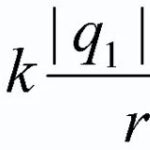A Wimshurst generator or electroforming machine is an inductive electrostatic device designed as a continuous source of electrical energy. In the twenty-first century it is used as an auxiliary technique to demonstrate physical experiments concerning various electrical effects and phenomena.
Contents
A little of the history of the invention
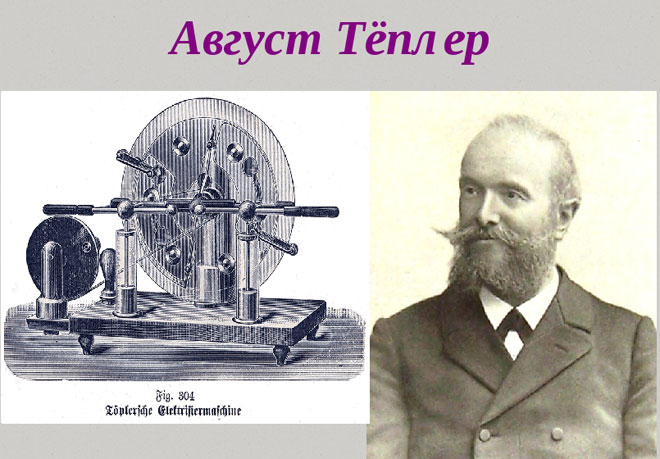
In 1865 a German experimental physicist, August Tepler, developed the final drawings of an electroforming machine. At the same time a second independent discovery of a similar machine was made by German scientist Wilhelm Holtz. The main difference of the device was the ability to obtain high power and potential difference. Holtz is considered the creator of the direct electric current source.

The simple initial design of the electroforming machine application was improved in 1883 by James Wimshurst from England. Its modification is used in all physics laboratories for visual demonstration of experiments.

The design of the electroforming machine is.
2 coaxial discs rotate against each other while carrying simple aluminum sector capacitors. Due to random processes at the primary moment, a charge is formed on a segment of one of the segments. The phenomenon is caused by the process of friction against the air. Because of the symmetry of the design, the final sign cannot be predicted in advance.
Two Leiden banks are used in the design. They create a single system of capacitors in series. This has the effect of doubly reducing the operating voltage requirements of each capacitor. It is necessary to select the same ratings, this is the key to an even distribution of the operating voltage.
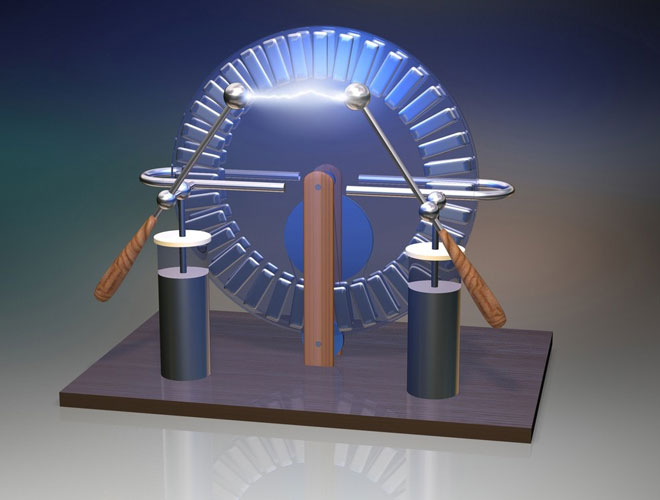

Induction neutralizers are designed to relieve the voltage. The whole construction resembles a metal comb hovering at some distance above the disk. Both disks with equivalent external surface signs come to the charge withdrawal point. The neutralizers are paired. The charge of the segments is greatly reduced after the discharge is realized. In additional designs, the brush is in easy contact with the edge of the disc.
The operator through the power of an electric drive or his own hand forcibly brings together the repulsive elements of the system. The charges interacting with each other try to position themselves as far apart as possible. The process promotes a sharp increase in the surface density of charges at all points of withdrawal.
Electricity is collected in Leiden jars from the crests of neutralizers. There is a rapid increase in voltage. An arrester attached to 2 electrodes helps to avoid failure of the system. It is possible to obtain arcs of different strengths by adjusting the distance between them. There is a correlation: the stronger the field strength between the 2 dischargers, the noisier effect accompanies the emptying of the Leyden jars.

The segments remain emptied after the point of charge removal. Potential equalizers or neutralizers are installed along the flow of motion according to the principle of operation. Each opposite side of the disc has already given up the charge at the different brushes. At the moment of passing the withdrawal point and after it, the residual signs of the charge are different.
A section of thick copper wire with brushes of the thinnest wires hovering at a low height or rubbing the segments contributes to the closure of the said opposites. The result is that the charges on both segments equate to zero, all energy is converted according to the Joule-Lenz law into heat generated on the thickened copper wire.
What are Leiden jars
The first electrical capacitor created by Dutch scientists Peter van Muschenbroek was the Leiden jar. The invented condenser is shaped like a cylinder with a wide or medium throat of different diameters. The Leiden jar is made of glass. Inside and outside it is lined with a special sheet of tin. The product is covered with a wooden lid. The main function of the invention is the accumulation and storage of large charges.

The creation of such a jar was stimulated by a wide study of electricity, the general speed of its propagation, as well as the properties of electricity conductivity of various materials. Thanks to it it was possible for the first time to produce an electric spark artificially. Now the Leiden jars are used only as an integral part of electroforming machines.
What is the principle of operation of an electroforming machine
Energy is taken from the operator's power to change the signs. Already between the equalizers and brushes the discs move with mutual repulsion towards each other. The number of revolutions per minute plays its part. The charge density is increased. The strongest charge of the opposing discs pushes the residue through the copper wire sections. From this comes the energy sufficient to change the sign.
By increasing the surface density values, the charge is removed in the unit. At a single point energy reserves are made in the Leiden jar, the other location serves to change the sign. Induction neutralizers are virtually indistinguishable. They both have the common function of neutralizing energy. General circuitry:
- There are 2 types of capacitors in the design: the Leyden jars, where the charge accumulates, and a combination of a segment of both disks with a dielectric and aluminum liner.
- Reducing the charge of the aluminum segments is handled by 2 types of neutralizers. The first is used to change the sign or polarization, the second to charge the Leiden jar.
All energy comes not from friction of aluminum and copper or electrification of the air. It is created by the forced filling of capacitors by the torsion force of the disk. All processes are performed due to a sharp increase in the surface density of charges at the removal points.
Application of the electroforming machine
Since the 1970s, the Wimshurst machine has not been used for the direct production of electrical energy. Today it serves as a historical exhibit, illustrating the history of the emergence and development of scientific and technological progress and engineering. A laboratory demonstration of what an electroforming machine is made for shows the various phenomena and effects of electricity.
It is acceptable to use induction neutralizers by removing charges from liquid dielectrics such as oil. It is dangerous to get a spark in the air in any production, it can lead to detrimental consequences, smoke and even explosion.
The history of discoveries and research in the field of electricity has a close connection with the use of various designs and devices for producing electric charges. The electroforming machine, the action of which is based on the excitation of electricity through induction, played a role in scientific research.
Related articles: