When working with station and linear electrical equipment great importance is given to protecting the employee from overvoltage and electric shock. For these purposes, special electrical protective equipment is used to provide reliable protection for people working in electrical installations. Complete information about the classification and list of protective equipment for work in electrical installations is contained in "Instruction on the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations" СО 153-34.03.603-2003.

Contents
- 1 Electrical protection means: types and requirements for them
- 2 High-intensity, collective and individual protection means against electric fields
- 3 Personal protective equipment
- 4 The order and general rules of the use of protective equipment
- 5 The procedure of storage of protection means
- 6 Registering of protection means and control of their condition
Protective equipment: types and requirements
According to the method of application all known protective equipment (PPE) is conditionally divided into those used by one person - personal protective equipment (PPE) and collective - constructively related to the production process, equipment, room. According to their functional purpose and the effect they have, they are:
- insulating or enclosing;
- used for high-altitude operations;
- shielding.
Additional information: According to the voltage value, these products are divided for operation in networks up to 1000 V and over 1000 V.
Insulating electrical protective equipment is usually divided into two types:
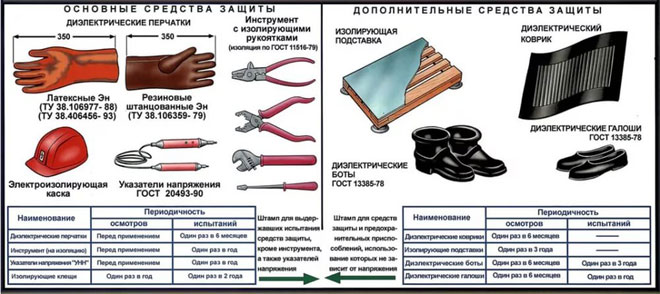
- Basic - whose insulation withstands the operating voltage of the electrical installation for a long time and allows you to work on live parts under voltage.
- Supplementary - complements the basic, serves to protect against step voltage and touch voltage, but they themselves do not provide protection against electric shock.
The requirements placed on them are generally determined by their intended use (their ability to withstand the voltage of the electrical installation). In addition, they must be in good working order and have a last test date stamped on them. Rubber products must be free of stale marks and cuts and punctures that are visible to the naked eye.
Insulating protective equipment for electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V
The following basic items represent this type of protective equipment and working tools:
- isolating rods;
- Isolating tongs;
- voltage indicators;
- devices and devices for ensuring safety of work during measurements and tests in electrical installations;
- special protective equipment, insulating devices and accessories for working under voltage in electrical installations 110 kV and above.
The category of additional include:
- dielectric gloves and boots, mats and insulating stands;
- insulating caps and pads;
- carrying and equipotential bonding rods
- extension ladders, insulating fiberglass ladders.
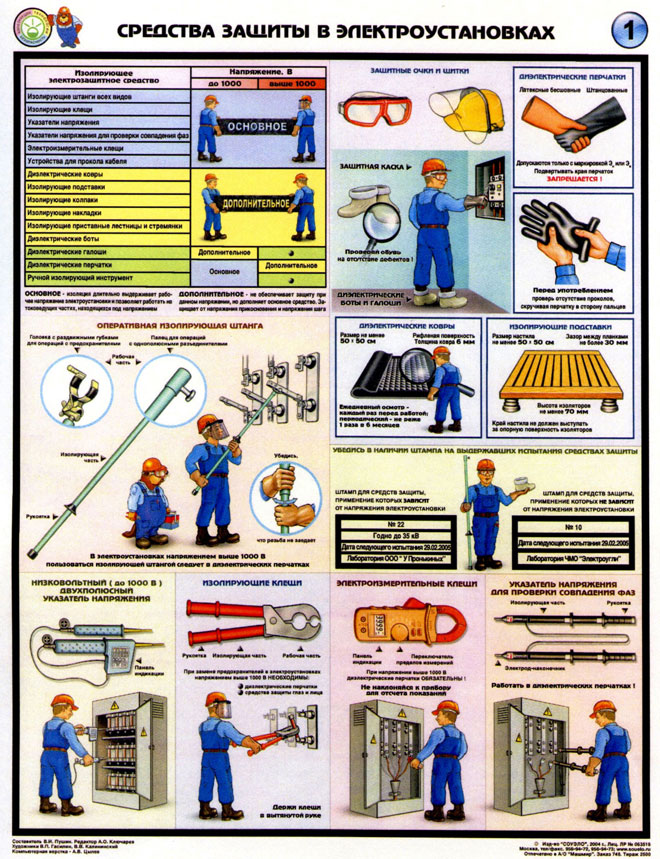
Insulating protective equipment for electric installations with voltages of up to 1000 V
For electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V, we can distinguish the following main names of the insulating means of protection:
- insulating rods and pliers;
- voltage indicators and electric clamps;
- gloves made of dielectric materials;
- special measuring pliers (current clamps);
- Hand-held insulating tools.

Additional insulating protective products include:
- insulating stands and dielectric mats;
- dielectric soles;
- Insulating caps, covers and pads;
- ladders, insulating fiberglass ladders.
Protective equipment against high intensity electric fields, collective and individual
When working on overhead lines and switchgear of 330 kV and above at an electric field strength of up to 5 kV/m, the time of stay in the work area without protective equipment is not limited. When the value of intensity from 5 to 25 kV/m is limited by state standard, and when the value of intensity above 25 kV/m is not allowed.
Protective equipment against electric fields of high intensity includes shielding kits used during work operations on overhead power lines (ALs) or at ground level in switchgear type switchgear. According to the method of arrangement, such shielding is subdivided into the following types:
- removable shielding devices (installed on machines and mechanisms);
- stationary, portable and mobile shielding devices;
- individual shielding kits.
Among the described products we will distinguish individual purpose shielding kits, made in the form of protective equipment worn on a person. Collective shielding systems are designed to protect an entire group of people. They are made of conductive material and connected to an earthed object (protective circuit).
Personal protective equipment
The category of PPE includes:
- safety helmets, goggles and shields;
- gloves, special protective clothing, gas masks and respirators;
- Safety harnesses and safety ropes.
The first products in the list are used to protect the head from mechanical shocks, as well as from the current effects of accidental contact with exposed wires. Goggles and shields are needed to protect the face and eyes from the blinding light of the electric arc, dirt and dust particles, UV and IR radiation.
The gloves used at work protect your hands from unexpected injuries, burns and cuts. Mounting belts ensure that personnel are protected from accidental falls from heights when working at height. Safety harness is designed to attach a carabiner safety harness to protect workers from falling from height when performing labor at height.
Sets used in welding are necessary to protect the body from the dangerous effects of the electric arc. They include a helmet with a protective face shield, heat-resistant helmet and gloves made of thick fabric.
Procedures and general rules for using protective equipment
Every worker performing work in an electrical installation shall be provided with the necessary protective equipment and shall be trained in the rules for its use and shall be required to use it and comply with the following general requirements:
- Only use products that have markings (indicating the manufacturer, product name or type, date of manufacture and test stamp);
- Before the next use, the personnel working on the electrical installation must check the serviceability of the used protective equipment, the absence of external damage and contamination and, according to the stamp, the shelf life;
- If it is found to be unsuitable for use, the protective equipment shall be removed and a record of this shall be made in the log or in the operational documentation.
When working, you must not touch directly the working area of the product, as well as that part of the insulation, which is located behind the limit stop.
Storage of protective equipment
The effectiveness of the protective equipment depends on many factors, including compliance with the rules for its storage. The following requirements must be met:
- Protective equipment must be stored indoors, in conditions that ensure its serviceability and suitability for use;
- Protective equipment made of rubber and polymeric materials shall be stored in cabinets or on racks separately from the tools and be protected from the effects of acids, alkalis, oils, etc., as well as from the effects of sunlight and thermal radiation of heating devices;
- protective equipment shall be placed in specially equipped places at the entrance to the room, on the control panels.
It should also be noted that the storage of protective equipment is allowed only in dry form.

Recording of protective equipment and monitoring its condition
All electrical protective equipment in use must be numbered. The following items are exceptions:
- safety helmets, dielectric mats;
- special insulating mats;
- safety posters and safety guards;
- booms for carrying and potential equalization.
Important note: When numbering the products it is allowed to use their serial numbers.
Numbers are assigned individually for each type of ES, taking into account the specific conditions of their operation. The serial number is either embossed on the metal parts of the products, or painted brightly on a clearly visible place. It is also possible to place it on a special tag attached to the protective equipment itself.
If the equipment or tool contains in its construction several parts - a separate tag shall be hung on each of them. In the relevant divisions of the enterprises associated with the maintenance of electrical equipment, it is mandatory to have a logbook of all protective equipment available in them, including those issued for individual use.
Their total availability and current condition are controlled by visual inspections, the frequency of which is set at least once every six months. For portable earthing, this figure is at least once a quarter. The employee in charge, who is entrusted to monitor their condition, after the inspection must record the result in the appropriate column of the special log.
Related articles: