Any object of the modern world, whether it is an industrial complex, a residential apartment building or the smallest private home requires electricity. This can be achieved by laying electrical cable to the end user.

Electrical cable is a complex structure consisting of many components that perform different functions, depending on the loads and conditions of use. It transmits energy or signals in large volumes and over long distances. It is impossible and impractical to use such bulky networks in all projects. Therefore, a lot of specialized electrical cables and wires have also appeared, for which have been introduced appropriate designation markings - letter and color.
Content
How to determine the purpose of a cable or wire
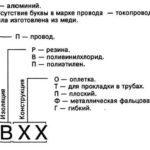
The letter designation of electric wires, according to GOST, is applied by the factory to the outside of the sheath and indicates the layout starting from the core. This makes it easier to understand the functionality of different types of electrical cables and wires for correct intended use.
The color coding of electrical wires is designed for quick and easy orientation during installation work. In addition, it can significantly reduce the risk of electric shock. The color of the insulation can be white, black, brown, orange, green, yellow, red, blue, purple, gray, pink and turquoise. Each color indicates the purpose of wires and cables in AC and DC networks.
The types of electrical cables depend on the materials used for their sheathing:
- rubber;
- PVC;
- polyethylene;
- paper core insulation with an outer sheath of lead or aluminum.
If necessary, the cable can be covered with several layers of insulation, including combinations of the above materials, for better sealing and reinforcement.
Types of Electrical Cables
Types of electrical wires and cables are classified based on conductor type, cross-sectional area and diameter, conductivity, insulation, heat resistance, flexibility, and application. Below is a brief description of the brands of cables and electric wires.
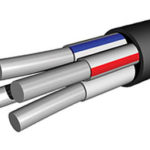
Thanks to a wide range of applications and resistance to various kinds of impact, including fire, temperature fluctuations of 100 degrees (-50 ... +50 ° C), high humidity (up to 98%), bending, breaking and aggressive chemicals, VVG cable has proven itself. It has a copper wire (flat or round) with polyvinyl chloride insulation and the same sheath without the use of external protection.
Designed to transmit electricity in the voltage range of 660-1000 V. This cable is most often colored black, and the insulation of conductive cores, due to the wide range of applications, can be colored in all the colors used for marking electrical wires.
There may be one or more cores (up to 5) inside the power VVG cable. Depending on the operating conditions, the cross section varies from 1.5 to 240 mm², and the conductors themselves may be single and multi-wire. The cross section of the conductor should be kept in mind, as it is possible for the cable to be refracted when laying and installing if the bending radius is greatly reduced.
There are 4 most commonly used varieties of VVG power cable:
- VVGp (flat);
- VVGz (specific division of the cores inside the cable using different fillers);
- AVVG (aluminum core);
- VVGng (increased insulation resistance to fire).
NYM-cable is an improved analogue of VVG, which has both advantages and some disadvantages. This abbreviation is deciphered as follows: the letter N stands for the name of the organization of the German Electrical Association and compliance with all necessary standards; Y - insulation material (PVC); M - the possibility of multi-purpose use.
The main characteristics are almost identical, except for a smaller cross-sectional range of conductors and a shift of the temperature limits to higher values. The conductors inside are exclusively round and multi-wire, which adds increased flexibility, but deprives it of the advantages of use inside the floor or walls. Another significant disadvantage is its price. VVG-cable is much cheaper.
KG is a cable with rubber insulation, copper conductors (1 to 6) with increased flexibility and a working temperature range of -60...+50°C. This cable can be used both for alternating current up to 660 V and for direct current of 1000 V. A few examples of popular uses for this cable are powering welders and construction cradles. There is a less flammable version.
VBBshv is a stronger, mechanically resistant version of VVG cable with identical characteristics to the latter. The strength is achieved by winding galvanized steel strips overlapping on the outer sheath of the cable, so that there are no gaps between the metal coils. In addition, the cable armored in this way is additionally placed in a PVC sleeve with the existing less flammable modification. VBNSHV-cable can be laid in the ground, pipes and outdoors.
There are the following types of electrical cables VBBBSHV:
- AVBBSHV - the conductors are made of aluminum;
- VBBShvng - less flammable cable;
- VBBShvng-LS - a special cable with low emission of toxic substances when operated in conditions of high temperature.
Description and Varieties of Electrical Wires
While a cable is a complex structure of many elements, a wire can be thought of as a structural unit of a cable. Wires are used to further transmit electricity received through cables. Electrical wires number quite a few types:
- winding copper or high resistance;
- lead wires (PVKV, RKGM, VPP);
- warming up;
- connecting wires (PVS, ORS, SHVP);
- for rolling stock;
- automotive;
- communications;
- heat-resistant;
- aircraft;
- installation (APV, PV1, PV2, PV3);
- insulated for overhead lines;
- non-insulated;
- mounting;
- thermocouple;
- for geophysical works.
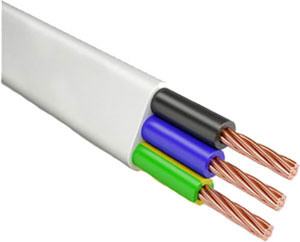
Electrical wire with single copper conductors (two or three), insulation and PVC sheath - PBPP. Its main purpose - power stationary sources of light. As it is more often installed indoors, it has a temperature range of -15...+50 °C. Withstands up to 250 V at 50 Hz.

Not too flexible, unlike PBPPg (the letter g indicates flexibility), specially designed for indoor work with the need to repeatedly round corners and make frequent turns. This is its main and only difference - multi-wire conductors. The wire is best suited for powering household appliances.
The PBPP modification with aluminum strands is designated by the abbreviation APUNP. This is the end of its differences. It is worth bearing in mind that such wire, as well as PBPP, comes only with single cores and has a limited bending radius.
PPV is a flat single-core copper wire with PVC insulation (single) and special jumpers between the cores, used for indoor installation of electrical network, in the cable duct or corrugation. It is also used in two other variants: with a different core material - aluminum wire APPV, as well as single-core (single or multi-wire) round - APV. Moreover, the APV wire can be of different thicknesses.
If it is a variant with a single core, the wire cross-section varies from 2.5 to 16 mm², while the wire with a core consisting of several wires can be from 2.8 to 5.5 mm thick. All these types of wires have a wide operating range of temperatures (-50 ... +70 ° C) and voltages (up to 450 V at a frequency of up to 400 Hz), excellent protective characteristics, so they can be used for installation of power lines, lighting systems, distribution boards, laid in plastic and metal boxes, cavities and various pipes.
More flexible versions of APV, with a copper core instead of aluminum, are called PV1 and PV3. Can have single and multi-wire cores, cross-sectional area 0.75 and 16 mm² respectively. The bending radius must not be smaller than 6 diameters. It is laid in places with frequent turns, bends, is used in electrical circuits of cars, switchboards.
PVS is a copper wire with several (2-5) stranded wires, insulated inside and outside with polyvinyl chloride, which, in addition to protection, gives the wire a rounded shape and high density with sufficient softness. Standard for PPV wire cross-section range, but a slightly lower maximum voltage of 380 V and a frequency of 50 Hz. Factory labeling of core insulation is multicolored, and the outer sheath is often white.
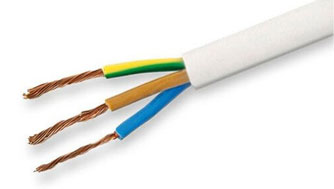
PPV is one of the most common household wires, as it is lightweight and resistant to bending and wear (can withstand about 3000 kinks). It is used for connecting any electrical appliance, making extension cords, installing sockets and lighting, repairing electrical networks. It is not flammable in case of single laying.

What other wires are there
We can mention the existence of other types of connecting copper wires - SHVVP. Their difference lies in the tinning of multiwire cores. VHFW wires are flexible and can withstand voltages of up to 380V with a frequency of 50 Hz. Because of the lack of variety in the thickness of this wire, it is used mainly to connect lighting devices and power equipment that does not require high power - radio electronics, small household appliances.