power, light output, efficiency and how it all relates to the choice and popularity of LED lamps, let's analyze each property in detail.
Power and light output
One of the important parameters of lighting devices is their light output. It is this characteristic can be understood how effective lighting fixtures and how much energy they consume. Light output depends on two parameters: the luminous flux and the wattage of the fixture.
What is luminous flux?
Luminous flux - is a quantity which represents the quantity of luminous energy delivered per unit of time. It is measured in lumens (indicated by lm or lm.). The power of a device - is the amount of electrical energy consumed and converted by the device.
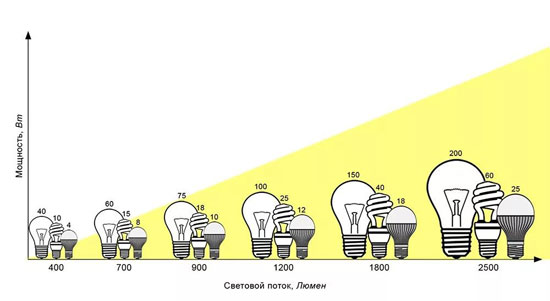
The light output of lighting fixtures indicates the ratio of the luminous flux to the power of the lamp. Incandescent lamps are outsiders in this characteristic and have a very low light output (This is due to the fact that the power is spent not only on light radiation, but also on heat radiation, and this, naturally, reduces the efficiency of the device). Advanced and high-quality LED products have a great light output, with low power, which increases the light output many times over.
Table 1. Comparative table of luminous flux ratio (lumens) to lamp power consumption (W) for LED lamps and incandescent lamps
| Power, W | Luminous flux, lm | |
|---|---|---|
| Incandescent | LED | |
| 25 | 3 | 255 |
| 40 | 5 | 430 |
| 60 | 9 | 720 |
| 75 | 11 | 955 |
| 100 | 14 | 1350 |
| 150 | 19 | 1850 |
| 200 | 27 | 2650 |
Heat output
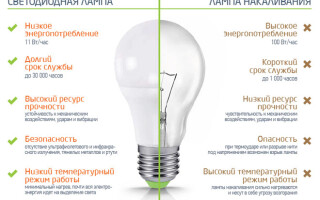
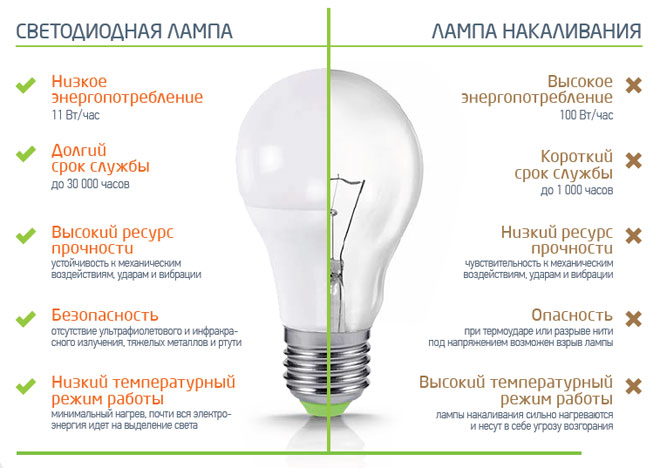
The heat output of a lighting fixture - is a negative and harmful characteristic of light bulbs. The higher the temperature of the device when it operates, the more energy it wastes on unnecessary heating. Moreover, the excessive temperature of the lamp can cause burns (if you accidentally touch the lamp) or fire and damage to the finishing materials (for example, the plastic or stretch ceiling could melt). On this parameter incandescent lamps are markedly inferior LED, they are very hot and spend a lot of energy on heating. This is certainly due to the principle of operation of this lighting device.
You can not say, of course, that LED lamps do not heat up. But compared to classic incandescent bulbs, they have a low heat output and high efficiency. They can be used in paper and plastic luminaires, without fear that they will catch fire.
Service life
Everyone is familiar with the situation when an incandescent bulb "burns out". Any surge in voltage while the device is running or a sharp switch-on when the tungsten filament wears out will cause the incandescent bulb to spoil. It is because of the high sensitivity of the filament that ordinary bulbs have a short life, and poor-quality incandescent bulbs even last for days.
Energy-saving LED lamps have a fundamentally different design and predictable service life. Such devices last dozens of times longer than incandescent bulbs and can last up to 50,000 hours (For comparison, the average lifetime of incandescent bulbs is less than 1000 hours).
Efficiency of light bulbs
Efficiency factor (EFFICIENCY) is closely related to all the preceding parameters of light bulbs. Each device has a "useful efficiency" - This is the work for which a device is created. With lamps, the main useful action is the emission of light. Everything else is superfluous and unnecessary work and reduces the efficiency. Incandescent bulbs have a very low efficiency, because most of its work is not related to the useful action, but to the side - the emission of heat. This value (EFFICIENCY) of such lamps barely reaches 5%. This means that only 5% of the consumed electrical energy is spent on light emission. And this is a very low figure. It indicates the inefficiency and uneconomy of the device.
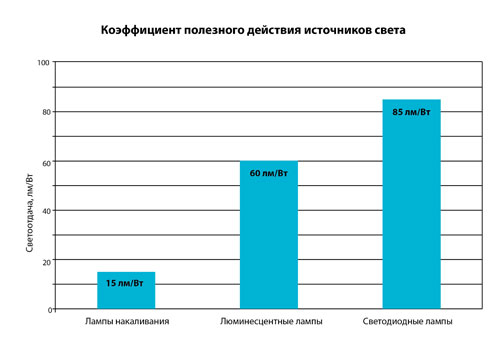
LED lamps have a high efficiency factor, which is about 90%. That is, LED devices do not waste energy on useless work and save electrical energy, and therefore save the user's budget.
Eco-friendliness .
Unfortunately, only in the XXI century people consciously began to think about the preservation of nature and ecological devices that they use. The key to preserving nature in the future is to consume and save energy wisely now. Modern ways of generating electrical energy are causing great damage to the natural wealth of our planet.
Water resources, the atmosphere and the soil are gradually being polluted by the use of non-renewable energy sources. This leads to global warming and rising ocean levels, and therefore to ecological catastrophe. Energy conservation is one of the ways to reduce the negative impact of mankind on the environment. Not for nothing, in the world, became popular the campaign "Earth Hour", when for one hour all people not indifferent to the nature turn off all the electric appliances in their houses.
In this sense, energy-saving LED lamps and the transition to them around the world have made a big step to reduce energy consumption. After all, LED lights are low-power, but efficient devices. LED bulbs make it possible to use electrical energy wisely.
Based on the above, there is no reason not to use LED lamps. Of course, they are somewhat more expensive than incandescent bulbs, but in all respects ahead of them. The use of modern LED lighting sources helps to save the budget and the environment in the world and certainly pays off in the long term, both for the individual and for mankind as a whole.
Related articles: