Rechargeable batteries are widely used in mobile devices, home appliances and electronics, including portable equipment. Structurally, they are a small source of electrical energy that can be recharged and used to power devices repeatedly. The principle of operation of rechargeable batteries lies in the reversible redox reactions that occur when the cells are charged.

Contents
Types of rechargeable batteries
Such cells differ in a number of parameters, which are taken into account by modern classification. Thus, by design, the following types of batteries are distinguished:
- Requiring maintenance. These batteries need to be refilled from time to time with fresh distilled water and monitor the condition of the electrolyte, otherwise due to the sulfation process, premature failure will occur.
- Maintenance-free. This type of batteries does not need to be topped up with distilled water and the electrolyte density is measured, it is more convenient to use, but it has disadvantages: a deep discharge can completely disable them.
- Dry-charged. This is a type of serviceable cells, which comes on sale without filling with electrolyte: charging must be carried out immediately before the battery is used. Such rechargeable types are lightweight and have a longer service life, and can be purchased in advance, as the risk of self-discharge is significantly reduced.
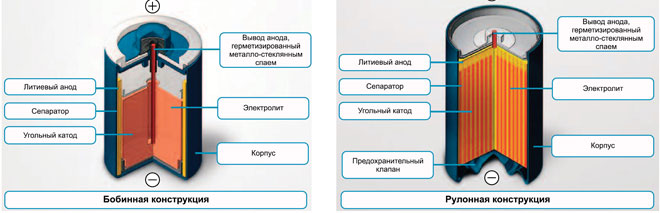
In addition, rechargeable batteries may differ in the composition of the electrolyte and the electrode used. There are lead-acid, lithium-ion and lithium-polymer, nickel-cadmium and nickel-zinc galvanic cells, the choice depends on the purpose and application.
Basic sizes
In terms of shape, batteries can be cylindrical, disc, tablet or parallelepiped shaped: these are the most popular options. In addition, there are a large number of AA and AAA sizes, and the following types are most common:
- Cylindrical rechargeable batteries. Their format is AA (finger) and AAA (pinky), the size of the former is 50.5 by 14.5 mm, the latter is 44.5 by 10.5 mm. They are used in the service of photo and audio equipment, charging of portable devices.
- Batteries in the form of a parallelepiped, aka "Crone". Their size - 48,5 by 26,5 by 17,5 mm, they are used for large clock mechanisms, radios, multimeters, electronic devices for various purposes.
- Batteries, labeled AG0-AG13. They range in size from 4.6 by 2.2 mm to 11.6 by 5.4 mm. They are used to charge wrist and desk watches, intercoms, alarms and other types of equipment that need a compact battery.
- Disk flat battery packs.
The most popular are finger and pinky batteries, which are used to equip mobile and portable devices, watches, photo, video, audio equipment and other types of equipment.
Classification by electrolyte type
This substance can be liquid, in the form of a gel or absorbed. For example, lead-acid batteries contain a sulfuric acid solution, nickel-cadmium batteries and nickel-zinc cells contain potassium hydroxide with the addition of lithium hydroxide. Lithium salts are used as the electrolyte in ionic batteries. Products with a solid electrolytic cell are used more rarely: their cost is higher. The most effective batteries include those with gel and liquid electrolyte.
How to choose rechargeable batteries?
When selecting such products, the following factors should be taken into account:
- Temperature rating. If you plan to use batteries to power devices working at reduced or, on the contrary, too high temperatures, it is better to choose nickel-cadmium devices.
- Service life. The nickel-metal hydride batteries and lithium-polymer varieties have the highest rate.
- The voltage of the battery. This parameter is set based on the requirements for the device in which the galvanic cells will be installed.
- The type of device for which the batteries are purchased. The shape and design of the battery product depends on this.
- The volume and number of charge-discharge cycles.
Properly selected batteries provide the longest possible life of the equipment, which saves on its maintenance.
Related articles:






