People use the energy of electric current in almost all spheres of their activities. Now it is not easy to imagine life without electricity, which with the help of special equipment is converted from mechanical energy. Let's take a closer look at how this process occurs, and how modern generators are arranged.
Contents
Converting mechanical energy into electrical energy
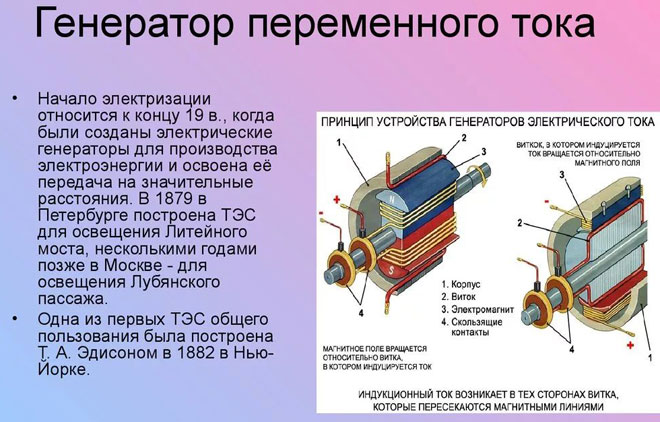
Every generator works on the principle of magnetic induction. The simplest alternator can be thought of as a coil which rotates in a magnetic field. There is also a variant in which the coil remains stationary, but the magnetic field only crosses it. It is during this movement that alternating current is generated. On this principle, a huge number of generators around the world, combined into a power supply system, operate.
Design and construction of an alternator
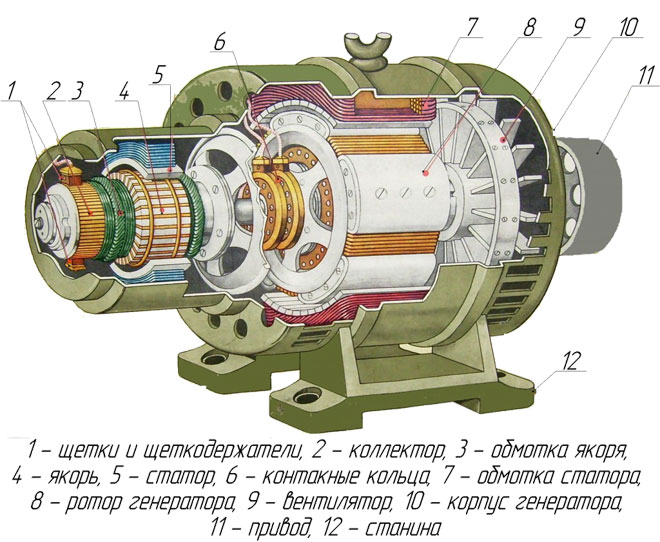
The standard genset has the following components:
- A frame to which the stator with electromagnetic poles is attached. It is made of metal and should perform the protective function of all elements of the machine.
- The stator to which the winding is attached. It is made of ferromagnetic steel.
- The rotor is the moving element, on the core of which is the winding that generates the electric current.
- Commutation node, which withdraws electricity from the rotor. It is a system of moving conductive rings.
Depending on the purpose, a generator has certain design features, but there are two components that any device that converts mechanical energy into electricity has:
- The rotor is a moving solid piece of iron;
- The stator is a stationary element, which is made of iron sheets. It has grooves inside which a wire winding is placed.
In order to get more magnetic induction, there should be a small distance between these elements. Generators are designed as follows:
- With a moving armature and a static magnetic field.
- With a stationary armature and a rotating magnetic field.
Nowadays, equipment with rotating magnetic fields is more common, because it is much more convenient to draw the electric current from the stator than from the rotor. The design of an alternator bears many similarities to that of an electric motor.
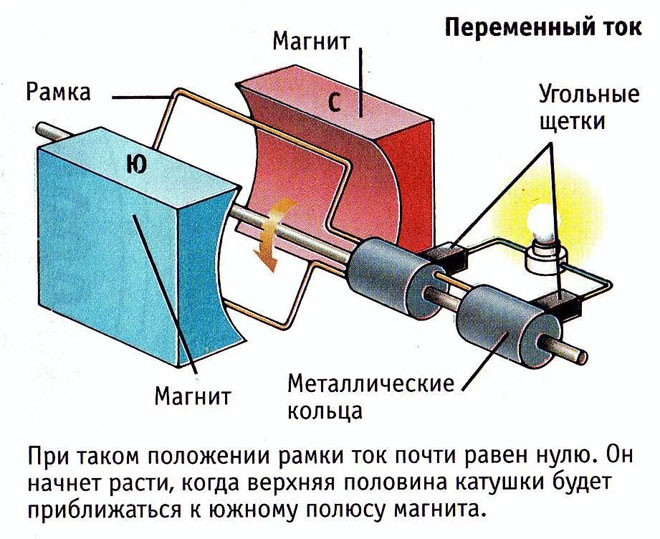
Diagram of an alternator
How an alternator works: the moment one half of the winding is on one pole and the other half on the opposite pole, the current flows through the circuit from its minimum to maximum and back again.
Classification and types of generators
All electric generators can be classified according to the criterion of operation and the type of fuel from which electricity is generated. All generators are divided into single-phase (voltage output 220 volts, frequency 50 Hz) and three-phase (380 volts, frequency 50 Hz), as well as by the operating principle and the type of fuel that is converted into electricity. More generators can be used in different areas, which determines their technical characteristics.
According to the operating principle
A division is made between asynchronous and synchronous alternators.
Asynchronous
Asynchronous generators do not have an exact relationship EMF to the rotor speed, but a term like "slip S" works here. It determines this difference. The value of slip is calculated, so there is still some influence of generator elements in the electromechanical process of an induction motor.
Synchronous
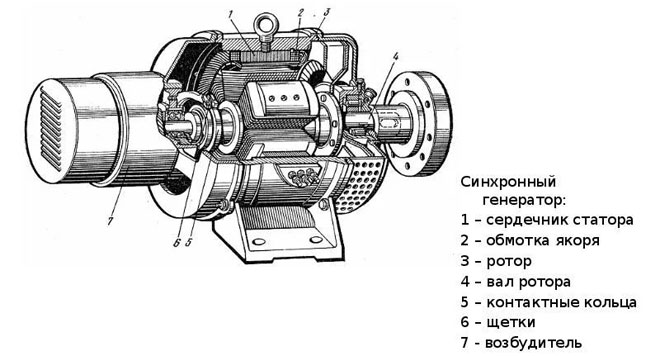
Such a generator has a physical relationship from the rotational motion of the rotor to the frequency of electricity generated. In such a device, the rotor is an electromagnet consisting of cores, windings, and poles. The stator is the coils, which are connected according to the star principle, and have a common point - zero. It is in them that the electric current is generated.
The rotor is driven by an extraneous force of moving elements (turbines), which move synchronously. Excitation of such an alternator can be either contact or non-contact.
According to the type of engine fuel
Remoteness from the power grid with the advent of generators no longer becomes an obstacle to the use of electrical appliances.
Gas generator

Here gas is used as fuel, during the combustion of which and produces mechanical energy, which is then replaced by an electric current. Advantages of using a gas generator:
- Safety for the environment, because gas in combustion does not emit harmful elements, soot and toxic decomposition products;
- Economically, it is very profitable to burn cheap gas. In comparison with gasoline, it costs much cheaper;
- The fuel supply is automatic. Gasoline and diesel fuel need to be topped up as needed, and the gas generator is usually connected to the gas supply system;
- Thanks to the automation, the unit comes into action by itself, but for this purpose it should be located in a warm room.
Diesel generator

This category consists mainly of single-phase units with a capacity of 5 kW. 220 volts and a frequency of 50 Hz are standard for household appliances, so the diesel unit does a pretty good job with the standard load. As you can guess, it requires diesel fuel to work. Why it is worth choosing a diesel generator:
- Relative cheapness of fuel;
- Automatics allowing the generator to start automatically in the event of a power outage;
- High level of fire safety;
- For a long period of time the unit on diesel is able to work without failure;
- Impressive durability - some models are able to operate for a total of 4 years of continuous operation.
Petrol generator .

Such units are quite in demand as household equipment. Despite the fact that gasoline is more expensive than gas and diesel, such generators have many strengths:
- Small size with high power;
- They are easy to operate: most models can be started manually, and more powerful generators are equipped with a starter. The voltage is adjusted for a particular load by means of a special screw;
- In case of generator overload a protection automatically actuates;
- Easily serviced and repaired;
- During operation, they do not make much noise;
- Can be used both indoors and outdoors, but should be protected from moisture.
Main applications
Depending on where the electric generator is used, its specifications are determined. Mainly, the relationship of the generator to a particular category in terms of application, determines its power. The following varieties of equipment are divided according to the areas of use:
- Household. Have a capacity of 0.7 to 25 kW. Usually this category includes gasoline and diesel generators. They are used for power supply of household appliances and low-power equipment, very often at construction sites. They can be used as a portable power source when going out in the countryside;
- Professional. It can be used as a permanent source of electricity in municipal institutions and small industrial enterprises. Its capacity does not exceed 100 kW;
- Industrial. Can be used in large factories and plants, where high-powered equipment is required. Such devices have a power of more than 100 kW, have considerable size and are difficult to maintain for an untrained person.







