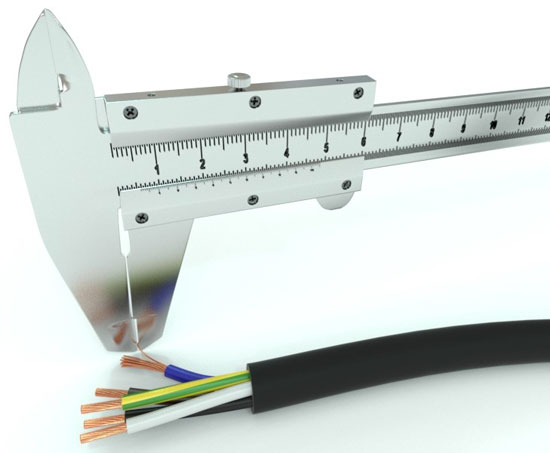
When calculating any electrical networks uses such a concept as the cross-sectional area of the conductor. This property directly affects the safety and durability of the entire system, so it is important that the calculated cross-sectional area of the electrical conductor match the actual cross-sectional area. This article will look at how to measure conductor diameter and cross-sectional area, and will also look at other options for determining wire characteristics.

Contents
How to measure the diameter of the wire
In order to calculate the cross-sectional area of a wire, you need to know its exact diameter. There are several ways to measure the diameter of a wire. These include measurements:
- Using a caliper: this requires an understanding of how a caliper works and the ability to take readings from its scales. In this case, it is possible to simplify measurements by using an electronic measuring device - it will show the exact value of the diameter on its screen.
- Using a micrometer: the readings of this device are slightly more accurate than a mechanical caliper, but it also requires some skill to take correct and accurate readings.
- Using an ordinary ruler: this method is suitable for those who do not have a measuring device such as a caliper or micrometer in their arsenal. Measuring the diameter of a conductor using a ruler will not be accurate enough, but it is possible to estimate the diameter approximately.
To measure the diameter of a conductor, first strip the insulation from the conductor with a knife or stripper. Next, if a micrometer or a caliper is used, the wire core is clamped tightly between the jaws of the device and the size of the conductor is determined by the scales of the device. If a ruler is used, the insulation is removed to a distance of 5-10 cm and the core is wound around the screwdriver. The coils of the conductor should be tightly pressed together (approximately 8-20 coils). Then the length of the wound section is measured and the resulting value is divided by the number of turns - you get a more or less accurate value of the diameter.
How to know the wire diameter for multicore or segment cables
If determining the diameter for a single-core conductor does not cause any problems, measuring a stranded or segmented cable can cause some difficulties.
Measuring the cross section of a stranded wire
When determining the core diameter of this cable it is not possible to measure this dimension for all wires of the core at once: the value will turn out to be inaccurate, because there is space between the wires. Therefore this cable must first be stripped of the insulation, then the stranded conductor must be untwisted and the number of wires in the core must be counted. Then any method (caliper, ruler, micrometer) measure the diameter of one core and determine the cross-sectional area of the wire. The value obtained is then multiplied by the number of wires in the bundle to obtain the exact size of the existing conductor.
Measuring a segmented conductor
Determining the size of a segmented conductor is somewhat more complicated than measuring a round single-core or multi-conductor cable. In order to correctly estimate the cross-sectional area of such a conductor, special tables should be used. For example, to calculate the cross-sectional area of an aluminum conductor segment, determine the height and width of the segment and use the following table:
| Cable | Segment cross-sectional area, mm2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 50 | 70 | 95 | 120 | 150 | 185 | 240 | ||
| Three-core single-wire sector, 6(10) kV | height | 5,5 | 6,4 | 7,6 | 9 | 10,1 | 11,3 | 12,5 | 14,4 |
| width | 9,2 | 10,5 | 12,5 | 15 | 16,6 | 18,4 | 20,7 | 23,8 | |
| Three-wire sector multi-wire, 6(10) kV | high | 6 | 7 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13,2 | 15,2 |
| wide | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 25 | |
| Four-core single-wire sector, up to 1 kV | higher | – | 7 | 8,2 | 9,6 | 10,8 | 12 | 13,2 | – |
| over | – | 10 | 12 | 14,1 | 16 | 18 | 18 | – | |
Table of correspondence of wire diameter to its cross-sectional area
To quickly determine the cross-sectional area of the conductor without making any calculations also use the table of correspondence of the diameter of the wire to its area.
| Wire diameter, mm | Cross-sectional area of conductor, mm2 | Rated current for the core of single core and double core cable, А | Rated current for the core of three-core cable, А |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0,80 | 0,50 | 7,5 | 7,0 |
| 0,98 | 0,75 | 11,0 | 10,5 |
| 1,13 | 1,00 | 15,0 | 14,0 |
| 1,24 | 1,20 | 16,0 | 14,5 |
| 1,38 | 1,50 | 18,0 | 15,0 |
| 1,60 | 2,00 | 23,0 | 19,0 |
| 1,78 | 2,50 | 25,0 | 21,0 |
| 1,95 | 3,00 | 28,0 | 24,0 |
| 2,26 | 4,00 | 32,0 | 27,0 |
| 2,52 | 5,00 | 37,0 | 31,0 |
| 2,76 | 6,00 | 40,0 | 34,0 |
| 3,19 | 8,00 | 48,0 | 43,0 |
| 3,57 | 10,00 | 55,0 | 50,0 |
This table shows the rated currents for each conductor cross-sectional area of a two-core and three-core electrical cable for easy calculation and evaluation of the conductivity of the core.
Calculation by formula
The main geometric measure of a conductor is its cross-sectional area. This size determines the carrying capacity of the electrical conductor and, consequently, its performance characteristics, which affect safety and durability. As mentioned above, this parameter is easily determined after measuring the diameter of the conductor. To do this, a formula is used to determine the area of the circle:

Ready-made tables are a great way to quickly determine the cross-sectional area of the wire, but to be one hundred percent sure of the resulting value - it is better to check and calculate yourself.
Calculator for calculating the cross-sectional area of a wire by diameter
To quickly calculate the cross-sectional area of a round conductor, you can use a special calculator that is designed for this purpose and can quickly and accurately calculate the size of the conductor using the formula above.
When using this online calculator, you will need to accurately measure the diameter of the conductor for a solid conductor or one of the wires of a stranded wire using a caliper, micrometer or ruler. For a stranded conductor, you will need to additionally count the number of wires.
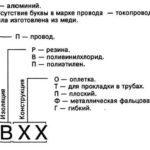
How to Know Wire Sension Based on Appearance
Determine the cross-section of the cable is possible without calculations. Cable in the factory is necessarily marked: on its outer sheath is stamped with a certain pitch manufacturer, type of cable, number of wires and cross-sectional area of the conductor.

For example, if the cable is marked VVG-NG-LS 3x2,5, it means that the cable has an outer sheath and insulation of the conductors of incombustible PVC with no release of hazardous gases when burning, and such cable has three current carrying cores with the cross-sectional area of each conductor 2.5 mm2.
The marking does not always indicate the true value of the core area, as compliance with this parameter is left to the conscience of manufacturers. This is due to the fact that most manufacturers do not adhere to GOST in the manufacture, and guided by their own specifications in the manufacture of cable products, which leads to a free interpretation of the methods of calculation of the cross-sectional area and is not properly regulated. Therefore, it is best to check that the cross-section of the cable corresponds to the stated in the label before using it for its intended purpose.
Related articles: