Often the concepts cable and wire are used synonymously and only specialists versed in electricity clearly understand that these products are different. Each has different technical characteristics, scope of application and design. In some cases it is possible to use only one of them. To understand the difference between cable and wire, it is necessary to consider both products in terms of their structure and purpose.

Contents
What is a cable?
A cable is a product in which there are 1 or more insulated conductors. They may be covered with armor protection if the application involves the possibility of mechanical damage.
According to the areas of use, cables can be:
- Power .. They are used to transmit and distribute electricity by means of lighting and power installations through cable lines. Can have aluminum or copper cores with a braid of polyethylene, paper, PVC and rubber. They are equipped with protective jackets.
- Control. They are used to supply low voltage machinery and to create control lines. Copper and aluminum are the basic material of the cores with a cross section of 0.75-10 mm².
- Controls. Designed for automatic systems. Manufactured from copper with plastic sheathing. Equipped with a protective shield against damage and electromagnetic interference.
- For transmission high-frequency (over long distances) и low frequency (local) communication signals.
- Radiofrequency. They enable communication between radio devices. The product consists of a central copper core and an outer conductor. The insulation layer is made of PVC or polyethylene.
What is a wire?
Wire - A wire is a product consisting of 1 bare or several insulated conductors. Depending on the conditions of installation, the braid may be made of fibre material or wire. A distinction is made between bare (without using coatings) and insulated (with rubber or plastic insulation) products.
The material of the cores in the wires can be aluminum, copper and other metals. It is recommended to install electrical wiring of 1 material.
Aluminum wiring is lighter in weight and cheaper, it also has high anti-corrosion properties. Copper conducts electricity better. A disadvantage of aluminum is a high degree of oxidation in the air, which leads to destruction of joints, voltage drop and intense heating of the junction point.
Wires can be protected and unprotected. In the first case, in addition to electrical insulation, the product is covered with an additional shell. Unprotected ones do not have such.
Wires are classified according to their application area:
- Installation .. They are used for flexible or fixed installation in electrical panels. Also, in the manufacture of radio and electronic devices.
- Power wires .. Used for wiring networks.
- Installation. They are used to connect installations, power transmission systems indoors and outdoors.
There is a separate category of wires - cords. They are designed to create a movable connection. Wires differ from the cord in the density of insulation of the cores, a large cross-section and power.
What is the difference between a cable and a wire?
The main difference between a cable and a wire is its purpose. Cables are used to transmit electrical current over long distances between houses, cities or inside buildings. They have additional protective layers for this purpose. Cables are usually used for indoor installation indoors or inside electrical cabinets.
Insulation
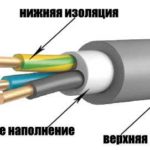
Since the cable may be installed in different, including corrosive environments, the cable insulation must be designed for this. For strength, additionally added armor - a metal braid, each core in addition to insulation, may be covered with additional film, and the space between the cores is filled with absorbent (talc) - to absorb moisture and reduce combustion.
The wire does not need all this, it has one layer of PVC insulation.
Labeling
All electrical products are provided with markings that describe their characteristics and purpose in detail. Labels on cables and wires have their own differences.
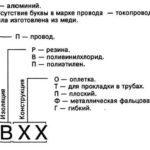
Wire marking is deciphered as follows:
- The presence of the letter "A" in the first place indicates that the conductor is aluminum. If the first is not "A" - copper.
- The letter "P" indicates 1 wire, "PP" - 2 or 3 flat conductors.
- The next letter tells about the material of core insulation: "P" - polyethylene, "R" - rubber, "V" - polyvinyl chloride, "L" - braiding made of cotton yarn.
- If the designation of the sheath is followed by "H", it indicates an additional protective layer of non-flammable nairite, "B" - PVC.
- If the wire has a flexible current-carrying core, it is indicated by the letter "G".
- Multi-core products with an antifoulant coating are marked "TO".
- Numbers in the code indicate the type of polyethylene and cross-section of the conductor.

When marking cables, GOST has established the following order:
- Core material ("A" - aluminum, no letter - copper).
- Type ("K" - control, "KG" - flexible).
- Insulation ("P" - polyethylene, "V" - polyvinyl chloride, "R" - rubber, "NG" - incombustible, "F" - fluoroplastic).
- Armor or outer shell ("A" - aluminum, "S" - lead, "P" - polyethylene, "B" - polyvinyl chloride, "P" - rubber, "O" - coating of all phases, "Pv" - vulcanized polyethylene).
- Protective layer ("B" - armor with anti-corrosion coating, "Bn" - non-combustible armor, "2g" - double polymer tape, "Shv" - polyvinyl chloride hose, "Shp" - polyethylene hose, "Shps" - self-extinguishing polyethylene hose).
In addition to these designations, there are many others that indicate special characteristics. For example, the letter "E" at the beginning of the code indicates that the cable is electric. The same letter in the middle indicates the presence of a shield.
Immediately after the letter designation follows a digital one, in which the first number reports the number of conductors, the second - their cross-section.
On cables necessarily indicated voltage index - "W". The number after it deciphers as follows: 1 - up to 2 kV, 2 - up to 35 kV, 3 - over 35 kV.

Conditions of use
Wires are used only for distribution inside electrical devices. In other cases, cable is used. This is dictated by the specifics of the equipment, the need to use a large number of cores. In addition, they have an increased protection against damage.
Service life
The service life of the cable can reach 30 years or more due to the presence of double protection in the form of insulation and armor. The wire is able to last about half as long.
Supply voltage
Depending on the application and according to the PUE, it may be important what current-carrying capacity the cable or wire has. The first type has at least double protection and increased resistance of the insulation material. It can be used for high voltages up to hundreds of kilovolts.
Wires, on the other hand, are used for voltages up to 1 kV. For this reason, all production and high-rise lines are assembled exclusively with cables, while the use of wires is implemented for the assembly of electrical appliances.
The choice between cable and wire
Choose a cable and wire should be based on the conditions under which it will be used.
Related articles: