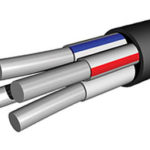
For transmission of electric energy on power and lighting overhead lines using self-supporting insulated wire (SIP). Lines using this type of cable were invented in the 1960s by Finnish engineers as an alternative to using uninsulated wires that were suspended on cables. This method of transmitting energy provides minimal losses and is suitable for installation on existing power line poles.

Contents
Field of application
Self-supporting insulated wire is used when constructing lines from the main trunk wires and step-down transformer substations to various buildings and structures and lighting networks of settlements. Such cable can be used in various climatic conditions, including aggressive environments. It is actively used in conditions of dense development between buildings and constructions.
Marking and deciphering of types
According to GOST 31946-2012 "Self-supporting insulated and insulated wires for overhead power lines". CIP cable is made of thermoplastic light-stabilized polyethylene, and the load-bearing cores of aluminum alloy, and is subdivided into the following types:
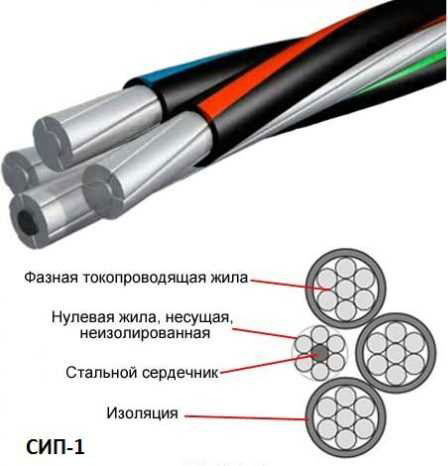
SIP-1 and SIP-1A.
The most common and commonly used type of overhead cable. Due to its design, the insulation can withstand heating up to 90 ° C under normal operation and even up to 250 ° C in a short circuit.
Structurally, it consists of 3-4 aluminum strands covered with polyethylene insulation. Zero conductor is also made of aluminum alloy and has a steel core woven into the center of the cable. It can be insulated or uninsulated. If the cable is marked with an "A" at the end of the name, the neutral conductor has polyethylene insulation (the same for CIP-2A.).
Deciphering of marking:
SIP-1 4*35 + 1*25 - self-supporting insulated wire with four current carrying cables of 35 mm cross-section2 with one non-insulated neutral core of 25 mm cross-section2.
NP-1A 4*25 + 1*16 - self-supporting insulated wire with four current carrying cables of 25 mm cross section2 with one insulated neutral core 16 mm cross section2.
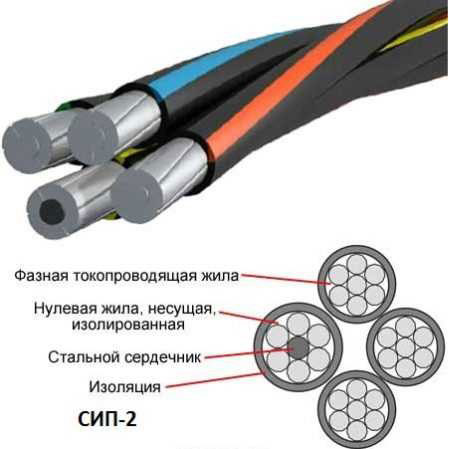
SIP-2
differs from SIP-1 in type of polyethylene insulation. Insulation is made with enhanced protective properties to mechanical damage and is very durable. This cable is imported marked 2F for wires with a core and 2AF - without the core.
SIP-2 is used in all climatic zones and weather conditions, as well as when exposed to aggressive environments.
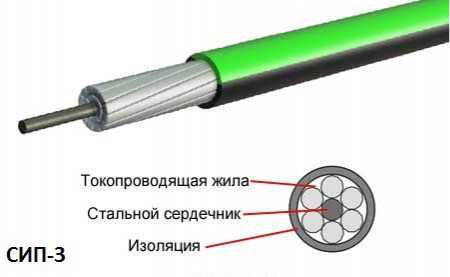
SIP-3
This type of cable is used for high voltage lines with light stabilized polyethylene insulation for 6-35 kV with thickness up to 3,5 mm. It has one multi-wire core with aluminum core and can be used at low air temperatures without losing elasticity. It is marked as follows:
SIP-3 1*185-35 kV - Designed for AC voltage up to 35 kV and has a core of 185 mm2.
It is resistant to mechanical damage, aggressive media and low temperatures. The insulation can preserve its properties under short-term overheating up to 250 °C.
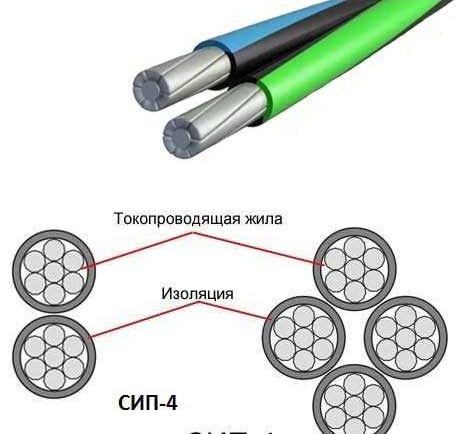
SIP-4
The main feature of the design of a self-supporting insulated wire of this type is the absence of a supporting core, only the current carrying conductor. That's why the application of SIP-4 is a bit different. It is used for short transmission lines, e.g. for power transmission from a transformer substation to a building or facility, or for branches from large highways. For this reason, SIP-4 is often called a tap line.
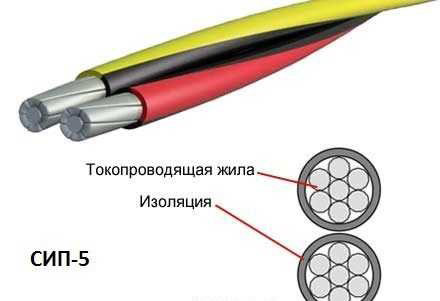
SIP-5
Is an analogue of SIP-4 and is visually similar to it. But the design of this type of cable still has differences: the insulation is made of non-combustible material and is able to withstand critical temperatures. It is used for transmission of electric current with voltage up to 1000 V to buildings or street lighting.

Technical characteristics
Conductor cross section of LV-ABC wire is 16 - 185 mm2The cable is capable of powering heavy consumers and transmitting currents up to 500A, and the allowable currents of single-second short-circuits can reach 16 kA. There is a wide choice of cable options in terms of cross-sectional dimensions and permissible current strength, so this wire is universal for construction of overhead lines.
The operating temperature has a range of -60 to +50 ° C, and the performance of the wire can be for both temperate and cold climate. Installation of the wire is possible at temperatures down to -20 ° C.
Service life reaches 45 years and most manufacturers give a warranty of up to 5 years.
Such cable is subject to mechanical load from wind, ice, snow, so such lines are necessarily calculated on the weight and the action of mechanical loads on them. For such calculation, data on the destructive force of the supporting cable depending on the type, cross-section and weight of the wire is used.
Cable structure
CIP-1 consists of three phase conductors and one neutral conductor. Each phase is a bundle of several aluminum conductors twisted around a core of aluminum. Phase conductors are insulated with polyethylene, the neutral conductor is uninsulated and has a steel core inside.
CIP-2 - differs from CIP-1 in insulation. It is made of cross-linked polyethylene and is very durable against mechanical and thermal effects. In addition, the neutral core is insulated as well as the phase core.
SIP-3 - single-core wire, which has a steel core around which wires made of aluminum alloy, copper and other additives are stranded. It has a wide range of cross-sections and is capable of operating in high-voltage networks under the influence of mechanical loads and harsh climate.
SIP-4 - has no neutral wire and consists of several pairs of aluminum alloy wires with insulation resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
SIP-5 - has the same design as SIP-4, but differs by 30% increase in strength and resistance to various influences (mechanical, atmospheric, etc.increased strength and resistance to various impacts (mechanical, atmospheric, etc.) on the insulation.
Installation of cable CIP
Mounting the cable can be both on old poles of power lines and on facades of buildings in settlements. No special insulators are required for mounting.
It is mounted to the facades of buildings on special fasteners, anchors and clamps, suspended from lines on intermediate clamps. Special powerful clamps are used for branching, depending on the cross-sectional area of the wire.
When installing, take into account that the point of entry into the building must be at a height of at least 2.7 m from the ground, and the clearance to the bottom of the sag between the poles not less than 6 m. The main support must be located from the facade of the building no farther than 25 m, and the location of the branch pole should be not more than 10 m from the facade or wall of the building.
Due to the fact that the installation of CIP wire is associated with high currents and high-voltage lines, it must be installed strictly in accordance with the electrical regulatory and technical documentation and only by qualified personnel in compliance with all standards and regulations of labor protection and safe working practices.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the wire are:
- Reduced losses due to cable insulation;
- Resistant to mechanical damage, climate, aggressive environments and various temperatures;
- Does not allow illegal connection to the mains;
- No overlap and, as a consequence, short circuits from the effects of wind;
- Large selection of types and cross-sections;
- Easier and faster installation, which can be carried out at low temperatures and in different weather conditions;
- Good flexibility and elasticity of the insulation in different temperature environments;
- Does not require insulators for fixing to poles and buildings;
- Safe for maintenance and operation;
- Requires fewer poles when installing overhead lines;
- No corrosion;
- It is possible to install CIP on the walls of buildings and structures;
- Long service life.
CIP has its own shortcomings:
- A large weight of the cable due to the presence of the supporting conductor and thick insulation;
- High cost of production;
- The need for specially trained qualified personnel to install and operate such overhead cable lines.
Wire CIP has more advantages than disadvantages and is a modern and technologically advanced electric cable for overhead lines of various purposes. It is produced by both domestic and foreign manufacturers of cable products. In the market, there are various versions of the wire on the properties of the insulation and allowable current, which allows you to choose the necessary wire for specific tasks and construction of electrical networks of varying complexity and power, as well as the conditions of the environment in which they will work.
Related articles: